The impact of MNCs on host countries (AO3)

The growing importance of international trade has intensified the role and importance of multinational companies across the world. A multinational company (MNC) is any business organization that has operations overseas, irrespective of whether it produces/sells goods and/or provides services, i.e., MNCs operate in two or more countries.
Although the MNC has its headquarters (or central administrative office) in one country, it has operations and premises (such as offices, factories, assembly plants, and retail outlets) in other countries. This means MNCs spend on foreign direct investment (FDI) in overseas markets. FDI refers to cross-border investment in which a foreign company establishes an ongoing and significant stake (financial interest and degree of influence) in its operations in another economy.
Examples of large multinational companies with operations in many parts of the world include Adidas, Amazon, Apple, BMW, Coca-Cola, HSBC, McDonald's, Royal Dutch Shell, Samsung, Saudi Aramco, Tesla, Toyota, and Walmart. In some cases, The biggest multinationals generate annual sales revenues in excess of the gross domestic product (GDP) of entire economies. For example, Saudi Aramco, the world's largest oil company, earns annual sales revenues that exceed the GDP Italy, Brazil, Canada, and Russia.
Note: a business that only exports products to overseas markets does not qualify it to be a MNC as it operates from the domestic (home) country.
The business operations of multinational corporations (MNCs) can have both positive and negative impacts on their host countries.
Positive impacts
The positive impacts of MNCs include the following points:
Employment opportunities – MNCs can account for a significant number of jobs in the host country. This has huge economic benefits, such as higher incomes, consumption, savings and tax revenues. Overall, this can raise the quality life for citizens in the host country.
Support for the workforce – In addition to job creation, MNCs create other opportunities for domestic workers. For example, the wages offered by MNCs are often better than those offered by local firms (even if the wages paid by MNCs are low by international standards). Local workers may also benefit from training and development opportunities.
Support for local businesses – MNCs can provide a range of benefits to local businesses, directly or indirectly. For example, they are likely to purchase stocks from domestic suppliers of raw materials, semi-finished goods and finished goods. This provides revenue for local firms and supports domestic industries. In addition, MNCs are also likely to use the services of local firms, such as insurance and distribution.
Choice and quality – MNCs offer consumers in host countries more choice and often better quality products. Domestic customers no longer have to rely only on local suppliers and must compete with the prices and quality of the products offered by MNCs.
Efficiency gains – Similarly, MNCs create increased competition for local suppliers, forcing the domestic businesses to improve their operational efficiency. This covers aspects of the prices, quality and customer care of local firms.
Tax revenues – The host country’s government benefit from profitable multinational companies as they pay corporate taxes. The additional finance can be spent to further improve the economy, such as better infrastructure to further entice foreign direct investment.

Multinational supermarkets use produce from local farms
Case study 1 - McDonald’s: the world’s largest fast food chain

McDonald’s is the world’s largest restaurant chain as measured by sales revenue. According to its website, the American fast food giant serves over 69 million customers every day in over 100 countries - that's the equivalent of almost 48,000 customers served each minute of each day!
The company employs over 210,000 workers, making it one of the world's largest private sector employers. The monetary value of the output from McDonald’s therefore contributes to the gross domestic product (GDP) and employment in the 100+ countries that the company operates in.
Negative impacts
The negative impacts of MNCs on their host countries include the following:
Negative impacts on local businesses – Many local firms, especially smaller ones, may lose customers to the larger foreign multinational companies. A fall in their market share and profit can eventually lead to bankruptcies and some job losses in the economy.
The repatriation of profits – Any profits declared at interest and tax payments are accounted for may be repatriated (sent back) to the home country, rather than the funds being used to invest further in the host country.
Exploitative business practices – MNCs have been known to be socially irresponsible, especially when operating in less economically developed countries where rules and regulations are less stringent. This has often resulted in workers being exploited (poor pay and working conditions) and business operations that cause damage to the environment (such as air pollution and destruction of natural habitats). For example, Coca-Cola’s bottlers have been accused of causing water shortages in certain parts of India and South America.
Loss of cultural identity – The growing presence of multinational companies, and the convergence of habits and tastes brought about by globalization, can cause a depletion of local cultures. MNCs and globalization have been blamed for causing a cultural shift in how people live, especially for the younger generation.

Multinational companies have positive and negative impacts on host countries
Did you know?
Did you know the following brands/companies are now owned by Chinese or Indian firms?
Chinese owned | Indian owned |
AMC Theatres | American Swan |
Club Med | Blackburn Rovers Football Club |
General Electric (GE) Appliances | Daewoo |
Hoover | Jaguar |
House of Frazer | Land Rover |
Motorola | Louis Philippe |
The London Taxi Company | Peter England |
Volvo | Tetley |
Time pending, investigate which countries these companies were established in. For example, Volvo was founded in Gothenburg, Sweden in 1927. Volvo Cars has been majority-owned by Geely Holding Group since 2010. The Chinese company paid a reported US$1.5 billion for the takeover of the former Swedish car manufacturer.
Did you know?

The Drive-Thru concept
Many people know that the Drive-Thru is an American cultural export. But, did you know that the first McDonald’s Drive-Thru was opened near a military base in Arizona, USA in order to serve soldiers as they were not allowed to get out of their vehicles while wearing military fatigues (combat uniform or army uniform)? The first commercial Drive-Thru was established in 1975, and the multinational company now has operations in over 100 countries, with Drive-Thru restaurants across the globe.
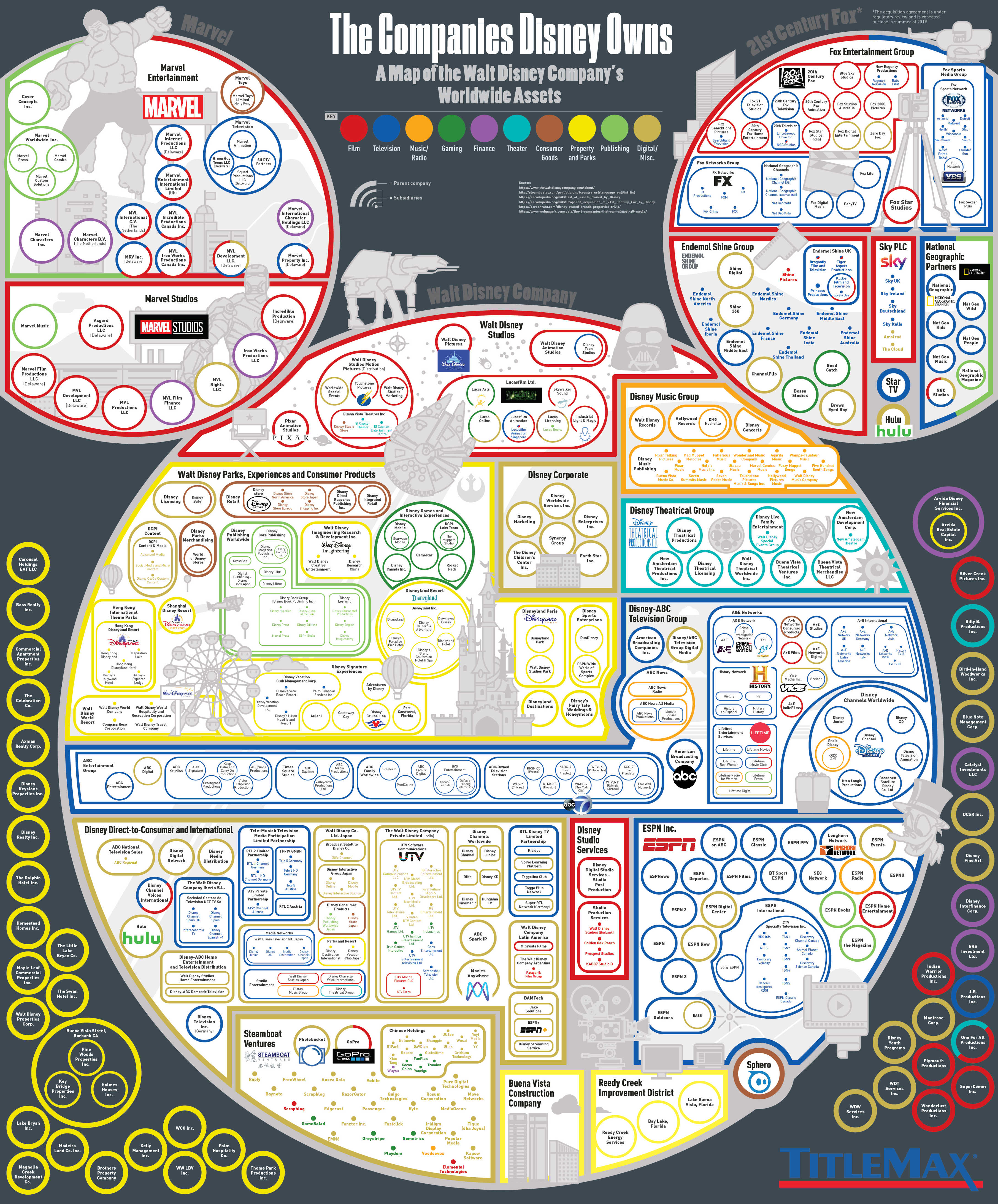
Case Study 2 - The Walt Disney Company
The Walt Disney Company is the world's largest entertainment company. The infographic below lists all the companies and subsidiaries owned by The Walt Disney Company at the time of writing. These companies include well-known companies and brands, such as ESPN, ABC, Marvel, Lucasfilm, Touchstone Pictures, The History Channel, Pixar, plus many more.
Besides these companies, The Walt Disney Company also owns other global businesses under its family brand name, including Disney Channel, Disney retail stores, Disney radio stations, and Disney theme and leisure parks (including Walt Disney World Resort, Disneyland Resort, Disneyland Paris, Hong Kong Disneyland, Disney Cruise Line, and a host of other vacation-related properties). The Walt Disney Company's media networks and its theme parks and property portfolio tend to be the corporation’s biggest cash cows.
Theory of Knowledge (TOK)
To what extent is it possible to determine if one country knows what is right or best for another country to do?
ATL Activity 1 (Thinking skills)
Have a go at this A – Z MNCs Quiz to see how many of these multinational companies you recognise.
ATL Activity 2 (Research and communication skills)
.png)
In small groups of 2 or 3, investigate the main ways in which host countries can attract more multinational companies. Use real-world examples to substantiate your findings. Be prepared to share your findings with the rest of the class.
Teachers' notes
The purpose of this task is to highlight why governments might want to attract more MNCs to operate in their respective countries due to the positive impacts of MNCs on the host countries.
Whether MNCs decide to expand in a particular overseas country will depend on both the objectives of the business and how welcoming the host country is towards MNCs operating in their nation.
This task also creates an opportunity to apply STEEPLE analysis as a business management tool (as part of the BMT). For example, possible ways that host countries can make things easier and more attractive to MNCs include:
Economic factors - economic growth rates, tax incentives for MNCs, government grants and subsidies, exchange rate stability, inflation rates, wages and salaries, cost of land/premises, access to raw materials, etc.
Political factors - political stability, the level of corruption, government attitudes and incentives towards FDI, national minimum wage legislation, legal constraints on business activities and oeprations, health and safety laws, employment rights, etc.
Social factors - availability of suitable/skilled labour, labour productivity rates, attitudes towards labour unions (trade unions), number of potential customers in foreign markets, etc.
Technological factors - infrastructure (transportation and telecommunications networks), reliable and affordable energy sources, cybersecurity, etc.
Essentially, the easier and more welcoming it is to operate in an overseas country, the more likely it will be to attract multinational companies to locate their operations in that nation.
ATL Activity 3 (Research and communication skills)
Foxconn is a Taiwanese company that makes electronics products such as the iPhone, PlayStation, Kindle, and Wii. It has operations throughout the world, including in Brazil, China, India, Malaysia, and Mexico. Investigate the various reasons why MNCs such as Amazon, Apple, Nintendo, and Sony might choose to outsource production to manufacturers such as Foxconn to make goods on their behalf.
Business Management Toolkit (BMT)
Discuss how knowledge of the external environment is essential for the success of multinational companies seeking to grow and expand in overseas markets.
You may use to refer to STEEPLE analysis when answering the above question.
Business Management Toolkit (BMT)
Explain how Ansoff’s matrix can help managers to decide whether to expand into overseas markets or which overseas markets to expand into.
Business Management Toolkit (BMT)
Discuss market development as a growth strategy for a multinational company of your choice.
You may wish to refer to Ansoff's matrix before answering the above task.
Business Management Toolkit (BMT)
How might Hofstede's cultural dimensions (HL only) be of significance for multinational companies and their operations in overseas markets?
To review your understanding of this topic, watch this informative video about multinational corporations.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to cross-border investment in which an overseas company establishes an ongoing and significant stake in its operations in another economy.
A multinational company (MNC) is any business organization that has operations overseas, i.e., it operates in two or more countries.
Exam Practice Question
(a) | Define the term multinational company (MNC). | [2 marks] |
(b) | Explain two drawbacks for countries that host MNCs. | [4 marks] |
Answers
(a) Define the term multinational company (MNC). [2 marks]
A multinational company (MNC) is any business that has operations overseas, i.e., it operates in two or more countries.
Award [1 mark] for an answer that shows some understanding of the term multinational company.
Award [2 marks] for an answer that shows good understanding of the term multinational company, similar to the example above.
(b) Explain two drawbacks for countries that host MNCs. [4 marks]
Possible drawbacks could include:
Negative impacts on domestic firms - Large foreign multinational companies can force smaller domestic businesses to lose sales revenue and market share. In extreme cases, they can even cause the domestic firm to collapse as the larger foreign MNCs are more efficient and cost effective.
The pressure to attract FDI and MNCs can be overwhelming. It can be complex, challenging, and expensive for governments to attract MNCS, such as the burden on taxpayers if the government uses grants, subsidies, and other forms of financial incentives to attract foreign companies to operate in their countries.
Globalization encourages more consumption, so causes the world to use up finite resource more quickly. This can raise the costs of production for businesses in the long term.
Growing interdependence brought about by internation trade and MNC operations can make the host country over-reliant on foreign companies to provide employment in the home country, thereby making it more vulnerable. If one country or region suffers from an economic recession, the downturn is likely to cause ripple effects in the host country too.
Accept any other valid drawback that is clearly explained.
Mark as a 2 + 2
For each drawback, award [1 mark] for a valid point and [1 mark] for an accurate explanation of that drawback.
Return to the Unit 1.6 - Multinational companies homepage
Return to the Unit 1 - Introduction to Business Management homepage

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team