BMT 2 - Ansoff matrix
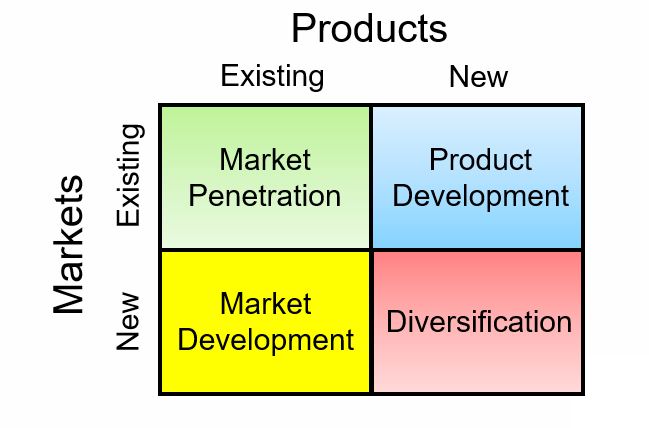
The Ansoff growth matrix
Source: adapted from Ansoff, I.: Strategies for Diversification, Harvard Business Review, Vol. 35 Issue 5, Sep-Oct 1957, pp. 113-124
The Ansoff matrix is a strategic decision-making tool, used to devise product and market growth strategies for an organization. It was developed by Russian American Igor Ansoff in his article ‘Strategies for Diversification’, published in the Harvard Business Review (1957). Essentially, the Ansoff matrix (or Ansoff growth matrix) shows four generic growth strategies that can apply to any business or any industry.
Market penetration
This growth strategy focuses on developing existing markets with existing products in order to increase sales revenue and market share.
If focuses on using strategies to increase the usage rate of existing customers.
It is a relatively low-risk strategy as it focuses on what the organization does and knows well.
There is little, if any, need for investment expenditure or further market research as the strategy focuses on marketing its existing products to its existing customers.
It is used to gain market dominance in growing markets and to reduce competition in mature markets.
Examples include: charging more competitive prices, using customer loyalty schemes, broadening channels of distribution (e.g., delivery services) and improved advertising campaigns.
Market development
This growth strategy involves selling existing products in new or unexplored markets.
It focuses on using customer loyalty to persuade them (and prospective customers) to buy a new product.
It also relies on a greater distribution network, such as retailers, to get the product to customers spread around the world.
This strategy carries an element of risk as the organization might not succeed in unexplored markets. After all, consumer habits and tastes vary in different part of the world.
It can also be expensive for a business to invest and establish itself in new markets, especially if these are in overseas locations.
Case Study 1 - Why Target failed in Canada
In 2015, Target closed all of its 133 stores in Canada. Watch this video from World Today to determine at least four major issues that the American retail giant faced which ultimately led to unhappy customers.
Possible reasons why this market development strategy failed include:
Lack of stock (inventory) - empty shelves and poorly stocked stores simply put off customers.
Target tried to grow too quickly by doing too much, too fast.
Prices fluctuated from what consumers had seen in US Target stores.
Canadians do not necessarily shop in the same way as their American counterparts, e.g., Canadian shoppers go to multiple stores to get the best bargains.
Local competition, with strong customer loyalty to these Canadian brands.
Supply chain issues meant that prices were close to 23% higher in Canada than in the US (which encouraged cross-boarder shoppers from Canada).
Case Study 2 - Nestlé expands into Indian pet food market
Multinational food giant Nestlé expanded into the Indian pet food industry back in 2018 as part of a market development growth strategy. The video above explains how Nestlé , one of the largest food companies in the world, aimed to expand into the potentially lucrative Indian pet food sector.
Along with Mars (which had a first-mover advantage selling pet food in India), Nestlé dominates the global pet food industry. However, whilst the pet food market in the US is worth $27.7bn (the world's largest by a distance) and the UK is worth $4.4bn (the world's second largest market), the situation in India is very different as 95% of Indian pet dogs are fed from home-cooked food rather than purchased dog food.
However, times are changing. A combination of economic growth and prosperity (rising average household incomes) and social change (couples waiting longer to get married and to have children) has increasing the demand for pets in India. The rise in pet owners means a rise in the demand for commercial pet food. Nestlé estimates that the value of the Indian pet food market will double within the next 5 years, albeit from a low base (of around $280 million).
The expected sales growth means that Nestlé has launched its Purina brand in India, to directly compete with market leaders in the pet foods market in India such as Mars and Royal Canin. Mars and Royal Canin operate mostly through specialised stores in India as well as increasingly through e-commerce.
Product development
This growth strategy involves introducing new products to existing customers.
If focuses on product differentiation in order to remain competitive or to improve its competitiveness.
Typically, products are developed to replace their existing ones (e.g., the latest iPhone) or to extend the product range (e.g., iTunes, iPads, and Apple Watch) and marketed at current customers.
It is a medium-risk growth strategy because product development can incur substantial investment costs, such as the expenditure on market research (to find out what customers want), prototyping, and test marketing.
Top tip!
It is not always easy to know whether a growth strategy is product development or market development. For example, marketing a new Lynx (deodorant) or LEGO product to females are examples of targeting new customers (i.e., market development) and new products (i.e., product development). The same applies to cosmetics companies, such as Maybelline, that have more recently targeted male customers with their makeup products. What is important is that students explain their answers and provide reasons for their arguments.
LEGO advert promoting Lego Friends, designed primarily for girls (first launched in 2012):
Diversification
- Diversification involves organizations moving into new markets with new products, e.g., Honda lawnmowers, Lenovo smartwatches, IKEA's infamous meatballs, or the Golden Arch Hotel of McDonald’s in Switzerland. Lego also has several Legoland Hotels around the world, with its different themed hotel rooms.
Case Study 3 - McDonald's Sneakers
Did you know that this product actually exists? Click the link here for McDonald's in Spain to find out more about the McDonald's Sneaker range.
Diversification is a high risk growth strategy as the organization enters a market that it has no experience or expertise in. Existing rivals may already have established themselves with brand recognition and customer loyalty.
There are two types of diversification:
Related diversification – the organizations operate within the same industry, e.g., Coca-Cola entering the energy drinks market.
Unrelated diversification – involves the organization entering new industries, e.g., McDonald’s entering the hotel industry or offering wedding reception services.
Case Study 4 - McWeddings
 Since 2011, McDonald’s has offered McWeddings as a service at some of its restaurants. The service includes hosting weddings, engagements, anniversaries, and bridal showers at designated McDonald’s restaurants. The wedding party packages including meals from McDonald’s menu, unique venue decorations, customized wedding party games, and special gifts for the newly-weds as well as guests.
Since 2011, McDonald’s has offered McWeddings as a service at some of its restaurants. The service includes hosting weddings, engagements, anniversaries, and bridal showers at designated McDonald’s restaurants. The wedding party packages including meals from McDonald’s menu, unique venue decorations, customized wedding party games, and special gifts for the newly-weds as well as guests.
You can read more about McDonald’s McWeddings here.
Find out more about the McWedding package from the McDonald's website here.
Case Study 5 - IKEA's meatballs

IKEA is best known for its inexpensive flat-packed furniture. Founded in Sweden in 1943 by Ingvar Kamprad, who was just 17-year-old at the time, IKEA became the world’s largest furniture retailer in 2008 due to its innovative ideas and cost leadership growth strategy.
However, in 2006, IKEA also launched its own brand food label, IKEA Foods, with a portfolio of more than 150 products, including its best-selling trademark Swedish meatballs. In fact, IKEA sells more meatballs (over 1 billion per year) than any other product, including its furniture. The Swedish company's food division brings in billions of dollars in additional annual sales revenue.
Further examples of diversification
"Only diversity makes change and progress."
- John Dewey, Democracy and Education (1916)
These companies have all diversified from their original line of business. Do you know what they originally produced or supplied? Click on the icon to reveal the answers.
| Company | Original line of business |
| American Express | Postal services |
| Colgate | Candles and soap |
| Hasbro | Textiles |
| Lamborghini | Tractors |
| Marriott | Food and drinks kiosk |
| Nintendo | Playing cards |
| Nokia | Rubber and paper |
| Peugeot | Tools |
| Samsung | Noodles, fish, fruits and vegetables |
| Shell | Collectable shells! |
| Tiffany & Co. | Stationery |
| Wrigley’s | Soap and baking powder |
Samsung is well-known for making smartphones, consumer electronics (such as tablet computers, and home appliances). But did you know that Samsung also makes helicopter engines, ultrasound machines, ships, toilet seats, and even cars? Watch this short video clip for the details:
Samsung is South Korea's largest company. For a more comprehensive account of Samsung’s hugely diversified product portfolio, including its involvement with the military, watch this 11-minute YouTube video:
Case Study 6 - The Sony Vision S electric car
In late 2020, Sony announced plans to enter the race to introduce an electric vehicle aimed at directly competing with Elon Musk's Tesla. Sony has already invested $5.3 billion into self driving sensor technology and developed the Vision S to compete with the Tesla Model 3. The main features of the Vision S include:
Touch screen infotainment system, which enables users to watch Sony movies
All passengers get their own set of screens and infotainment system, including their own set of speakers to listen to their own music/sound tracks
10 cameras around the car to provide driver assistance
Acceleration of 0 - 60 mph in 4.5 seconds (although the Tesla Model S does this in just 2.4 seconds)
A top speed of 149 mph.
In early 2023, Sony announced the launch of its Afeela branded electric cars from 2025. Sony is combining its expertise in the games console market with the driving forces for change in the auto industry, in partnership with Honda.
Summary and evaluation of the Ansoff matrix
.png)
In summary, the Ansoff Matrix is a simple visual Business Management decision making tool that enables managers and decision makers to consider four generic growth strategies. However, there are numerous limitations of this Business Management tool:
It only considers two dimensions of growth (products and markets), whereas strategic analysis of an organization’s growth options is far less limited in the real world.
It does not quantify the risks or rewards associated with the respective strategies. Indeed, the risks involved in the four growth strategies differ substantially. Hence, managers will still need to assess the degree of risks, the likely costs, as well as the potential rewards, associated with each growth option.
Selection of any of these growth strategies still requires further research and analysis, such as the research and development (R&D) costs of product development or the cost of overseas expansion for a market development strategy.
Recap your knowledge and understanding of this important section of the Business Management Toolkit (BMT) by reviewing this short video:
Essentially, the Ansoff matrix provides business with four generic product/market growth strategies that any business can use to attempt to grow depend, based on whether it markets new and/or existing products in new and/or existing markets.
Market penetration is the growth strategy that involves a business focuses on selling existing products in existing markets, such as using special promotional offers.
Market development is the growth strategy that involves a business focusing on selling its existing products in new markets, such as opening a new retail store/outlet in new geographical locations.
Product development is the growth strategy that involves a business focusing on introducing new products in existing markets, such as launching new and innovative products to the existing customer base.
Diversification is the growth strategy that involves a business focusing on marketing new products in new markets. There are two types of diversification - related and unrelated diversification.
ATL Activity (Research skills) - The Ansoff matrix in practice
Recommended time: 45 minutes
For an organization of your choice, research and construct a fully labelled Ansoff matrix identifying at least one example of a strategy the business has adopted in each of the quadrants. Your findings must be original rather than from a pre-prepared analysis.
Be prepared to present your findings to the rest of the class, explaining why you have placed the strategies in the particular quadrants of the matrix.
Possible examples that can help students get started include:
Market penetration – In 2020, Pret a Manger, the multinational coffee and sandwich retail chain, launched a subscription service in the UK. The service, as part of Pret a Manger’s attempt to gain further market share in a saturated market, offers subscribers up to five coffees (or other drinks) each day for a monthly subscription fee of £20 ($28). Customers who sign up get the first month free, as an introductory offer. This strategy involves Pret A Manger offering existing products to existing customers.
Market development – Nike Inc.’s growth strategy in different regions across the world has included the use of new distribution channels, namely moving from selling via retail outlets to selling using e-commerce and mail order following the global COVD-19 pandemic.
Product development – McDonald’s is continually offering new products to existing customers across the world, such as festive additions for Valentine's Day, Halloween, and Christmas. The customer base is the same - loyal McDonald’s customers or fans of McDonald’s.
Diversification – In 2021, PayPal announced it would acquire Pinterest for $45 billion. PayPal is a financial technology company based in San Francisco, USA. Pinterest, also based in San Francisco, has over 480 million active users on its social media platform, primarily offering users a way to store and share their favourite images. PayPal's takeover of Pinterest would enable it to compete directly with Instagram (owned by Facebook), which is also used as a platform for promoting online retail.
Top tip!
As with all tools in the BMT, be a critical thinker and consider both the purpose and limitations of the specific tool. For example, it is not always straightforward to categorise a growth strategy using the Ansoff matrix. In September 2021, Lady Gaga released a full jazz album with American singer Tony Bennett. Is this an example of a market penetration strategy as it is another music album - the seventh for Lady Gaga and the final, but 61st, for Tony Bennett(!), appealing to current fans of both artists? Or is it a market development strategy as Lady Gaga tries to appeal to a broader market of music fans? Or does this represent a product development strategy for Lady Gaga?
There can be justifications for any of these growth strategies in Ansoff's matrix. For example, jazz fans would be a new market segment for for Lady Gaga's pop music fans (customers in an existing market). As long as students can fully justify their answer, then it doesn't really matter. In this example, you could even go as far to suggest this is a diversification strategy for Lady Gaga as a full jazz album is a new product (for her) being targeted at new customers (for her) because jazz music is a new market for her.
Return to the Business Management Toolkit (BMT) homepage
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team


