BMT 5 - Business plans
 "Never start a business just to make money. Start a business to make a difference."
"Never start a business just to make money. Start a business to make a difference."
- Marie Forleo (b.1975), American entrepreneur and New York Times bestselling author
“The rich man plans for tomorrow, the poor man for today.”
- Chinese Proverb
“By Failing to prepare, you are preparing to fail.”
- Benjamin Franklin (1706 - 1790), one of the Founding Fathers of the USA
“A good plan today is better than a perfect plan tomorrow.”
- George S. Patton (1885 - 1945), US Army General
A business plan is an official document with details of an organization and the proposals for reaching its aims and objectives (goals). As a management planning tool, a business plan is also likely to include background information about the organization, the key personnel (staff), market research findings, competitor analysis, its planned marketing strategy and details of its financial position.
The purposes of creating and using a business plan include:
To devise a suitable and feasible business strategy for growth
To determine the future needs and direction of the organization
Allows entrepreneurs and decision-makers to make informed and objective decisions about their business, and
To secure sources of finance (from lenders, such as commercial banks) and to attract potential investors (such as strategic partners, shareholders, and business angels).
Most small businesses, especially start-ups, have very limited resources. Market research can be both time consuming and costly, so is avoided or done poorly. Having an effective, well-thought out business plan helps to improve planning and analysis, so that entrepreneurs do not have to rely on their gut instincts. Poor planning, or a lack of it, is a major cause of business failure.
Advantages of business plans
Advantages of creating and using business plans include:
The relative strengths and weaknesses of a proposal can be inferred from a business plan.
It adds substance to a business idea or proposal, in order to support strategic planning and decision-making.
The business plan helps to provide a logical structure to thinking about the business idea or proposition.
Entrepreneurs are more likely to succeed if their business strategy is carefully planned.
It helps to reassure investors and financiers, especially if the business is seeking external sources of finance to fund its operations.
A business plan can have many functions (uses), from trying to secure external sources of finance to measuring the success of the business.
It is a means for making all employees aware of the business's strategic plan and direction.
It can be used as an objective method to measure actual performance of the business.
Elements of a business plan
The main elements of a business plan will typically include the following:
Executive summary (or Abstract) – The first part of a typical business plan provides an overview of the organization, its corporate objectives, and intended business strategy. This section provides a summary of the business plan.
Introduction / Overview – This section contains an introduction to the business, its legal status (type of organization), its vision and mission statements, and intended aims and objectives. It will also include a brief about key personnel in the organization (such as the owners or senior executives), and may include an organizational chart.
Market analysis – This part of the business plan includes details of the market or industry in which the organization operates. It will usually include a competitor analysis, outlining the main rivals in the industry and their respective market share. It should include projected sales figures and marketing opportunities. The market analysis may include a SWOT analysis, with a focus on strengths and opportunities.
Product analysis – This important section describes the planned product being offered. For example, authors needs to convince publishers that their idea for a book will be commercially viable. Ideally, the business plan should show the unique or distinctive selling points of the proposed product or idea.
Financial analysis – This section of the business plan contains details of the finances of the business. For new businesses, this will include projected cash flows. For established businesses, this will include the latest final accounts (balance sheet and profit & loss account). Detailed financial analysis can help the business to secure external sources of finance from investors and financiers.
Marketing strategy – The market analysis and other parts of the business plan should steer the firm’s marketing strategy. It should include details of the firm’s marketing mix, e.g., pricing strategies, distribution networks, promotional campaigns, and product strategy.

The elements of a business plan must be specific to the needs of the organization
Watch this review video on the importance of the need for businesses to write an effective business plan. The video mentions the main reasons why businesses collapse - students might be surprised to hear the number one reason.
ATL Activity 1 (Social and Thinking skills) - The benefits of business planning
Suggested time: 15 minutes
Split the class into four groups. Each group should focus on a different type of business organization:
A small local business operated by a sole trader
A large multinational company with its headquarters in your country
A start-up business run by three partners
A non-profit organization that operates on a national scale.
Each group should discuss and brainstorm a list of the key benefits of creating and using a business plan for their designated type of business above. All members should be prepared to share their responses with the rest of the class.
Top tip!
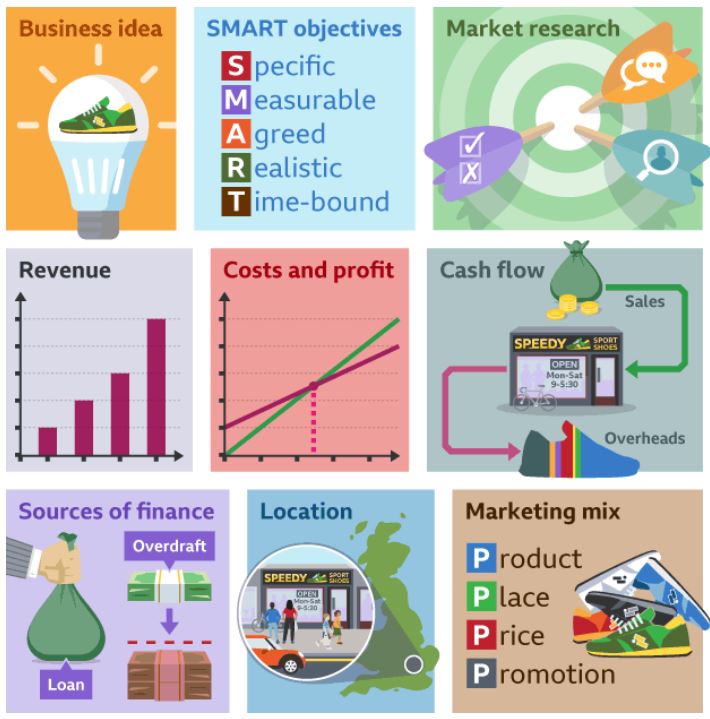
Note that a business plan is not used only when a new business starts up (although it is a vital and common step in setting up a new business). A business plan is rather versatile and can be used as an organization grows and seeks to pursue various growth strategies.
ATL Activity 2 (Thinking and Communication skills) - Dragon's Den
In the corporate world, it really does pay to be prepared and to have a plan.
Watch this short sales pitch on Dragon's Den. This sales pitch features Hannah Saunders, founder and director of Toddle, a supplier of skincare products for children.
Suppose you are the marketing director of Toddle. Prepare a business plan to launch the full range of Toddle products to retailers such as supermarkets.
Be prepared to share your business plan with the rest of your team (your classmates).
Business Plan Template
Your can download a PDF template with top tips for creating business plans by clicking the icon below. This has been created by Shopify and Project Management to support entrepreneurs, but is highly suitable for IB Business Management students.
Business Management Toolkit (BMT)
Examine the usefulness of STEEPLE analysis for the creation of business plans.
To test your understanding of this section of the Business Management Toolkit, have a go at the following multiple choice questions.
What is not included in a business plan?
Business plans do not include details of the pay and remuneration paid to employees and managers. This is not required by investors or other stakeholders interested in examining a business plan.
Which of the following is unlikely to feature in a business plan?
Details about barriers to effective communication in the workplace are more suitable for a SWOT analysis.
A competitor analysis in a business plan does not include information about which of the following?
A business plan will not include the various sources of finance of competitors.
Which of the following is unlikely to feature in the financial plan of a business plan?
The financial plan will include details of the projected financial statements (income statement and balance sheet) as well as cash flow forecasts. The amount the firm expects to spend on employees does not need to be included in a typical business plan.
What is the main purpose of a business plan?
Whilst the other options are important for a business plan, the ultimate purpose of creating such a plan is to get funding from investor and/or financiers (such as banks).
How often should a business plan be reviewed and updated?
A business plan needs to be dynamic in nature, so the creator will often update this as and when required. After all, the plan includes projections, such as financial forecasts, so changes may mean the business plan should be updated accordingly.
A business plan should be primarily focused on which of the following?
Whilst the other options are all typically included in a business plan, the focus of the plan is to provide strategic direction to achieve the organization's business objectives.
Who is the primary audience of a business plan?
Whilst any stakeholder might be interested in the business plan of an organization, the intended purpose of the document is to secure finance. Hence, the main audience is potential investors and/or financiers (lenders).
What is the focus of the executive summary in a business plan?
The business plan is likely to include all of the above, although the executive summary (as the name suggests) provides an abstract of the main findings or key points within the full business plan.
What is a financial plan within a business plan?
The financial plan refers to the projected earnings (profit) of the business should its plan succeed.
| (a) | Define the term business plan. | [2 marks] |
| (b) | Explain why a bank might be interested in a firm's business plan. | [2 marks] |
| (c) | Explain two benefits to an entrepreneur of using business plans to aid strategic planning. | [4 marks] |
Answers
(a) Define the term business plan. [2 marks]
A business plan is an official document detailing an organization's proposals for reaching its corporate aims and objectives.
Award [1 mark] for a limited response that shows some understanding. Award [2 marks] for a clear and accurate definition, similar to the example above.
(b) Explain why a bank might be interested in a firm's business plan. [2 marks]
A bank would be interested in a firm's business plan before deciding whether to lend the business money. Essentially, the bank would want to ensure that it can get its money back if it provides the business with a commercial loan or mortgage.
Award [1 mark] for a limited response that shows some understanding. Award [2 marks] for a concise and accurate explanation, similar to the example above.
(c) Explain two benefits to an entrepreneur of using business plans to aid strategic planning. [4 marks]
Possible benefits could include:
By completing a business plan, the entrepreneur gains a full and better understanding of each element of her/his business, and hence the chances of success or failure.
The business plan enable the entrepreneur to amend the things as necessary in order to minimise the risks associated with setting up a business or expanding the existing business.
Business plans and strategic planning are vital for new businesses and entrepreneurs as the risk business failure within the first year is extremely high.
It encourages the entrepreneur to consider the marketing, human resource, operations and financial aspects of the business idea or proposition in order for it to succeed.
- Accept any other relevant benefit of using business plans.
Mark as a 2 + 2
For each benefit, award [1 mark] for stating a relevant answer and [1 mark] for the explanation.
This tool is applicable to almost all sub-units in the syllabus. It could be beneficial to introduce business plans towards the beginning of the course and revisit aspects of this tool when studying different topics. Suggested units for integration of business plans in teaching the contents of the syllabus include (not exhaustive):
Unit 1.1 - Examine how a business plan can help entrepreneurs with the challenges and opportunities for starting up a business.
Unit 1.2 - Discuss the reasons why entrepreneurs and business owners use business plans.
Unit 1.2 - Compare and contrast the business plans for a social enterprise and other for-profit organizations.
Unit 1.2 - Explain the role of a business plan for an organization changing its legal status (for example, from a sole trader to privately held company, or changing from a privately held company to a publicly held company).
Unit 1.3 - Examine the role of business objectives in a business plan.
Unit 1.3 - Distinguish between organizational objectives in a business plan for private sector organizations and public sector organizations.
Unit 1.4 - Explain the stakeholder groups who are most likely to be interested in an organization's business plan.
Unit 1.5 - Examine how a business plan might be useful as a business management tool for both a new start-up and a long-established business planning expansion in overseas markets.
Unit 2.1 - Discuss the importance of inclusion of human resource planning in a business plan.
Unit 3.2 - Explain the relationship between business plans and internal and external sources of finance.
Unit 3.2 - Explain how a business plan could be useful for a business in securing external sources of finance.
Unit 3.4 - Explain the purpose of final accounts in a business plan for different stakeholder groups.
Unit 3.7 - Explain the advantages of including cash flow forecasts in business plans.
Unit 3.9 (HL only) - Explain the importance of accurately constructed budgets in a business plan.
Unit 4.3 (HL only) - Evaluate the use of sales forecasting in a business plan
Unit 4.4 - Explain why business organizations conduct market research before developing a business plan.
Unit 5.2 - Explain the role of a business plan for an organization choosing to change its operations methods.
Unit 5.5 - Discuss the inclusion of break-even analysis in a business plan.
Unit 5.5 - Evaluate the use of break-even in a business plan.
Unit 5.7 (HL only) - Distinguish between a business plan and a contingency plan.
Unit 5.9 (HL only) - Evaluate the role of big data and data mining in developing an effective business plan.
Key concept - Discuss how change can be incorporated in a business plan.
Key concept - Discuss the links between creativity in a business context and business plans.
BMT (STEEPLE analysis) - Examine the usefulness of STEEPLE analysis for the creation of business plans.
Return to the Business Management Toolkit (BMT) homepage

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team