Indirect taxation
-1.jpg) Introduction
Introduction
While this lesson focuses on the impact of indirect taxation on a good or service there is also a discussion of how taxes are spent and reasons why a government places a tax on a good or service. Your classes will need to understand that when a government places an indirect tax on a good or service then this raises the price of the product, reducing the quantity purchased.
Students should also be able to make the link between the tax placed on certain items and the provision of public services which governments finance out of tax revenues.
Enquiry question
An understanding of why governments place taxes on goods and services and a recognition that goods and services respond differently to the imposition of a sales tax. Teacher notes
Teacher notes
Lesson time: 90 minutes
Lesson objectives:
Understand why governments impose indirect taxes on different goods and services
Distinguish between specific and ad valorem taxes
Illustrate using diagrams the impact of specific and ad valorem taxes on the market for different products
Discuss the consequences of imposing an indirect tax on the stakeholders in a market, including consumers, producers and the government.
Teacher notes:
1. Opening activity - Either ask students to complete this activity in their notebooks or have a volunteer complete the exercise on the whiteboard. (10 minutes)
2. Processes - technical Vocabulary - your classes can learn the required vocabulary watching the video and studying the class handout which follows. (15 minutes)
3. Reinforcement activities - attached to the class handout are a number of activities to test the students skills in this topic.
Activities 1 and 5 are graphical exercises, while activity two is a research exercise.
Activity 6 contains a series of short answer questions, based on the information in the table provided and activity 6 requires students to consider the costs and benefits of generating tax revenue via indirect taxation. Allow 35 minutes to complete all the activities.
4. Link to TOK - should marajuana be legalised and subject to indirect tax. Start this activity with a vote on the question and then show the video. Have any of your class changed their opinion on the topic after watching the video. (15 minutes)
5. Link to the assessment - this page includes a typical paper one style question on this topic, which you can project onto the whiteboard for your classes to read and discuss. (10 minutes)
6. Further reading on this subject can be downloaded using the link enclosed. (Homework exercise)
1. Beginning activity
Draw three supply and demand curves in your notebooks. These diagrams should be for products with different PED elasticity, e.g. cigarettes, used cars (unitary PED) and a good with elastic PED. Draw the impact of a sales tax on the good or service, including the new equilibrium points. Be careful that you do not illustrate the impact of the tax by changing the demand curve, rather than supply.
(a) Highlight the burden of tax paid by the consumer, in the form of higher prices and lost consumer surplus and the burden paid by the producer, in the form of lost sales and lower profit margins.
(b) Which of the three products provides the government with the most tax revenue?
(c) Which has the most significant impact on reducing sales for the product?
Key terms:
Indirect tax - tax placed on a good or service, raising the production costs of the business. It is a tax on expenditure rather than a tax on income.
Specific tax - this is a fixed amount placed upon a good or service, e.g. a government may impose a specific tax of say $ 4 on each pack of cigarettes sold.
Ad valorem tax - this is a tax placed on a range of goods and services which is a percentage of the total selling price. For example in the EU the majority of states place a 20% tax on the sale of most goods and services.
Producer taxes - a tax on sales but paid for by the manufacturer or producer, rather than the consumer.
Excise taxes - taxes applied to a narrow range of products, such as cigarettes or alcohol. These are imposed to reduce consumption of those products.
Import tariffs - a tax on imported goods designed to protect domestic industry.
Incidence of taxation - the share of tax paid by both the consumer, in the form of higher prices / lower consumer surplus and the share paid by the producer in the form of lost sales and lower producer surplus.
The class handout can be accessed as a PDF file at: ![]() Sales taxes
Sales taxes
Activity 1
Start by watching the following short video and then complete the tasks that follow:
(a) Add a flat rate indirect tax to the following diagrams and then answer the questions that follow:
(b) Illustrate the change in price and quantity demanded for each of the three products, highlighted in the diagrams above.
(c) Illustrate the change in consumer and producer surplus resulting from the indirect tax.
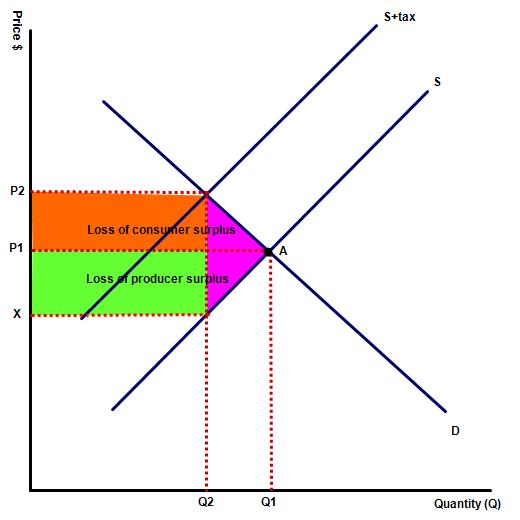
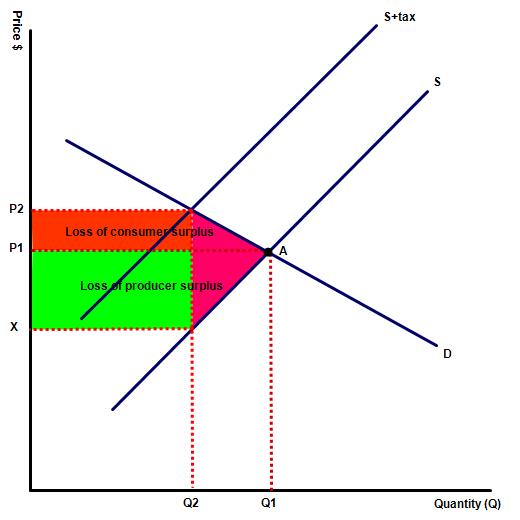
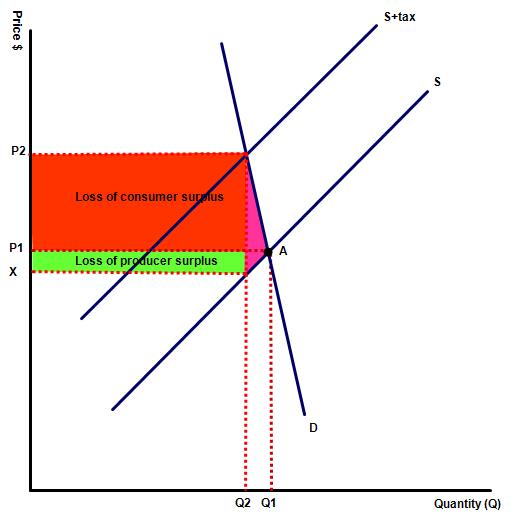
On each diagram both the consumer and producer surplus declines. However, this does not count as wefare loss because in each case the consumer / producer loss is gained by the government. On each diagram the deadweight community loss is indicated by the purple triange, which shows production which no longer happens as a result of the tax.
 Activity 2: Research activity
Activity 2: Research activity
Sales tax can be divided into general sales taxes applied to all goods and services and specific taxes on certain products, that the government wishes to reduce the consumption of. Examples might include taxation placed on tobacco and alcohol products while some governments place taxes on luxury goods imported from overseas.
Research the goods and services that your government places a specific tax on and decide the likely motivation for the tax?
Hint:
Taxes are generally placed on a good or service for one of two reasons:
- to reduce consumption levels
- to raise tax revenue.
The prime motivation for taxes applied to all goods and services is to raise tax revenue to pay for public services.
The motivation for specific taxes on certain products is because the government wishes to reduce the consumption of those products e.g. tobacco and alcohol products.
Another important consideration for any government is the PED elasticity of the good or service being taxed. A tax on PED elastic goods will be effective in reducing consumption levels, while a tax on PED inelastic goods will be effective in raising tax revenue.
 Activity 3
Activity 3
The diagram to the right illustrates the market for a good.
(a) Illustrate the impact of a tax on the market for this good by drawing a new supply curve to the left of the original.
(b) Illustrate the new equilibrium price and quantity.
(c) Illustrate the burden of tax paid by both the consumer and producer and the 'dead weight' loss.
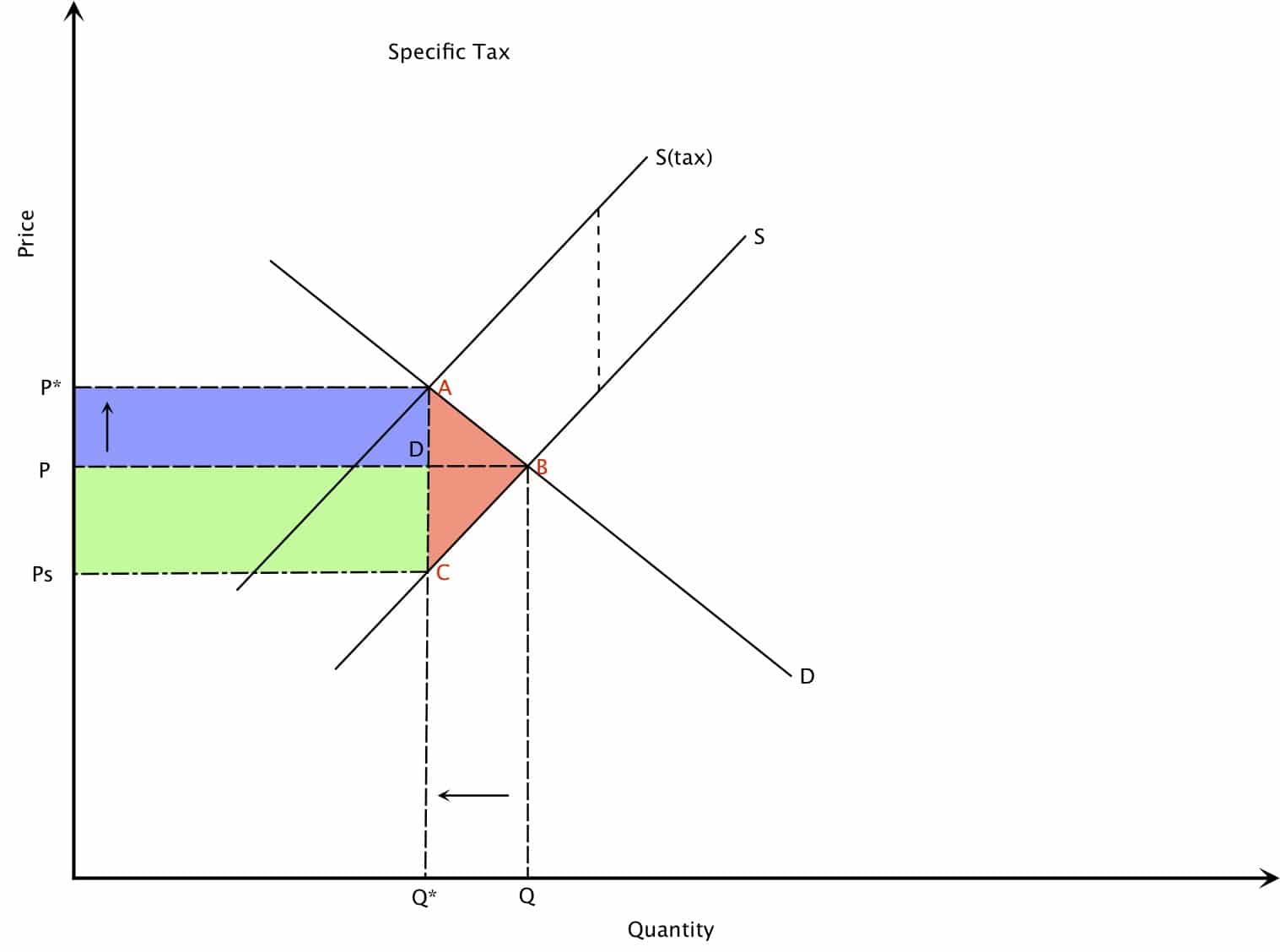 In the diagram the tax burden paid by the producer is represented by the green rectangle. This is found by drawing a horizontal line to the Y axis from point C, where the new output intersects the original supply curve. The blue shaded area represents the tax burden paid by the consumer in the form of higher prices. Lastly, the pink triangle represents the 'dead weight' loss. This represents the loss of value caused by market inefficiency - as a result of the sales tax the price of the good is higher and the output lower than without the tax.
In the diagram the tax burden paid by the producer is represented by the green rectangle. This is found by drawing a horizontal line to the Y axis from point C, where the new output intersects the original supply curve. The blue shaded area represents the tax burden paid by the consumer in the form of higher prices. Lastly, the pink triangle represents the 'dead weight' loss. This represents the loss of value caused by market inefficiency - as a result of the sales tax the price of the good is higher and the output lower than without the tax.
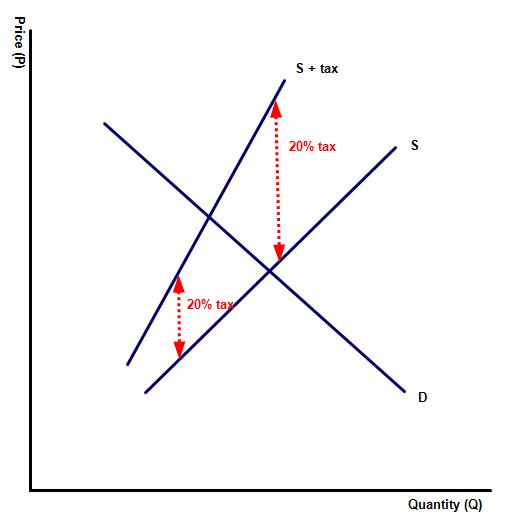 Activity 4
Activity 4
The diagram to the left illustrates an ad valorem tax, a fixed percentage tax, added to the production cost of the good or service.
(a) Explain why the new supply curve is not parallel to the original, as with a fixed rate tax.
With any percentage tax the amount paid grows as the price of the product increases. Simply put if the price of a product is £ 5 then a 20% ad valorem tax would be £ 1 while the same tax on a good or service costing £ 10 would be £ 2.
(b) Explain one advantage of a % tax over a flat rate indirect tax.
An advantage of ad valorem taxes is that as the economy grows and national income rises, the amount of tax revenue to the government rises automatically. This makes the tax self regulating meaning that it does not require annual changes to the tax rate, as with flat rate taxes. Of course in times of recession government revenue will fall at a time when many governments need more revenue in order to pay for higher welfare and unemployment payments. In 2008 the UK government actually reduced the VAT (sales tax) rate to try and stimulate the economy.
Activity 5
Draw the impact of a percentage or ad valorem tax on the product, represented by diagram 1. On diagram two, illustrate the impact of a flat rate tax on the same good or service.


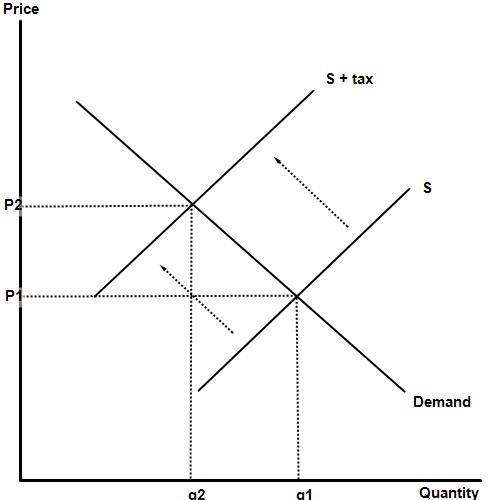
Activity 6
The table below shows the demand and supply schedules for a good:
Price ($) | QD | QS (pre-tax) | Qs (post-tax) |
10 | 100 | 900 | 700 |
9 | 200 | 800 | 600 |
8 | 300 | 700 | 500 |
7 | 400 | 600 | 400 |
6 | 500 | 500 | 300 |
5 | 600 | 400 | 200 |
4 | 700 | 300 | 100 |
3 | 800 | 200 | - |
2 | 900 | 100 | - |
1 | 1,000 | 50 | - |
Questions:
(a) What is the initial equilibrium price and quantity?
Price of $6 and an equilibrium quantity of 500 units
The government imposes a tax of $2 per unit, with the new supply schedule as shown in column 4.
(b) Find the new equilibrium price after the tax has been imposed
The new price becomes $7 and the equilibrium quantity becomes 400 units
(c) Calculate the total tax revenue going to the government
The tax revenue collected by the government is $2 x 400 = $800
(d) How have consumers and producers been affected by the sales tax?
As a result of the tax equilibrium output has fallen by 100 units. Consumers have lost out as they are now paying an extra $1 for their purchase and a number of consumers will no longer purchase the good (loss of consumer surplus). The producer has also lost out as a result of reduced sales and a lower profit margin.
Activity 7: Countries with the highest sales tax
Nations with the highest sales tax in 2022 are represented on the following diagram:
| Rank | Country | Sales tax rate % |
| 1 | Hungary | 27 |
| 2 | Croatia | 25 |
| 3 | Denmark | 25 |
| 4 | Norway | 25 |
| 5 | Sweden | 25 |
| 6 | Finland | 24 |
| 7 | Greece | 24 |
Questions:
(a) Describe the likely impact of high sales tax rates on levels of investment within a nation?
While businesses will accept that governments need to collect tax revenue from somehow in order to provide the goods and services that the public needs, sales tax discourage investment. Clearly, investors would prefer countries with low sales tax to those with high sales tax. High sales tax rates reduce profit margins. Besides, high sale tax that is uniform across all goods and services regressive. By this, it tends to deprive the low-income earners more than the high-income earners. This is because sales rate does not vary depending on a person’s wealth.
(b) Describe some of the benefits of generating tax revenue from indirect taxation?
- collecting tax revenue via sales is often cheaper than through collecting revenue from income tax or corporation tax
- sales taxes are easier to collect and mean that the % of citizens contributing to tax is greater, for example many developing nations have a very low tax base which makes it difficult to collect sufficient revenue to pay for the public services the country needs
- unlike taxes on income and company profits, sales taxes do not discourage citizens from working hard or starting a business.
(c) Outline some of the weaknesses of indirect taxes?
- setting the 'correct' tax rate e.g. one that generates sufficient revenue, without discouraging consumption is difficult to calculate
- cost of collection can be high, though not normally as high as other methods of tax collection e.g. income tax
- in situations where a government is trying to reduce demand for certain addictive goods e.g. alcohol and tobacco products, the inelastic demand of those products means that higher indirect taxes have little immediate effect on demand
- by definition indirect taxes impact on low-income households most
Activity 8: Should marijuana be taxed
Start this activity with a short vote on the question, should the narcotic be legalised or not?
Now watch the following short video which argues that the production of marijuana should be legalised and then subject to a sales tax, just as cigarettes and alcohol are under the current law in America. Summarise the main arguments for and against the legalisation of this product? Has the video in anyway changed you opinions on the merits of legalising the product?
 The arguments stated in the video argue that under the current legislation marijuana consumption is already at very high levels. Individuals wishing to consume the drug simply purchase it illegally from dangerous criminals or if they are lucky, from a supplier that they know and trust. Therefore by legalising the product governments will take away the income stream from some of the worlds most dangerous people and instead provide significant tax revenues to the government.
The arguments stated in the video argue that under the current legislation marijuana consumption is already at very high levels. Individuals wishing to consume the drug simply purchase it illegally from dangerous criminals or if they are lucky, from a supplier that they know and trust. Therefore by legalising the product governments will take away the income stream from some of the worlds most dangerous people and instead provide significant tax revenues to the government.
A counter argument may be that as an addictive product the legalisation of the drug may well increase consumption rates further, some of whom may then progress towards more dangerous drugs once novelty of the soft drug has worn off.
9. Link to the assessment
 Government intervention from a microeconomics perspective can be found in papers one and three. Examples of paper one questions include:
Government intervention from a microeconomics perspective can be found in papers one and three. Examples of paper one questions include:
Part (a)
Explain why governments impose indirect taxes on specific goods and services. [10 marks]
Command term: Explain
Governments place a tax on a product one of two reasons:
Firstly, it can be a good way of generating tax revenue. While some other taxes such as income tax and corporation tax can be more difficult to collect, especially in LEDCs, taxing goods and services represents a relatively simple way to collect the tax revenue that a government needs to pay for public services.
Sales taxes can also used as a way of encouraging responsible consumption as governments can tax heavily harmful products such as alcohol, petrol and tobacco products while leaving some goods and services free from tax. Goods in this category might be children's clothing or fresh fruit and vegetables.
Part (b)
Using real world examples, evaluate the effectiveness of indirect taxes in reducing the consumption levels of demerit goods such as tobacco, petrol and alcohol products? [15 marks]
Command term: Evaluate
Evaluate requires candidates to determine how effective indirect taxes are at reducing consumption levels of cigarettes, alcoholic beverages e.t.c.
Key terms to define: indirect taxes, demerit goods, negative externality
Relevant real life examples might include examples from the candidates own nation as to how effective taxes have been in reducing the consumption of various demerit goods. Many nations, for example, have placed high taxes on alcoholic beverages and tobacco products and have successfully reduced consumption levels - but only in the long term.
In answering this question a key consideration is the PED elasticity of the good or service being taxed. Demerit goods such as tobacco, petrol and alcohol products are all PED inelastic in the short run. Consumers are unlikely to give up any  of these products immediately, regardless of how expensive they become and so the tax will initially be ineffective in substantially reducing consumption levels. However, the tax will be effective in raising tax revenue for the government as consumers pay the higher prices.
of these products immediately, regardless of how expensive they become and so the tax will initially be ineffective in substantially reducing consumption levels. However, the tax will be effective in raising tax revenue for the government as consumers pay the higher prices.
Long term indirect taxes are more effective in reducing consumption levels. For instance USA and many EU countries have successfully reduced smoking rates by prohibitive tax rises over a number of years.
To be really effective, however, taxes would only be part of a set of government policies aimed at reduced consumption of certain products. Other policies would include education campaigns, or in the case of road congestion an electronic road pricing scheme or investments in public transport.
Paper three
Relevant questions from the paper three exam might include illustrating the impact of an indirect tax on a good or service, using a given set of data. Paper three questions on this topic might also require candidates to calculate the change in price / quantity demanded or the size of the consumer and producer surplus, after the imposition of a sales tax.
10. Further reading
Can be accessed at: //ourworldindata.org/taxation
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team