Cybersecurity and cybercrime

Cybersecurity is a key aspects of management information systems (MIS) and is specifically used to tackle the problems faced by businesses and their customers that are associated with cybercrime.
Cybercrime refers to any form of illegal activity carried out using electronic methods to deliberately and maliciously attack computer hardware or software, including computer networks, devices, and critical infrastructures. Most cybercrime is committed by hackers (or cybercriminals). Cybercrime typically disrupts the activities of a business and can temporarily halt its operations. This results in the business suffering from a loss of sales revenue, and potential damage to its corporate image, while the issue is fixed or repaired.
Examples of cybercrimes include:
Computer malware - A computer malware or virus is a malicious code or programme that once activated infects a computer system and changes how it works, or stops the device from functioning.
Cyberextortion - This means the cybercriminal demands money so as to prevent a threatened cyber attack.
Data breaches - A data breach (also known as data leak) is a security violation that involves sensitive, protected, and/or confidential data being viewed, copied, transmitted, or stolen by an unauthorized person.
Identity theft - This occurs when personal data and information are stolen and used illegals, such as banking and credit card fraud.
Online scams - This refers to fraudulent behaviour using Internet technologies, such as email fraud.
Phishing - This is the unethical and illegal act of using reputable business names, telephone numbers, emails, and websites to deceive people so that they reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers.
The cost of cybercrime to organizations is growing, as illustrated in the infographic below, signifying the importance of this matter for businesses.
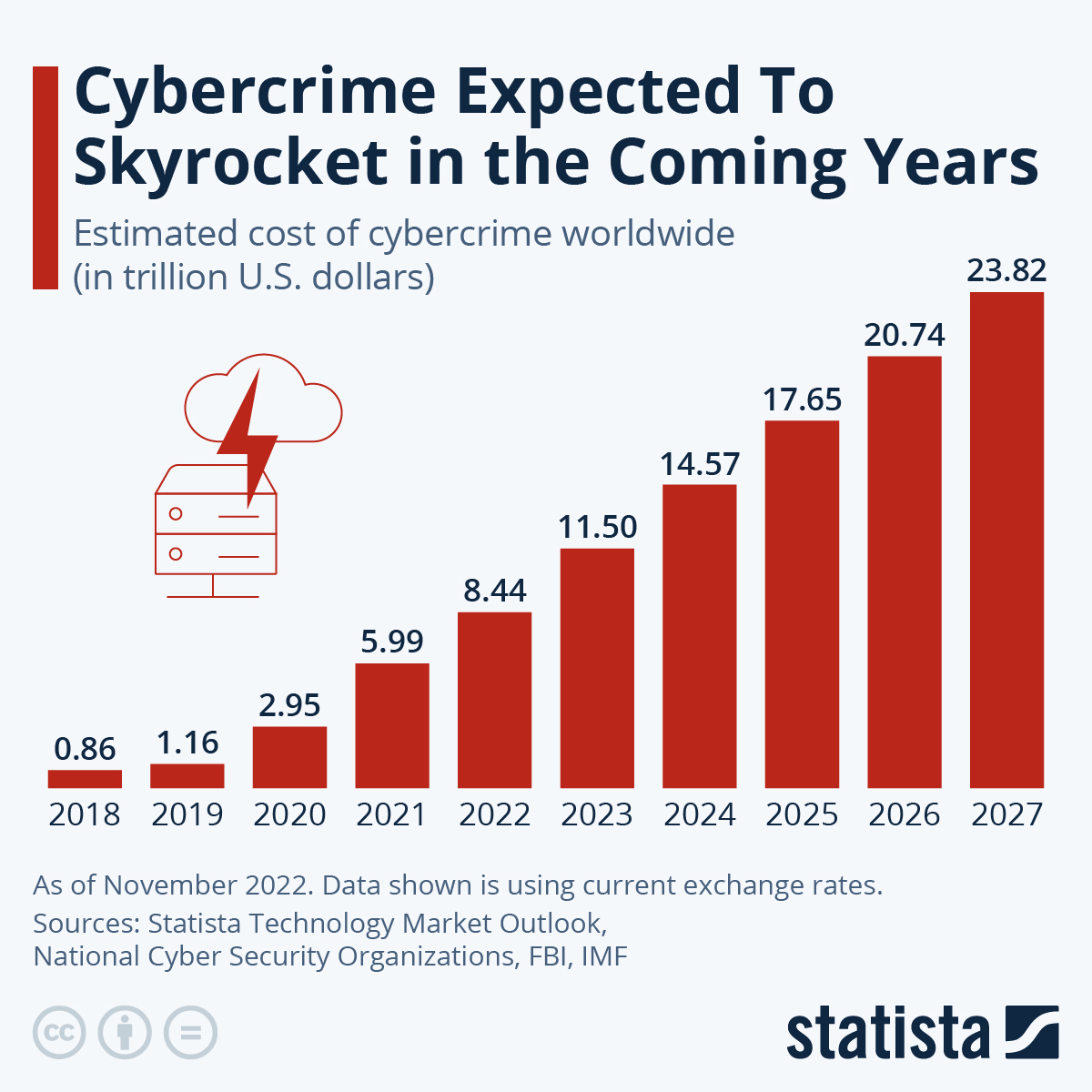 Source: Statista
Source: StatistaWatch this video to discover some of the most common types of cybercrime including viruses, malware, and phishing scams.
Cybersecurity is used to deal with cybercrime. Cybersecurity refers to the policies, processes, and procedures used to safeguard an organization's computer systems and networks from unwarranted attacks, such as information disclosure, data theft, or physical damage. Firms that do not take cybersecurity seriously can get into trouble with the authorities (see Case Study below).
Case Study 1 - Didi

Didi is China's largest taxi hire ride-hailing company, with over 550 million registered users. It is often referred to as China's Uber. In July 2022, the Chinese government fined Didi 8.026 billion yuan ($1.2 bn) for breaking its national cyber security laws.
The government cites data collection concerns, including illegally storing the personal data of more than 57 million drivers in an unsecure format as well as passenger details without their knowledge or consent. The authorities also fined Didi’s founder and Chief Executive Officer, Cheng Wei, and the company's President, Jean Liu, a sum of 1 million yuan ($148,000) each.
Case Study 2 - Optus
Businesses that do not take cybersecurity serious enough risk huge financial penalties. For example, Optus, an Australian telecommunications business headquartered in New South Wales, failed to prevent serious and repeated privacy breaches and was fined $50 million under new cybersecurity laws.
Watch this news video which features the Australian prime minister who warned Optus to pay its customers for the data breach. The data leak caused huge inconveniences for Optus's customers across the country who had to make arrangements for replacement driver licences, passports and healthcare accounts. Such cybercrime is both frustrating to customers and costly to businesses.
Discuss how significant the damage is for Optus, from this data breach, both in terms of the financial costs and potential impact on its business.
How easy is it to get someone's password?
This short video clip is from the Jimmy Kimmel Show, in which he reveals that the most common password in the US is "password123". He suggests that we need to do a better job of protecting ourselves from hackers. The interviewer in the video asks people on Hollywood Boulevard for their passwords - see what happens...
Watch this short video from Zurich about how employees and businesses can use cybersecurity to combat the issues of cybercrime. This matter had become increasingly important for businesses during the COVID-19 era when many employees started working from home (WFH).
Did you know...?
Did you know that since 2004, October is Cybersecurity Awareness Month?
Cybersecurity Awareness Month was first introduced in the USA to educate and remind individuals and businesses to protect themselves online, especially as cybercrimes become more commonplace. Raising awareness helps to change our behaviour online and improves the ways in which we can tackle or prevent cybersecurity threats. The ultimate goal is to reduce cybercrime, thereby protecting confidential data and private information.
ATL Activity (Thinking and Research skills)
Research the cybercrime issue experienced by a business of your choice. Examine the cybersecurity measures taken by the business (such as security awareness training) in order to maintain and protect their data and management information systems.
Be prepared to share your findings with the rest of the class.
Theory of Knowledge (TOK)
What is truth? How can we determine truth in Business Management?
Cybercrime is any form of illegal activity carried out using electronic methods to deliberately and maliciously attack computer hardware or software, including computer networks, devices, and critical infrastructures.
Cybersecurity refers to a firm’s policies, processes, and procedures used to safeguard its computer systems and networks from unwarranted attacks, such as information disclosure, data theft, or physical damage.
A data breach (or data leak) is a security violation of private and confidential data, with the data being viewed, copied, transmitted, or stolen by an unauthorized person.
Return to the Unit 5.9 - Management information systems (HL only) homepage
Return to the Unit 5 - Operations management homepage
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team
