The business cycle
 Introduction
Introduction
This page introduces the concept of the business cycle which you will focus on during the coming weeks. I have placed this topic in unit 3.1 but it could easily be completed as part of the section on aggregate demand or aggregate supply
Enquiry question
What is the business cycle in economics?
 Lesson time: 45 minutes
Lesson time: 45 minutes
Lesson objectives:
Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterised by the phases of the business cycle.
Explain the long-term growth trend in the business cycle diagram as the potential output of the economy.
Distinguish between a decrease in GDP and a decrease in GDP growth.
Teacher notes:
1. Beginning activity - begin with the opening activity and allow 10 minutes for your classes to complete this.
2. Processes - technical vocabulary - the students can learn the key concepts through the notes, the first part of which which should take 5 minutes to go through and discuss.
3. Worksheet - this activity contains short questions which will help introduce the lesson. (10 minutes)
4. Business cycle game - this short business game will help introduce the relationship between unemployment and the stages of the business cycle. (10 minutes)
5. Final reflection - complete this lesson by reviewing some of the terms discussed in this lesson e.g. growth, decline, peak, trough and cyclical unemployment. Which jobs are more or less secure during periods of economic decline? This would also be a suitable time to discuss why the long term trend for any country is upwards, despite the peaks and troughs. (10 minutes)
Opening activity
Begin by watching the following video which introduces the concept of the business cycle. Watch the short video and then complete the activities which follow:
(a) Investigate the following key terms:
i. Aggregate demand
Aggregate demand is calculated by adding up the sum of all final goods and services produced in an economy, over a period of time at a given average price.
ii. Aggregate supply
Aggregate Supply measures the total supply of all goods and services produced in a national economy, over a period of time at a given average price.
iii. Recession
A period when the level of real GDP falls over two, 3 month periods in a row.
iv. Economic growth
A rise in the value of real GDP / GNI over a time period.
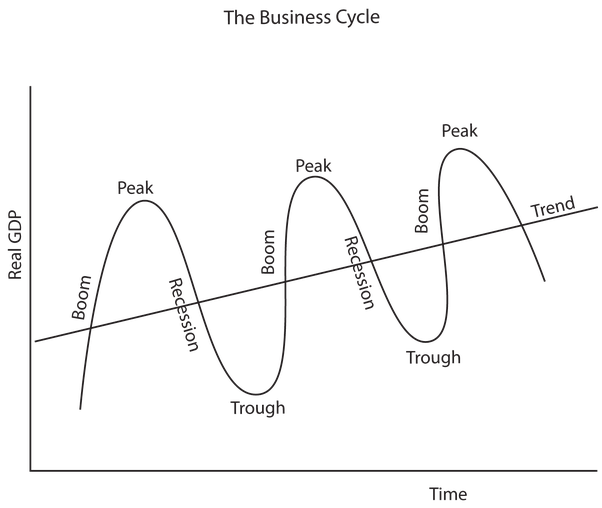
 The business cycle
The business cycle
The diagram to the right illustrates a business cycle in economics. Time is shown on the X-axis and the Y-axis illustrates the level of real GDP in an economy. Like any relatively successful economy, the level of growth in this economy follows an upward trend. However, you can observe note that the rise in real GDP is not linear but follows a period of troughs and booms, as the economy contracts and expands.
Activity 1
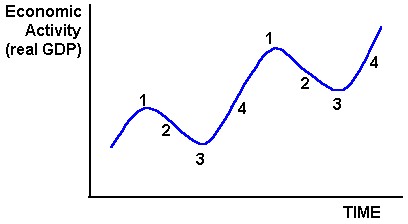 (1) Label the following diagram with the following labels:
(1) Label the following diagram with the following labels:
Peak, trough, decline, growth
(2) Use a line of best fit to draw a long term trend line on the diagram
(3) Read each of the following headlines (a-h) and place the proper letter next them that correspond with the business cycle. G = growth, P = peak, C = contractionary, T = trough.
1 = Peak
2 = Contractionary
3 = Trough
4 = Growth
________ The price of bread has increased 5% over the past three months.
G
________ Interest rates at a low of 2% cause consumers to take out loans and buy homes.
G
________ The sale of durable goods is down for the 5th consecutive month.
T
________ Due to factory closures unemployment has risen to a five year high of 10%
T
________ Due to increased consumer spending, the Federal Reserve raises interest rates to slow the economy down.
P
________ The DOW Jones industrial average reaches an all-time high.
P
________ GDP declines for four consecutive months, causing the Federal Reserve to lower interest rates.
C
________ The unemployment rate is at 3.4%, a new 15 year low.
P
(4) How can predicting / understanding the business cycle influence your future financial decision?
By understanding the business cycle it is easier for governments, central banks and individual businesses to plan their staffing and production needs for the future.
The activities on this page are available as a PDF file at: ![]() Business cycle
Business cycle
Activity 2: Business cycle game
To complete this game you will need the following resources: the powerpoint presentation included and the occupation cards.
Steps of the game
1. Explain the rules of the game and then provide each student with an occupational slip. You may choose to select other professions. The available positions are Factory worker, Clothing sales person, housebuilder, waiter, air steward, hair stylist, computer software designer and luxury TV salesperson
2. Read and list (from the Powerpoint) the economic conditions. At first the economy would rise, individuals of each sector would get jobs, and conditions would simulate economic expansions. The economy would grow until it reaches its peak, in which all students are standing. Next, students would begin to lose their jobs. As students lose their jobs they would recognise this as an economic contraction. This anticipatory set would simulate how the business cycle is directly related to the job sector.
Activity 3: Final reflection
Explain what you have learnt from this lesson?
What do the terms growth, decline, peak, trough and cyclical unemployment mean?
Which jobs are more or less secure during periods of economic decline?
Why is the long term trend for any country normally upwards, despite the peaks and troughs?
Explain the difference between a decrease in GDP and a decrease in GDP growth
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team