Benefits, risks, & ethical implications of MIS
- /
- Unit 5 - Operations Mgt/
- 5.9 Management Information Systems (HL)/
- Benefits, risks, & ethical implications of MIS
This final section of the syllabus requires HL students to understand the benefits, risks, and ethical implications of advanced computer technologies (collectively referred to here as “management information systems”) and technological innovation on business decision-making and stakeholders. (AO3)
The term management information systems (MIS) is a collective term used to describe the advanced computer technologies and technological innovations that influence business decision-making and stakeholders of a business.
Technological innovation refers to the partial or full replacement of an existing technology by one that improves a firm's productivity, its product quality, and competitiveness in the market. For example, machine Learning (which is a discipline within the field of artificial intelligence) allows computers to learn for themselves, such as learning from data analysis, and carry out tasks autonomously.
Management information systems (MIS) and technological innovations have benefits, risks, and ethical implications on business decision-making and stakeholders. The points are outlined in the sections below.
The benefits of management information systems (MIS) and technological innovations on business decision-making and stakeholders include, but are not limited to, the following:
Improved decision making - Using advanced computer technologies such as artificial intelligence enables a business to automate and improve decision-making. For example, data analytics can provide managers and employees with an in-depth understanding of an organization’s performance, allowing them to make more informed decisions. Furthermore, predictive data analytics can help to provide insights into potential future outcomes, thereby allowing for more confident decision-making.
Better operational efficiency - MIS and technological innovations can be used to streamline processes and reduce costs due to the improved operational efficiency. This has the potential to improve the profits of the business as well as provide better services to its various stakeholders groups.
Improved customer services - MIS and technological innovations can be used to track customer data, such as purchasing habits and preferences, thereby providing vast amounts of data. This provides this business with valuable insights into customer behaviours and their changing needs and wants. Furthermore, MIS and innovative technologies can provide a business with real-time customer feedback, such as through the use of chatbots (or virtual assistants). In turn, this can be used to improve customer services and product offerings, as well as enhancing customer loyalty programmes.
Enhanced competitive advantages - By using the latest MIS and technologies, businesses can gain more insights into their competitors and the markets in which they operate, thereby identify potential threats as well as opportunities for innovation. For example, a business can use predictive data analytics to gain a better understanding of consumer behaviours and trends, which can then be used to develop new products that better meet the changing needs and preferences of customers.

Chatbots can be used to improve customer services
The risks associated with advanced computer technologies (collectively referred to in the syllabus as “management information systems") and and technological innovations evolve around the issues of data security and privacy rights. The risks of MIS on business decision-making and stakeholders include the following points:
Cybercrime - This refers to any form of illegal activity carried out using electronic methods to deliberately and maliciously attack computer hardware or software, including databases, computer devices, and critical infrastructures. With large volumes of big data and sensitive information about customer and employees, there is always the potential risk of unauthorized access, malicious attacks, or data theft.
Set-up and maintenance costs - It can be extremely costly to instal and upgrade management information systems, such as artificial intelligence, customer loyalty programmes, cycbersecurity, and virtual reality (VR). Additionally, training must be provided to staff to ensure that they are able to use the MIS and technologies correctly and efficiently, although the costs of training can be high.
Regulatory compliance - There are legal and regulatory risks associated with the use of MIS and technological innovations. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires all businesses operating in the European Union (EU) to protect the data of their customers. Failure to comply with the regulations can lead to significant financial penalties.
Hence, these risks mean that businesses need to consider the potential for cyberattacks when designing and using their management information systems. This could involve the following measures:
Using firewalls (computer security systems that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic), intrusion detection systems, anti-virus software, and multi-layered data encryption.
Providing ongoing cybersecurity training for managers and employees on the use of the data security systems and cybersecurity measures.
Creating and maintaining detailed and updated contingency plans (backup plans) in the event of a system failure or data breach. These plans can businesses to recover any lost information as quickly as possible, minimize the risks to their stakeholders, and ensure business continuity.

Cybersecurity measures are vital to minimize the risks of MIS
It is important for a business to think about how it will gain the trust of its customers when the time comes to ask them for their personal data, such as their names, contact telephone numbers, emails, and home addresses, for example. MIS and technological innovations can have both positive and negative ethical implications for businesses and their stakeholders.
The UK's Information Commission's Office (ICO) suggests the following tips regarding data protection:
The ideal time for a business to think about data protection is during the first few months of trading.
A business should make sure it only collects and holds what it needs.
Hence, a business should know what personal data it has about customers, suppliers, and employees (such as the name, date of birth, and home address of its employees). The business also needs to tell these stakeholders what it plans to do with the data.
The data must be securely stored (such as a secured database or cloud computing platform. The data must also be disposed of safely and and when appropriate.
The business must respect people's data privacy rights.
Other ethical considerations of MIS and technological innovations on business decision-making and stakeholders, such as employees, include the following points:
Improved decision making - MIS and technological innovations can help businesses make more informed decisions and better serve their stakeholders in an ethical way. For example, MIS allow businesses to collect customer data to better understand their needs and preferences, leading to improved customer services. Such decisions are made more objectively, without the potential of human bias in the decision making process.
Data manipulation - This refers to the deliberate misuse of data in order to influence a particular decision or outcome. Hence, data manipulation is unethical, especially if is intended to mislead or deceive. Examples of data manipulation include deliberately and intentionally adding or removing data, changing data values, or misrepresenting the data.
Lack of human touch - MIS and innovative technologies rely on automated processes and make decisions based on algorithms and computer programmes, which can eliminate human input in the process. This means there is an absence of emotions and empathy in decision-making, which can be unethical even if it follows the protocol and policies of the organization.
In order to protect the interests of all stakeholders, businesses need to consider cybersecurity measures and contingency plans to minimize the potential risks of using advanced computer technologies. This is a priority that businesses must give to safeguard their customers and employees, not just on ethical grounds but also on a legal basis.
Data manipulation refers to the deliberate misuse of data in order to influence a particular decision or outcome.
Management information systems (MIS) refers to the advanced computer technologies and technological innovations that influence business decision-making and stakeholders of a business.
Technological innovation refers to the partial or full replacement of an existing technology by one that improves a firm's productivity, its product quality, and competitiveness in the market.

There are a lot of key terms in this unit of the syllabus. Have a go at the following quiz to see how many of the key terms you can get correct.
| No. | Definition | Key term |
| 1. | The combination of algorithms that are programmed so that computers carry out actions that until now were carried out by humans, allowing computers to learn for themselves and carry out tasks autonomously. | Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
| 2. | MIS that allow files to be saved and retrieved online without needing external storage equipment, thereby allowing users to enjoy access from any place in the world by connecting their device to the Internet. | Cloud computing |
| 3. | MIS that collects and manages large volumes of data that are then analyzed and used for a specific purpose such as to support decision making or to improve the quality of output of the final product. | Big Data |
| 4. | The set of management processes and tools that are implemented to safeguard the private, confidential, or sensitive data and information that any organization generates. | Cybersecurity |
| 5. | The crucial computer systems, structures, networks, and facilities required for the effective functioning of an organization in the modern and digital corporate world. | |
| 6. | The physical facilities or the locations of computer systems with networks and infrastructures that support organizations in accommodating their telecommunications and data storage systems. | Data centres |
| 7. | These are a feature of critical infrastructure and refer to the use of learning algorithms that can learn things, solve problems, and make decisions independently by processing new data as these are received. | Artificial neural networks (ANN) |
| 8. | Illegal activity carried out using electronic methods to deliberately and maliciously attack computer hardware or software, including computer networks and critical infrastructures. | Cybercrime |
| 9. | These are marketing strategies designed to retain customers by using a rewards programme that give loyal customers direct benefits, such as reward points that can be redeemed for purchases at discounted prices. | Customer loyalty programmes |
| 10. | This is the management process in which large sets of raw data are extracted to gather useful and valuable information. The data can then be used for analysis and predictive purposes. | Data mining |
To test your understanding of this topic (Benefits, risks, and ethical implications of management information systems), have a go at the following true or false quiz.
| No. | Statement | True of False? |
| 1. | Management information systems (MIS) and technological innovations can improve a business's profitability. | True |
| 2. | MIS and technological innovations can be used to automate and improve decision-making. | True |
| 3. | MIS and technological innovations are only beneficial for business decision-making. | False - There are other benefits too |
| 4. | Cybercrime is a form of illegal activity carried out using electronic methods. | True |
| 5. | MIS and technological innovations can provide businesses with real-time customer feedback. | True |
| 6. | MIS and technological innovations can have both positive and negative ethical implications for businesses and their stakeholders. | True |
| 7. | Automation means that cybersecurity training is not necessary for managers and employees. | False |
| 8. | MIS and technological innovations can be used to track customer data, such as purchasing habits and preferences. | True |
| 9. | Contingency plans are not important for businesses that use the most up to date management information systems in an efficient way. | False |
| 10. | Predictive data analytics can help to provide insights into potential future outcomes and decisions. | True |
| 11. | Businesses do not need to consider ethical matters if they protect the interests of their stakeholders by using cybersecurity measures. | False |
| 12. | Data manipulation is ethical if it follows the protocol and policies of the organization. | False |
| 13. | Data analytics can provide managers and employees with an in-depth understanding of an organization’s performance. | True |
| 14. | Businesses should know what personal data they have about customers, suppliers, and employees. | True |
| 15. | Ethical implications of using MIS and innovative technologies mean that data must be securely stored and disposed of safely in an appropriate and secure way. | True |
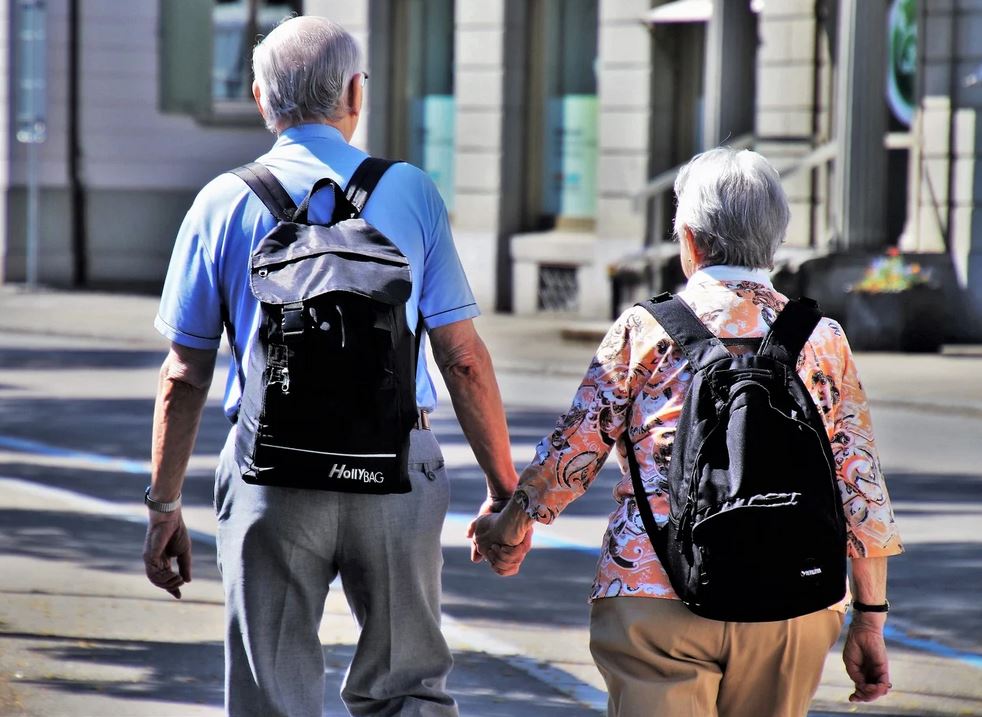

Asia's elderly population is growing, and technology companies are providing solutions to watch over them - from wearable GPS tags and CCTV to robots and AI-based speakers. Human Rights experts have raised concerns over privacy, data risks, and the need to let senior citizens make informed decisions about the tech implemented in their lives.
By 2050, one in four people in the Asia Pacific region will be over 60. Smart home technologies are being rolled out to help care for them, but critics say it can violate their human rights. Emergency services have been used to help senior citizens who use the SOS feature on AI-based smart speakers. Motion sensors and CCTV (closed-circuit television) are being used to monitor vulnerable people. Companies also provide a service to check on senior citizens if they do not answer an automated call.
Source: Adapted from Context News
(a) | State two examples of the technologies that are being used to help care for Asia's elderly population. | [2 marks] |
(b) | Explain two ethical impacts of management information systems on the elderly in Asia. | [4 marks] |
(c) | Explain two implications of the increasing elderly population in the Asia Pacific region on the use of MIS technologies used to help care for them. | [4 marks] |
Answers
(a) State two examples of the technologies that are being used to help care for Asia's elderly population. [2 marks]
Possible examples include:
Wearable GPS tags
Motion sensors and CCTV
AI-based smart speakers
Smart home technologies
Automated call
Award [1 mark] for each valid example.
(b) Explain two ethical impacts of management information systems on the elderly in Asia. [4 marks]
Possible ethical impacts could include an explanation include:
Human rights – MIS technologies could potentially be used to violate the privacy rights of elderly people, especially as the technology can track the movements and activities of elderly people without their consent.
Safety – MIS technologies can monitor elderly people and protect them from harm, but can also create a false sense of security.
Wellbeing – MIS technologies can provide a service to check on elderly people, but can also be intrusive and create feelings of isolation.
Accept any other valid explanation, written in the context of the case study.
Mark as a 2 + 2.
For each ethical impact, award [1 mark] for a valid point, and a further [1 mark] for an appropriate explanation.
(c) Explain two implications of the increasing elderly population in the Asia Pacific region on the use of MIS technologies used to help care for them. [4 marks]
Possible implications could include an explanation of:
Increase in demand for MIS technologies – as the elderly population grows, the demand for MIS technologies used to help care for them will also increase.
Access to MIS technologies – elderly people need to have direct and ease of access to the MIS technologies in order to benefit from it.
Regulation – governments may need to regulate the use of MIS technologies in order to protect the rights of the elderly and to safeguard their wellbeing.
Cost – MIS technologies can be expensive and may not be affordable for all elderly people.
Accept any other valid explanation, written in the context of the case study.
Mark as a 2 + 2.
For each valid implication, award [1 mark], and a further [1 mark] for an appropriate explanation.
Return to the Unit 5.9 - Management information systems (HL only) homepage
Return to the Unit 5 - Operations management homepage
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team
