Unit 3.7(1) Market based supply-side policies
The market-based supply-side approach involves the government trying to increase aggregate supply by using policies that allow markets to function more efficiently and to achieve the macroeconomic objectives of sustained economic growth, price stability and low unemployment. Through market-based supply-side policies, the government tries to create the market conditions needed to allow the private sector of the economy to find solutions to economic problems.
- Aims of supply-side policies

- Use of the long-run aggregate supply curve to show the effect of supply-side policies
- Explanation of market-based policies: competition policy, deregulation, privatisation, trade liberalisation, monopoly regulation
- Explanation of labour market policies: reducing the power of labour unions, reducing unemployment benefits, reducing minimum wages
- Explanation of incentive-related policies: decreasing income tax and business tax
- Market-based supply-side policies to increase economic growth, reduce unemployment and achieve price stability
- Evaluation of market-based supply-side policies
Revision material
 The link to the attached pdf is revision material from Unit 3.7(1) Market-based supply-side policies. The revision material can be downloaded as a student handout.
The link to the attached pdf is revision material from Unit 3.7(1) Market-based supply-side policies. The revision material can be downloaded as a student handout.
Aims of supply-side policies
Government supply-side policies aim to affect aggregate supply and achieve the macroeconomic objectives of:
- Sustainable economic growth
- Low unemployment
- External balance of the current account balance of payments
- Low inflation or price stability
Supply-side policies and long-run economic growth
Long-term growth
Supply-side policies are often viewed as a long-term strategic set of policies to facilitate future economic growth over a period of time. For example, increasing the numbers in university education to improve the skill level of the labour force may take 10 to 20 years to have a significant effect on the growth of the economy.
Increasing productive capacity 
To achieve long-term economic growth, supply-side policies are often targeted at improving the productive potential of the economy. This means using policies that increase potential output, shifting the production possibility curve and long-run aggregate supply curve of an economy outwards. This is illustrated by diagram 3.43 where the long-run aggregate supply curve increases from LRAS to LRAS1. A government spending programme on significant improvements to infrastructure in the economy would be aimed at increasing productive capacity.
What are market-based supply-side policies?
The market-based approach
The market-based supply-side approach involves the government trying to increase aggregate supply by using policies that allow markets to function more efficiently and to achieve the macroeconomic objectives of sustained economic growth, price stability and low unemployment. Through market-based supply-side policies, the government tries to create the market conditions needed to allow the private sector of the economy to find solutions to economic problems.
Market-based supply side can be looked at as three distinct policy approaches:
- Policies that encourage competition in markets. This is based on the assumption that more competition between businesses increases economic efficiency.
- Policies that try to increase efficiency in the labour market. This is particularly important for employment and worker productivity.
- Incentive-related policies to increase efficiency, investment and innovation.
Increasing potential output
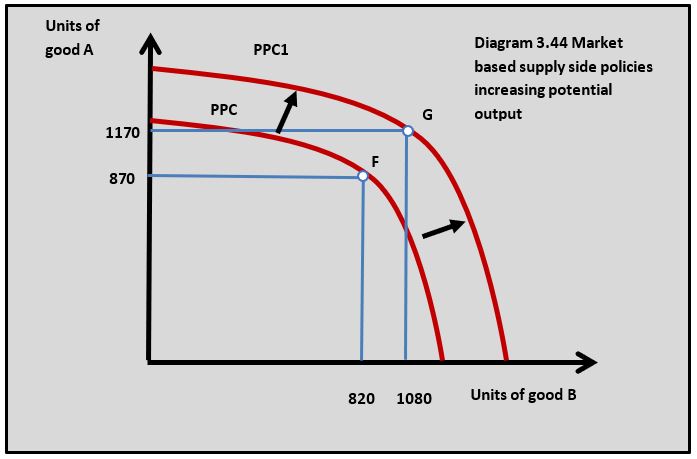 The increase in investment and innovation brought about by market-based supply-side policies will cause the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift outwards from LRAS to LRAS1 in diagram 3.43. This can also be shown by a shift outwards in the production possibility curve from PPC to PPC1, which is shown in diagram 3.44.
The increase in investment and innovation brought about by market-based supply-side policies will cause the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift outwards from LRAS to LRAS1 in diagram 3.43. This can also be shown by a shift outwards in the production possibility curve from PPC to PPC1, which is shown in diagram 3.44.
Increasing actual output
The improvement in efficiency brought about by market-based supply-side policies can lead to an increase in actual output which is illustrated in diagram 3.45 by a shift from A to B as the economy moves closer to potential output.
A market-based approach to achieving long-run economic growth
Deregulation of markets
Over time, markets can become increasingly regulated to protect workers, the environment, health and safety and the consumer. For example, a clothing manufacturer might be required by law to pay a minimum wage, put in place health and safety systems on the production line and use sustainable materials when manufacturing its products. Even though the aims of these regulations might be to improve welfare they can add to business costs and reduce productive efficiency by making decision-making more complex. By reducing or removing regulations, business costs might fall and productive efficiency might increase.
Privatisation of industries
Many industries have been owned and controlled by the government. This is particularly true in utilities such as energy and water, but also transport and communications. In the UK, for example, British Gas, Royal Mail, British Telecom, British Rail and British Airways have all been state-run enterprises in the past. Over the last 30 years, all these industries have been privatised. This means the assets have been sold to private investors and they have employed management to run the businesses. The theory of privatisation is that private sector organisations run more efficiently than public sector enterprises, and this increases overall efficiency in the wider economy.
Trade liberalisation
 Most economists believe that free international trade increases efficiency in an economy through increased competition and specialisation of resources. Many countries use trade barriers, such as tariffs and quotas, to protect certain markets. When trade is liberalised and trade barriers are reduced or removed, this increases free international trade and the efficiency gains that go with it. The ASEAN free trade agreement, for example, between countries such as Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand etc, increases trade liberalisation and the efficiency gains that go with it.
Most economists believe that free international trade increases efficiency in an economy through increased competition and specialisation of resources. Many countries use trade barriers, such as tariffs and quotas, to protect certain markets. When trade is liberalised and trade barriers are reduced or removed, this increases free international trade and the efficiency gains that go with it. The ASEAN free trade agreement, for example, between countries such as Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand etc, increases trade liberalisation and the efficiency gains that go with it.
Monopoly and competition regulation
When monopolies become established in markets they reduce competition and this leads to a fall in business efficiency. Section 2.11 of this book focuses on monopoly as a market failure and how the existence of monopolies reduces economic efficiency. As part of a market-based supply-side approach, the government puts in place laws and regulations that prevent monopolies from occurring or regulate monopolies if they do exist. The European Union, for example, has specific laws in its Single Market that prevent monopoly practices such as cartels occurring amongst member countries of the EU.
Reducing the power of trade unions
A trade union is where a group of employees join together to try to maintain and improve the wages and employment conditions of their members. Many economists who advocate a market-based supply-side approach believe that the power of trade unions should be reduced because they reduce business efficiency and prevent innovation and change. In 2019 many transport workers in France went on strike because of proposed changes to their working conditions. The French government were trying to push through market reforms that could reduce business costs and increase efficiency.
Changes in taxation
Changes to tax rates and the tax system are seen as an important way of creating greater incentives in the economy to increase efficiency, investment and innovation. Cutting taxes means that workers will keep a larger proportion of their income, which may increase their incentive to work harder and improve productivity. Reducing corporation tax on businesses means they can keep a higher proportion of their profits, which they can use to fund new investment and research and development. Lower tax on businesses may also encourage new firms to start up in the economy.

On Wednesday the Indian government approved the privatisation of 5 state-owned enterprises. It includes the Bharat Petroleum Corporation, the Shipping Corporation of India, the Container Corporation of India, the energy provider THDC India, and the North Eastern Electric Power Corporation. This strategic move by the Indian government is part of a drive for greater efficiency in key industries on the supply side of the economy.
One government minister said, ‘we have no business to be in business.’ The government believes the efficiency gains they have seen through privatisation of the telecoms and aviation sectors have justified privatisations in other markets.
Questions
a. Define the term market-based supply-side policy. [2]
A market-based supply-side policy means the government uses policies to increase aggregate supply by allowing markets to function more efficiently.
b. Using a PPC diagram explain how privatisation of different state-run businesses in India might lead to economic growth. [4]
 The market-based supply-side policy of privatisation aims to make large state-run businesses more efficient as private firms. This is because they are free of government control when they are privatised. This causes the production possibility curve to shift from PPC to PPC1 in the diagram.
The market-based supply-side policy of privatisation aims to make large state-run businesses more efficient as private firms. This is because they are free of government control when they are privatised. This causes the production possibility curve to shift from PPC to PPC1 in the diagram.
c. Outline two other market-based supply-side policies the Indian government could use to increase potential output. [4]
Outline any two market-based supply-side policies from:
- Deregulation of markets to allow them to operate more efficiently.
- Liberalisation of free international trade by reducing trade barriers which increases competition and reduces costs.
- Regulations that encourage free competition in markets to reduce prices.
- Reduce the power of trade unions to create greater efficiency in the labour market.
- Reduce income tax and tax on company profits to incentivise workers and businesses to be more efficient.
Investigation
Research into a privatisation that has taken place in a country. Find out why the enterprise was privatised and what the potential costs and benefits might have been.
Evaluation of market-based supply-side policy to achieve economic growth
Strengths
- Market-based supply-side policies use the power of the market to achieve economic growth. The interaction of private business and consumers might be more powerful in affecting economic growth in the long run than interventionist supply-side policies.
- The market-based approach does not involve the government expenditure costs of the interventionist approach.
- Similar to interventionist supply-side policies, the market-based approach does not cause inflation in the same way as expansionary demand-side policies do.
Weaknesses
- A market-based approach can work in the long run, but it is relatively ineffective compared to expansionary demand-side policies in achieving an increase in the current rate of economic growth. The market-based approach will not be as effective in a recession when a government needs to respond quickly to a fall in economic growth.
- If the deregulation aspect of the market-based approach involves reducing environmental laws, it can have a negative effect on the environment.
- The market-based approach can have a negative impact on low-income workers who may see their incomes and working conditions negatively affected if the government decides to decrease minimum wages and cut back on employment protection.
- If the market-based policy involves reducing income and corporation tax, this could widen income inequality in the country.
- Trade liberalisation involves a country reducing trade barriers, which leads to some industries being exposed to low-cost foreign competition which could cause business failure and unemployment.
- Privatisation of certain industries may lead to private sector monopolies which may cause prices to rise. In the energy and public transport markets, this can have a particularly negative impact on the consumer.
Market-based supply-side approach to unemployment
Direct tax and benefits
Reducing direct taxation creates a greater incentive for workers to take available jobs which can reduce the amount of unemployment. If governments reduce unemployment benefits this also increases the incentive for workers to accept jobs. A combination of lower direct tax and reduced benefits makes the opportunity cost of not accepting a job higher because the difference between someone’s income in work increases relative to the transfer payments they might receive if they are out of work.
Trade unions

Reducing the power of trade unions takes away some of the impediments that prevent firms from hiring new workers. This is particularly true where trade unions negotiate wages above their market equilibrium level and cause the quantity demanded of labour to fall.
Minimum wages
Minimum wages can cause a disequilibrium in the labour market, which means the quantity demanded for labour is less than the quantity supplied of labour. If a government reduces the minimum wage in the economy, the quantity demanded for labour rises and there is a decrease in unemployment. Reducing minimum wages is often seen as important to small businesses and this can encourage them to hire more workers.
Labour market regulations
Governments can reduce the amount of labour market regulation that prevents firms from taking on new employees. If there are over-protective regulations, such as statutory redundancy payments, then firms are less likely to take on workers because of the high cost of making workers redundant.
Evaluation of market-based supply-side policy to reduce unemployment
Strengths
- Market-based supply-side policies can make the labour market more dynamic and reactive to change. For example, reducing regulations can make it easier for firms to take on workers more quickly when they are expanding.
- There is evidence that the private sector is better at creating jobs than the public sector.
- The increased incentives associated with market-based supply-side policies can increase worker productivity.
Weaknesses
- Market-based supply-side policies can have harsh effects on the unemployed. If unemployed people cannot find jobs in a recession, then cutting their benefits will lead to increased poverty.
- Decreasing employment regulation can reduce the protection workers have in their jobs, which in turn leads to greater job insecurity and can cause the exploitation of workers.
- Reducing direct tax might mean unscrupulous employers reduce pay rates because they know workers are going to receive a rise in their disposable income.
- Taking away minimum wages legislation means pay rates will fall in certain industries, which can lead to greater levels of poverty.
 In 2018 Jair Bolsonaro became the new Brazilian President with a promise to put in place significant supply-side reforms to the Brazilian economy. This government’s political reforms included reductions in environmental regulations, streamlined employment laws, privatisation of key industries and tax cuts.
In 2018 Jair Bolsonaro became the new Brazilian President with a promise to put in place significant supply-side reforms to the Brazilian economy. This government’s political reforms included reductions in environmental regulations, streamlined employment laws, privatisation of key industries and tax cuts.
Bolsonaro’s free-market approach is aimed at increasing business efficiency and stimulating long-run economic growth. It has, however, been greeted with criticism and concern. Many opposition politicians are fearful of the effects Bolsonaro’s policies will have on workers' rights and on the poorest in society. There are also considerable fears of increased deforestation in the Amazon as regulations are reduced.
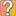 Worksheet questions
Worksheet questions
Question
Using a real-world example, evaluate the effectiveness of market-based supply-side policies to reduce unemployment. [15]
Answers might include:
- Definitions of market-based supply-side policies and unemployment.
- A diagram to show the impact of market-based supply-side policies on potential output which can increase employment.
- An explanation that market-based supply-side policies such as: reducing minimum wages, deregulating the labour market, decreasing direct taxation and reducing the power of trade unions can all lead to a decrease in unemployment.
- An example of how market-based supply-side policies have reduced unemployment such as those used in Brazil.
- Evaluation might include discussion of the negative impact of market-based supply-side policies on employee welfare; how the policy would not be that effective with cyclical unemployment and the length of time it takes for the policy to reduce unemployment. The evaluation could also consider alternative policy approaches such as fiscal and monetary policy.
Investigation
Research into other examples of where governments have used supply-side policies but with a significant environmental cost.
Market-based supplied policies to reduce inflation
Monopoly and competition regulation
Market-based supply-side policies that increase competition in the economy and reduce the power of monopolies can lead to increased efficiency and lower prices. This is illustrated in diagram 3.43 where the increase in long-run aggregate supply from LRAS to LRAS1 causes the average price level to fall and reduces the rate of inflation.
Reducing the power of trade unions
Trade union activity can push up wages in the economy, which increases business costs. This can lead to cost-push inflation. Market-based supply-side policies to reduce the power of trade unions mean that union activity is less likely to push up wage costs.
Changes in taxation
Reducing direct and indirect taxes can lead to lower business costs and increase business efficiency, which leads to reduced inflationary pressures in the economy. For example, a reduction in VAT can directly reduce the average price level in the economy.
Privatisation of industries
The increased efficiency privatising key industries can bring to the economy can lead to lower prices and reduced inflation. Privatisation of energy companies can be particularly significant because gas and electricity costs are a major part of consumer expenditure and business costs.
Deregulation of markets
Removing and reducing regulations on businesses can increase efficiency and reduce business costs, which creates the conditions for lower prices and reduced inflation.
Evaluation of market-based supply-side policy to reduce inflation
Strengths
- The market-based supply-side approach can reduce the average price level and inflation in the long run at the same time that national income increases. Contractionary demand-side policies reduce inflation, but often at the cost of falling national income.
- Increasing economic efficiency and competition in markets can create the conditions for price stability in the long run.
Weaknesses
- A market-based supply-side approach is a long-run approach to achieving price stability and often a rise in inflation requires an immediate policy response. Governments normally use contractionary fiscal and monetary policy to achieve this.
- Reducing inflation using a market-based approach can have negative consequences in terms of inequality, workers’ rights and increased foreign competition.
When he was elected President in 2016, Donald Trump embarked on a market-based supply-side approach. In 2017 his government introduced a range of tax cuts including a reduction in personal income tax and a huge cut in corporation rate from 35% to 21%. Trump’s advisors believed this would create the supply-side incentives needed to drive the US economy forwards. The administration also announced significant cuts to government regulations in areas including withdrawing the US from Paris Climate Agreement, scrapping the clean power plan and loosening regulations on toxic air pollution.
Trump’s supply-side approach did coincide with a period of good economic growth, with the American economy averaging a nearly 3% growth rate over the last 3 years, but it would be difficult to put this down entirely to the supply-side benefits of his policies. Many people have also warned about the environmental costs of cutting so many environmental regulations.
Questions
a. Using a diagram explain how the market-based supply-side policies used by the US might lead to a fall in inflation. [4]
 The market-based supply-side policies used by the US government such as deregulation and reduced direct tax can cause the LRAS curve to shift outwards from LRAS to LRAS1 which leads to a fall in the average price level and a fall in inflation.
The market-based supply-side policies used by the US government such as deregulation and reduced direct tax can cause the LRAS curve to shift outwards from LRAS to LRAS1 which leads to a fall in the average price level and a fall in inflation.
b. Explain two problems of using market-based supply-side policies to reduce the rate of inflation. [4]
Explanation using any two of the policies:
- Market-based supply-side policies are a long-term approach and take time to work. They would not be effective at dealing with a current problem of rising inflation.
- Market-based supply-side policies can have a negative effect on the environment if environmental laws are deregulated.
- Market-based supply-side policies can have a negative effect on the welfare of the workforce if employment laws are deregulated.
Investigation
Research into the supply-side policies of Donald Trump's regime.
Donald Trump and Republican Party in the US have celebrated the economic achievements of their government right up until the start of the pandemic in early 2020. Achieving an average economic growth rate of around 3 per cent, unemployment below 4 per cent and a general feeling of rising prosperity may well be attributable to the successful application of market-based supply-side policies by the US government. Cutting direct taxation and wide-ranging deregulation have been central to Trump's market-based supply-side approach.
But how sustainable is this approach, particularly when it involves reducing and removing regulations on carbon emissions?
Which of the following is least likely to be an objective of market-based supply-side policies?
Market-based supply-side policies often widen income inequality.
Which of the following is most likely to be an effect of market-based supply-side policies?
Market-based supply-side policies aim to increase long-run aggregate supply and increase potential output.
Which of the following is unlikely to be a market-based supply-side policy to reduce unemployment?
Decreasing interest rates is a tool of monetary policy and is a demand-side policy.
Which of the following is least likely to be a disadvantage of using market-based supply-side policies to increase economic growth?
Market-based supply-side policies are normally associated with cuts in taxation
Which of the following outcomes is the most likely result of effective market-based supply-side policies?
Market-based bases supply-side policies lead to an outward shift in LRAS which increases real GDP and decreases the average price level.
Which of the following is the least likely to be a consequence of reducing welfare payments to decrease unemployment?
The opportunity cost of not working increases if unemployment benefit decreases because people without work receive lower benefit payments.
A market based supply-side economist would support a policy of:
The aim of reducing tax to increase investment is to increase economic growth by increasing LRAS.
Which the following is most likely to be a problem of using market-based supply-side policies to increase economic growth?
If direct tax is decreased a higher proportion of income will go to the richest people in the economy.
Which of the following is most likely to be a problem with using market-based supply-side policies to increase economic growth?
Market-based supply-side policies often involve deregulation which could lead to environmental problems.
Which of the following supply-side policies is most likely to be used to decrease the rate of inflation?
The aim of privatising key industries such as energy, transport and water is to achieve greater efficiency and lower prices.
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team
