The market for foreign exchange
 Introduction
Introduction
This page looks at the factors that lead to changes in currency demand and supply, including foreign demand for a country’s exports, domestic demand for imports, relative interest rates, relative inflation rates, investment from overseas in a country’s firms (foreign direct investment and portfolio investment) and speculation. This lesson also describes the balance any government / central bank must strike in attempting to protect the interests of all stakeholders in the economy - consumers, exporters, importers and domestic businesses.
Enquiry question
What are the factors that lead to changes in currency demand and supply and what exchange rate should central banks and governments aim for?
.jpg) Lesson time: 70 minutes
Lesson time: 70 minutes
Lesson objectives:
Explain the factors that lead to changes in currency demand and supply, including foreign demand for a country’s exports, domestic demand for imports, relative interest rates, relative inflation rates, investment from overseas in a country’s firms (foreign direct investment and portfolio investment) and speculation.
Examine the possible consequences of overvalued and undervalued currencies.
Evaluate the possible economic consequences of a change in the value of a currency, including the effects on a country’s inflation rate, employment, economic growth and current account balance.
Teacher notes:
1. Beginning activity - begin with the prezi and the opening question and then discuss this as a class. (Allow 5 minutes in total)
2. Processes - technical vocabulary - the students can learn the background information from the opening video, activity 1 and 2 and the list of key terms. (20 minutes)
3. Applying the theory - activity 3 is a discussion based exercise and considers why the UK£ may have risen following a government decision to call an early election. (10 minutes)
4. Developing the theory - activities 4 and 5 consider the impact of a depreciation / devaluation on the other macroeconomic indicators. (15 minutes)
5. Revision exercise - activity 6 contains a paper two style question which makes an ideal homework or classwork exercise. (20 minutes)
The activities on this page are available as a class handout at: ![]() The exchange rate market
The exchange rate market
Key terms:
Determinants of the market for a currency - the relative popularity for a nation's products, average price level, relative income levels, interest rates and investment transactions.
Devaluation - an official lowering of the value of a country's currency, either covertly or discretely within a fixed or managed exchange rate system.
The market for foreign exchange
Begin by watching the following short video focusing on the exchange rate market for US and Canadian $ and then apply the theory to the questions that follow:
Activity 1: Demand and supply for a currency
1. Start by drawing the supply and demand for two currencies e.g. US and UK$. Presume an initial exchange rate of £1 = $1.25 / $1 = £0.8
Market for $

Market for £

2. According to the video what are the 4 determinants of supply and demand (the video calls this shifters).
- tastes and preferences for both US / UK goods and services
- average price level
- income level (disposable income)
- interest rates
3. Illustrate the impact on the two diagrams if US products become less popular, relative to UK goods and services in both nations.
Market for $

Market for £

If US products were less popular in both nations then we would expect demand for $s (from the UK) to fall and the supply of £s to fall. This is because more UK citizens would wish to purchase American imports.
4. Explain the likely impact on the $ / £ exchange rate if the level of inflation in the UK was higher over a period of time.
Over time goods and services in the UK would become increasingly more expensive, relative to US products. This means that demand for £s would fall and the supply would rise, meaning a depreciation in value.
5. Explain the likely impact on the $ / £ exchange rate if US raises interest rates relative to those offered in the UK over time.
Market for $

Market for £

If US interest rates rise, relative to those offered in the UK, then we would expect demand for $s (from the UK) to rise and the supply of £s to rise, as more UK citizens would wish to purchase US$ to take advantage of the higher rates.
Activity 2
The following supply and demand curves represent the market for Єs, relative to the $. Illustrate the impact on the market for Єs of the following:
A rise in US GDP A fall in Euro zone interest rates


A rise in the demand for Єs A fall in the demand for Єs
The imposition of tariffs on German cars More US holidays sold in the EU


A fall in the demand for Є A rise in the supply of Єs
A fall in Euro zone GDP A rise in US income tax rates


A fall in the supply of Єs A fall in demand for Єs.
Activity 3: Political considerations
Watch the following video which outlines the impact on the value of the UK£ following the news that Boris Johnson won a substantial majority in the 2019 general election. Explain why this news will have strengthened the £.
Hint:
The video highlights that following the news of the victory for the standing government the £ made significant gains in value. This was widely believed to be the currency market reacting to the stability that a enhanced majority was likely to bring to the nation.
However, the video also stated that moving forward Theresa May's enhanced position might actually weaken the value of the £. The reasoning behind this is that a stronger position in the Parliament might make the UK Prime Minister negotiate a harder 'Brexit', which could effect the UK's future trading position.
Activity 4: Currency devaluation
Watch the following short video before discussing why China might be trying to devalue its currency?
(a) Why might China be deliberately trying to reduce the value of their currency?
Cheaper exports may cause an increase in AD through a rise in net exports. Though this may also lead to falls in real wages as inflation rises, causing a fall in AD. This in turn may reduce cyclical unemployment levels.
(b) Illustrate the impact of a depreciation on AD and AS.
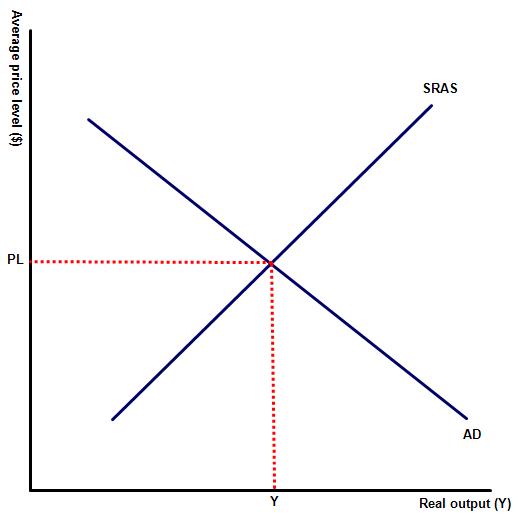

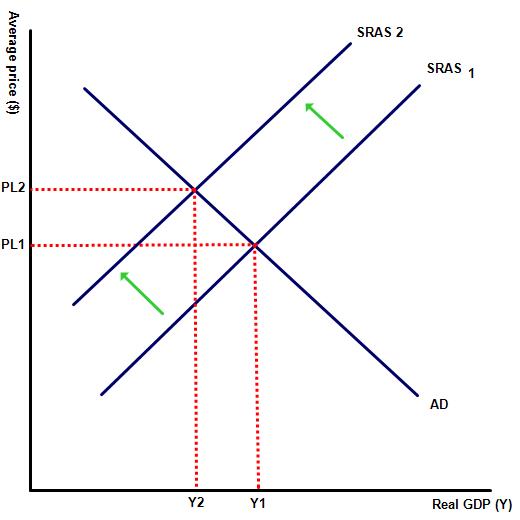

(c) Based on your responses (a - b), is China correct in trying to devalue the Chinese Yuan?
This depends, China would expect to see a rise in net exports but a fall in consumption as cost push inflation eats into real wage levels.
Activity 5: How a devaluation the UK economy?
In the aftermath of the UKs decision to leave the trading bloc the £ fell by 15% against the U$. The table below highlights the impact on the UK economy. Does it support the above theory that a devaluation will provide both advantages and disadvantages for an economy?
| Time period | Current account £ million | Inflation | Economic Growth |
| Pre-referendum (June 2016) | (33,034) | 0.75 % | 1.8% (year on year) |
| Post-referendum (2017) | (23,182) | 3 % | 1.7% (year on year) |
| Post-referendum (2018) | (23,700) | 2.5 % | 1.4 % (year on year) |
The table would appear to support this view. In the year after the referendum decision a number of UK products have been reduced in size to reduce costs (a term known as shrink-flation). At the same time inflation crept up to 3%, above the Bank of England target rate, forcing the bank to raise interest rates for the first time in ten years, following its October meeting.
At the same time UK manufacturers have enjoyed the weaker sterling value with the sector growing and the has helped Britain reduce its current account deficit. This sector will also have contributed to the UKs growth figures and compensated, in part, for the fall in consumer sales in 2017 and 2018. Though it is noticeable that economics growth rates were lower following the result, suggesting that any gains from an improvement in net exports is not sufficient to compensate for the rise in import costs.
Activity 6: Link to the assessment - paper two type question (old syllabus)
Argentina raises rates as peso plummets
(a) Define the following terms:
i. exchange rate (line 8) [2 marks]
Level | Descriptor | Mark |
0 | The work does not reach any of the standard described below | 0 |
1 | The idea that it is something to do with the relative price of currencies | 1 |
2 | An accurate definition that it is the price of one currency in terms of another | 2 |
ii. interest rates (line 12) [2 marks]
Level | Descriptor | Mark |
0 | The work does not reach any of the standard described below | 0 |
1 | The idea that it relates to the price of money | 1 |
2 | An accurate definition that it is the price of borrowing money, money added to the value of a loan that must be repaid | 2 |
(b) i. Calculate the % devaluation of the Peso, relative to the US$ and the fall in national income between 2018 and 2021. [3 marks]
Economic growth % base year = (0.1% + 0.2% + 15.5% + 1.4%) = 17.47%
Currency devaluation % (100.2 – 37.69) / 37.69 x 100 = 165.8%
Mark as 2+2 (maximum marks 3)
ii. Describe the inflation described in the passage? [2 marks]
Level | Descriptor | Mark |
0 | The work does not reach any of the standard described below | 0 |
1 | A vague definition that it is caused by a rise in output costs not AD | 1 |
2 | An accurate definition that the Peso devaluation and higher interest rates have caused cost push inflation (higher output costs) | 2 |
(c) List four factors that contribute to the demand for a currency. [4 marks]
Demand for a nation's currency is derived from a combination of the following:
- the popularity of a country’s exports (including tourist revenues)
- the level of investment by overseas citizens in a nation
- foreign currency derived from remittances from abroad
- speculators looking to make a profit on changes in currency values.
Mark as 1 for each factor identified
(d) Using a diagram, explain how a fall in inward foreign investment can affect the value of the Peso. [4 marks]
Level | Descriptor | Mark |
0 | The work does not reach any of the standard described below | 0 |
1 | An accurate diagram showing a decline in the value of the Peso, relative to the US$ as a result of falling demand for its currency OR an explanation that the fall in demand for the Peso is a consequence of fewer foreign citizens choosing to invest in the country. When an institution chooses to invest in a country, in this case Argentina, they must first convert their foreign currency into Pesos. | 1-2 |
2 | An accurate diagram showing a decline in the value of the Peso, relative to the US$ as a result of falling demand for its currency AND an explanation that the fall in demand for the Peso is a consequence of fewer foreign citizens choosing to invest in the country. When an institution chooses to invest in a country, in this case Argentina, they must first convert their foreign currency into Pesos. | 3-4 |
Mark as 2 (diagram) + 2 (explanation). Incorrectly labelled diagrams can be rewarded with a maximum of 1. Suitable labels include: P and Q; Price of Peso relative to $; Peso / $ and the X index should be labelled quantity of Peso; Quantity or Q.
(e) Using an AD/AS diagram, explain how a fall in the value of a currency can lead to higher levels of economic growth in an economy. [4 marks]
Level | Descriptor | Mark |
0 | The work does not reach any of the standard described below | 0 |
1 | For an accurate AD / AS diagram showing a shift to the right (a rise in in AD) and an increase in real GDP OR an explanation that a weaker currency increases the international competitiveness of the nation's products and hence net exports. For example, more tourists may choose to visit the nation, encouraged by lower prices. With net exports forming one of the components of AD this may result in higher levels of growth in real GDP. | 1-2 |
2 | For an accurate AD / AS diagram showing a shift to the right (a rise in in AD) and an increase in real GDP AND an explanation that a weaker currency increases the international competitiveness of the nation's products and hence net exports. For example, more tourists may choose to visit the nation, encouraged by lower prices. With net exports forming one of the components of AD this may result in higher levels of growth in real GDP. | 3-4 |
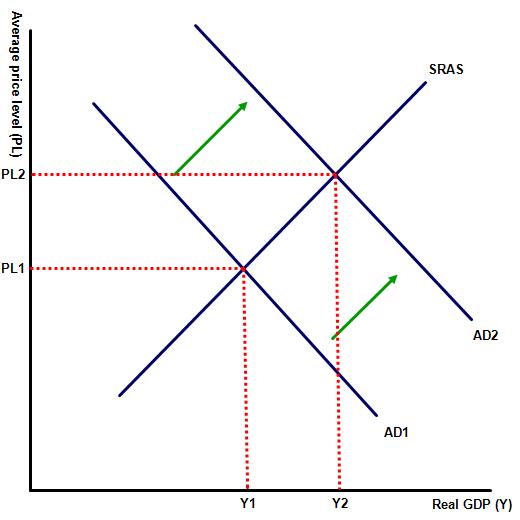 Mark as 2 (diagram) + 2 (explanation). Incorrectly labelled diagrams can be rewarded with a maximum of 1. Suitable labels include: Average price or AP and real GDP, Y, real national income or real Y.
Mark as 2 (diagram) + 2 (explanation). Incorrectly labelled diagrams can be rewarded with a maximum of 1. Suitable labels include: Average price or AP and real GDP, Y, real national income or real Y.
(f) Illustrate using an appropriate diagram why a further rise in interest rates might reduce the downward pressure on the Argentina Peso? [4 marks]
Level | Descriptor | Mark |
0 | The work does not reach any of the standard described below | 0 |
1 | For an accurate diagram showing the supply and demand for the Argentina Peso, with a left shift supply and / or a right shift in demand for the Peso OR an explanation that following the rise in interest rates fewer Argentinians will choose to purchase overseas assets (hence the fall in supply) and more overseas citizens will place their savings in Argentinian banks (hence the rise in demand for the Peso). | 1-2 |
2 | For an accurate diagram showing the supply and demand for the Argentina Peso, with a left shift supply and / or a right shift in demand for the Peso AND an explanation that following the rise in interest rates fewer Argentinians will choose to purchase overseas assets (hence the fall in supply) and more overseas citizens will place their savings in Argentinian banks (hence the rise in demand for the Peso). | 3-4 |
Mark as 2 (diagram) + 2 (explanation). Incorrectly labelled diagrams can be rewarded with a maximum of 1. Suitable labels include: Price; P; price of Peso or Price of Peso / US$. The X axis should be labelled Q; quantity or quantity of Peso.
(g) Using your knowledge of economics, evaluate the likely impact of a depreciating currency on the performance of the Argentina economy. [15 marks]
Command term: Evaluate
This command term asks candidates to reflect on both the positive and negative impacts of a depreciating currency on the performance of the economy and reach a plausible conclusion supported by appropriate evidence.
Positive impacts of a depreciating currency on the economy:
- A weaker currency improves the competitiveness of a nation's products, making exports cheaper and imports more expensive. This should increase the level of net exports, which will increase real GDP in the economy. This in turn can improve employment levels. This may be particularly true for the nation's tourist sector which is very labour intensive.
- a recognition that the exact impact on export revenues and import expenditure will ultimately depend on the price elasticities of demand for traded products.
Negative impacts of a depreciating currency on the economy:
- a depreciating currency value increases the price of imported goods, including raw materials that the nation depends upon, increasing the costs of production and leading to cost push inflationary pressures.
- a depreciated currency may also encourage complacency and reduced inefficiency among domestic producers.
- rising inflation, unless accompanied by higher rates of GDP, will reduce real income levels and this will be noticed particularly by citizens travelling overseas or those consuming imported products
Responses for question (g) should be graded according to the following mark bands:
Marks | Level descriptor |
0 | The response is below the standards described below. |
1-3 | The response indicates little understanding of the demands of the question The response uses little relevant theory Little attempt is made to make use of the text/data. |
4-6 | The response indicates some understanding of the demands of the question The response makes limited use of theory There is limited evaluation contained in the response The response makes limited use of the text/data to support their arguments. |
7-9 | The response indicates an understanding of the demands of the question Some relevant theory is used in the response The response contains some evaluation The response makes some use of the text/data. |
10-12 | The response indicates an understanding of the demands of the question The response uses relevant theory appropriately Evaluation is used appropriately There is appropriate use of the text/data. |
13-15 | The response indicates an understanding of the demands of the question The response makes effective use of relevant theory Evaluation is used effectively The response makes effective use of the text/data. |
The P2 style question is available as a PDF file at: ![]() Argentina Peso
Argentina Peso
Mark scheme is available as a PDF file at: ![]() Markscheme
Markscheme
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team