A comparison of monopoly and perfect competition? (HL only)
 Introduction
Introduction
This lesson compares monopoly and perfect competition and asks which offers greater benefits to any society? Much of the response to this will depend on personal opinion but IB students should be aware that both structures enjoy advantages over the other. I will sometimes encourage my IB classes to use this part of the syllabus as a focus for part of their internal assessment. Relevant articles might include one focused on government regulations of monopolies or anti competition laws.
Enquiry question
Which is the more efficient type of business structure - monopoly or perfectly competition businesses. Will monopolies always charge higher prices to consumers than competitive businesses.
 Lesson notes
Lesson notes
Lesson time: 1 hour
Lesson objectives:
To what extent are monopolies efficient? Evaluate reasons why, despite inefficiencies, a monopoly may be considered desirable?
Understanding some of the policies that a government may implement to regulate monopoly power.
Use diagrams to explain the advantages and disadvantages of monopoly compared with perfect competition.
Teacher notes:
1. Beginning activity - begin with the opening activity and allow 10 minutes for your classes to complete the question and discuss the video. (10 minutes)
2. Processes - technical Vocabulary - the students can learn the key concepts through activity 1, which should take 15 minutes to go through and discuss.
3. Practise activities included on the handout should take around 25 minutes. These are a combination of short answer and diagrammatic exercises. (30 minutes)
4. Final reflection exercise - contains a relevant paper one style question on this topic that your students can look at and discuss. This topic of course can be included on papers one and three of the examination and this page contains both types of questions to practise on. This activity could also be set as a homework or classwork exercise. (10 minutes)
The activities on this page are available as a worksheet in PDF form at: ![]() Monopoly v PC
Monopoly v PC
Beginning activity
Express your vote by a show of hands, which industrial structure offers the better deal for the consumer - monopoly or competitive businesses?
Watch the following short video and then discuss the question which follows.
The video paints a very negative picture of monopolies. Is the video correct or can monopolies actually be beneficial to a society?
Hint:
The majority of economists would certainly agree with parts of the video. This is why many nations actively regulate monopolies such as the anti trust laws described in the video. However there are industries which are probably well suited for a monopoly. For example no rational individual would suggest that the American space programme, NASA would be better served by a competitive environment and industries such as the royal mail are examples of monopolies set up by the government. Other industries such as telecommunications, rail and air travel might also be better served by one dominant business, rather than small competitive businesses.
 Activity 1
Activity 1
The diagram to the right illustrates the total market for potato salesmen in Örtaköy, Istanbul - a market under perfect competition.
(a) Highlight the equilibrium price and output for the product and shade in the size of the consumer surplus.

(b) Presume that all of the firms in the industry merge, creating just one business, which is now a monopoly. Draw the new equilibrium price and output for the new firm and draw the new consumer surplus.
(c) Shade in the welfare loss resulting from the merger.
(d) Using your answers from a-c, summarise the impact of the merger on price and output.
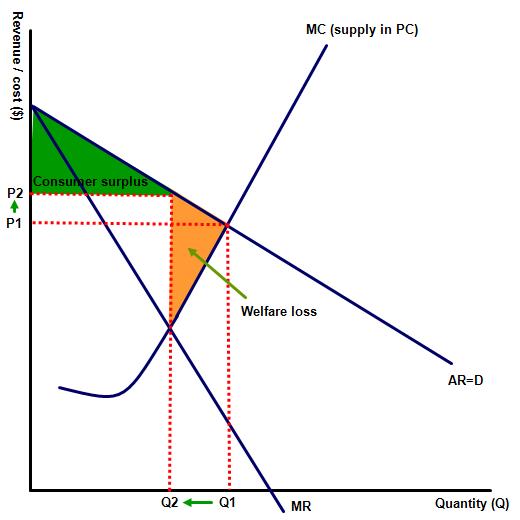 When the firms merged and were able to take advantage of their monopoly status they acted immediately by restricting supply in the market from Q1 to Q2, which forced up priced from P1 to P2. In turn this caused a reduction in consumer surplus, shown on the diagram.
When the firms merged and were able to take advantage of their monopoly status they acted immediately by restricting supply in the market from Q1 to Q2, which forced up priced from P1 to P2. In turn this caused a reduction in consumer surplus, shown on the diagram.
A welfare loss was also created shown by the orange triangle.
(e) Draw the effect on equilibrium price and quantity, on a new diagram, in a situation where the new merged firm was able to enjoy significant economies of scale.
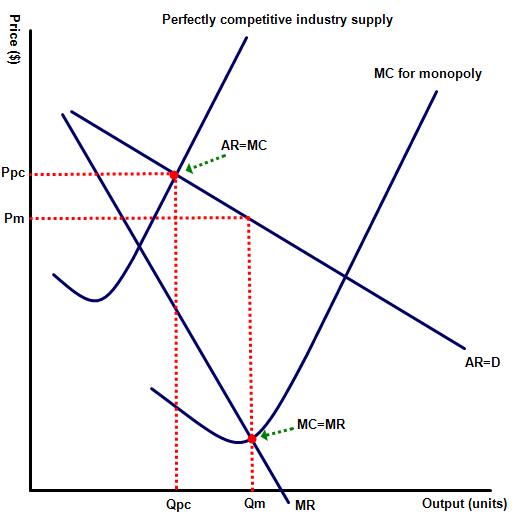
(f) Which business offers consumers the lower prices - the newly merged industry (with significant economies of scale) or the old perfectly competitive industry?
The newly created monopoly - Pm compared to Ppc
(g) Which of the two business offers the higher equilibrium output?
The newly created monopoly - Qm compared to Qpc
(h) Use your answers in activity 2 to answer the following question, 'which of the two industry structures provides the greater benefits to consumers'?
This depends on the ability of the monopoly firm to take advantage of the potential gains made from economies of scale and the extent to which the monopolist passes these on to the consumer in the form of lower prices and higher output.
Activity 2
Go back to the section on productive and allocative efficiency in perfect competition and answer the following question: Will monopoly businesses be either allocative or productively efficient in the long run?
If you have reread your notes correctly you will be aware that firms in perfect competition are both productively and alloactively efficient in the long run. In monopoly firms by contrast the output level will be neither allocatively effcient. Instead the monopolist will restrict supply, to below the productive efficiency level, in order to force up the selling price so that AR > MC.
Unlike firms in perfect competition, as the only producer in the market, they are able to control the level of supply in the industry.
Activity 3
Which of the following market structures do you think would be better served by a monopoly and which would be better served by a competitive market structure? Explain the reasons for your responses.
Schools in a local area
Schools should remain competitive environments as it makes little sense to have just one enormous school serving many thousands of students, within the same geographical area. Such a school would enjoy certain economies of scale but would also experience significant diseconomies of scale through its sheer size. With very few schools in the area also many children would have to travel long distances each morning, clearly a negative consequence for those families involved.
The airline industry
There is a strong argument that given the significant economies of scale available to an airline this industry may provide the consumer with a better service in a monopoly environment. Competition would already be in place for travellers from other modes of transport as well as national carriers of other countries so there is little chance of the consumer being exploited.
Telecommunications
This industry has some of the characteristics of a natural monopoly and could be considered a natural monopoly.
Activity 4
Watch the following short video and decide if you believe that the existence of monopolies is sufficient reason to support the view that governments should bring in legislation to reduce monopoly power.
As the video highlights, the problem facing many governments is that the greater the legislation designed to cap monopoly profits, the lower the incentive is for other competing businesses to enter the market and provide competition. Reducing start up costs are probably the most effective way of driving down prices and the growth of the Internet has helped this.
Activity 5
Should Facebook be broken up?
Watch the following video, an interview with former co-owner Chris Hughes and then decide for yourself.
Chris Hughes claims that Facebook is currently too big and too powerful in its current status. is claim is based n the fact that they were able to purchase Instagram, Whatsup e.t.c, effectively using their financial power to impose impenetrable entry barriers to the industry.
Mark Zuckerberg was not featured in the video but he would no doubt point to the economies of scale generated as evidence that the firm operates in the public interest - Facebook remains free for users for example, but not advertisers.
Activity 6: Link to the assessment
Examples of paper one questions include:
a. Explain different ways that a monopoly may emerge. [10 marks]
.jpg) Command term: Explain
Command term: Explain
Key terms to define: monopoly, barriers to entry
Monopolies emerge as a result of a firm establishing very high barriers to entry. This prevents other firms from entering the market, ensuring they remain the only business in the market.
Examples of barriers to entry include:
- when the government sets up a public service such as the postal service and prohibits other businesses from entering the market
- natural monopolies where the market size is insufficient for the presence of more than one firm
- brand loyalty e.g. Coke and Pepsi which are now synonomous with the fizzy drinks market
- when a firm has a patent or an exclusive contract to sell and market a product
- when the benefits from increasing returns to scale are so sufficient that new firms would find it impossible to enter the market without substantial funds made available for development and marketing.
b. Using real world examples, evaluate whether a monopoly or a perfectly competitive market provide the greater benefits to consumers. [15 marks]
 Command term: Evaluate
Command term: Evaluate
Key terms to define: monopoly, perfect competition
With the command term being evaluate responses must make a decision as to the validity of the claim stated in the question.
Real life examples might include industries best served by monopoly such as telecommunications where the gains from economies of scale are very large or where the market is not sufficient for more than one business to succeed in this market (natural monopoly). Responses should also include examples of where a market is poorly served by a lack of competition in the market, where perhaps prices are high and the quality of service offered low.
This ultimately depends on two factors, the first being whether firms in that industry are likely to enjoy significant economies of scale from production. The second is whether the monopolist in this example retains the benefits from increasing returns to scale in the form of higher profits or instead uses some of the gains to lower prices and improve product choice / quality. Diagram one illustrates an industry where as a result of economies of scale the consumers are benefitting from lower prices (Pm rather than Ppc) and higher output (Qm rather than Qpc) 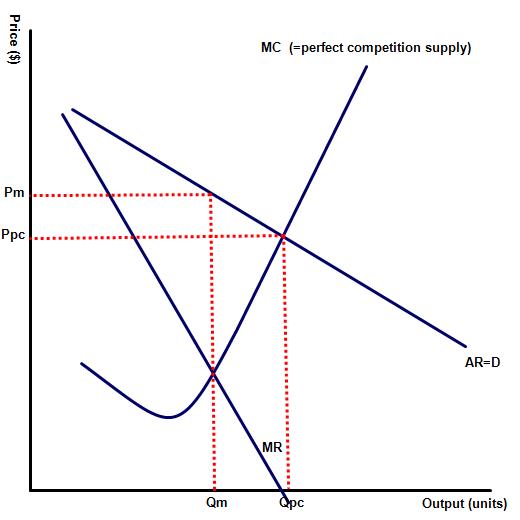 than in a competitive environment. However, in diagram two, illustrating an industry where the gains from economies of scale are small, the customer has benefitted from a competitive environment. In this example the competitive industry offers lower prices (Qpc < Qm) and higher output than in monopoly - (Qpc > Qm).
than in a competitive environment. However, in diagram two, illustrating an industry where the gains from economies of scale are small, the customer has benefitted from a competitive environment. In this example the competitive industry offers lower prices (Qpc < Qm) and higher output than in monopoly - (Qpc > Qm).
Therefore, the validity of the claim is determined by the type of industry. Examples of industries where a monopoly might offer greater benefits to the consumer include airlines, telecommunications (where high profits can be ploughed back into the development of new products), postal delivery services and natural monopolies such as space travel. Industries likely to offer greater benefits from increased competition include cafes, coffee shops, hotels, taxi services and services such as hair dressers where the gains from increasing returns to scale are relatively limited.
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team