Unit 3.3-3.4: Multiple choice
 Unit 3.3-3.4: Multiple choice questions
Unit 3.3-3.4: Multiple choice questions
1. An increase in aggregate supply can be caused by the following:
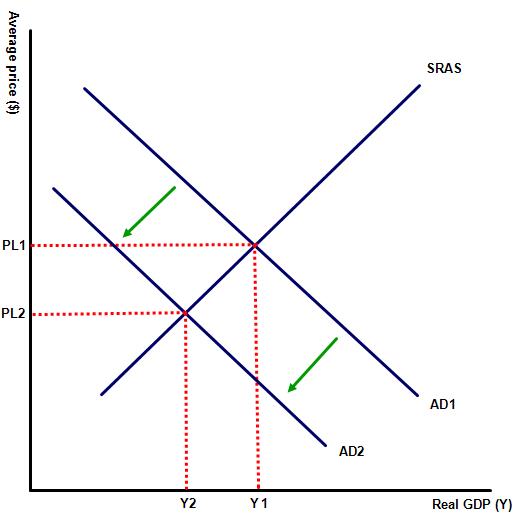 2. The diagram illustrates a fall in aggregate demand. This could have been caused by which of the following combination of policies?
2. The diagram illustrates a fall in aggregate demand. This could have been caused by which of the following combination of policies?
3. The shape of the LRAS curve in keynesian economic policy can be explained by the following:
4. The size of the multiplier depends on which of the following:
5. An economy has an output gap of $ 50 billion and the MPC is 0.6. According to keynesian multiplier theory the government must inject $ ? billion into the economy.
6. According to keynesian economic theory government spending is more effective in raising national income than tax cuts because of the following:
7. Unemployment can be defined as:
8. Which of the following is not an example of equilibrium unemployment?
9. Which of the following does not contribute to the difficulties of calculating unemployment?
10. The natural rate of unemployment includes which of the following types of unemployment?
11. A worker is laid off because the factory where he works closes down due to competition from low wage economies overseas. This type of unemployment is called:
12. A university graduate finishes her studies and starts looking for work. She has received a number of interviews but is weighing up her options before deciding on her next position. What type of unemployment is this?
13. Cyclical unemployment can best be solved:
14. Which of the following is not an economic cost of inflation?
15. Which of the following statements about inflation and deflation is true?
16. Which of the following statements about inflation is incorrect?
17. Deflation is considered bad for the economy because:
18. The following makes it more difficult to calculate the rate of inflation in the economy:
19. The Phillips curve:
20. Which of the following statements about income inequality is not true?
Available as a PDF file at: ![]() Unit 3.3-3.4 macroeconomic objectives
Unit 3.3-3.4 macroeconomic objectives
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team