Role of HRM
.jpg)
Human resource management (HRM) is a broad term used to describe the overall management of an organization's workforce. This includes roles such as attracting, selecting, training, assessing, motivating, rewarding, and retaining employees. Essentially, the role of HRM is to make the most efficient use of an organization’s workers. Due to the evolving workforce planning needs of an organization, human resource management is an ongoing function of the personnel department of an organization.
Effective human resource management is vital for any organization to achieve its business objectives. The role of human resource management is therefore important as the effectiveness of the workforce has a major impact on the current and future success of the organization. HR managers play a vital role in ensuring that the right people in the right numbers are hired, at the right time, deployed in the right places, and at the right time.

HRM plays a vital role in the smooth running of any business
Human resource management involves numerous roles or functions, which include:
Recruitment - hiring the right number of appropriately qualified and suitable workers at the right times to fill job vacancies.
Induction - training for new employees to get acclimatised with the norms and operations of the organization.
Retention - retaining/keeping workers at the organization by meeting the needs of employees.
Appraisals - the formal procedure of assessing the performance and effectiveness of employees in relation to their job description.
Absenteeism - dealing with issues that arise when employees are unable to attend work (see Case Study 1).
Dismissal - letting go of workers no longer needed, often due to underperformance or misconduct in the workplace.
Redundancies - letting go of workers if/when their jobs are no longer needed, perhaps due to a prolonged economic recession.
Training and development - improving the competencies, productivity, and skills of workers.
Performance appraisals - holding workers accountable for their performance/conduct at work.
Ultimately, effective human resource planning enables an organization to develop competitive advantages, as the workforce is more effective in achieving the firm’s aims and objectives.
Case Study 1 - The absenteeism costs of the common flu in the USA
The USA spends $10.4bn per year in direct medical expenses - that's around $28,493,150 per day!
The country loses $15.3bn a year from the common flu due to loss of earnings (which is equivalent to 17 million workdays a year!)
Productivity losses amount to more than $21 billion a year (or over $57.53 million per day).
Source: adapted from www.healthline.com/health
ATL Activity 1 - To work or not to work, that is the question
On average, women have a higher life expectancy compared to men. This may be due to inherent biological factors. However, women also retire earlier in many countries as compared to men. The gap between the retirement age of men and women is smaller in high-income countries and larger in low-income and medium-income countries due to economic and social factors.
So, if men live shorter lives and are expected to work more (retire at a later stage in life), is this fair? What about equality for males? Are governments biased?
Refer to these three sources and discuss the above questions in small groups.
Key concept - Ethics
“Ethics is a code of values which guide our choices and actions, and determine the purpose and course of our lives”.
- Ayn Rand (1905 – 1982), Russian-American writer and philosopher

Ethics can be defined as the moral codes of conduct that drive business behaviour. Ethical business behaviour is what is deemed by society to be morally acceptable, i.e. what is “right”. By contrast, unethical business behaviour is what society regards as being immoral, unjust and unfair, i.e. what is “wrong”.
Ethics can affect all aspects of human resource management and decision-making. For example, unethical practices of some offshored businesses, such as the immoral exploitation of workers, have led more organizations to re-shore their operations. Other ethical considerations include:
- Should employers allow workers to have tattoos? Is it appropriate (acceptable) for teachers in international schools to have visible tattoos? Should there be a law about exposing tattoos in the workplace?
- Should employment laws be enforced across the globe to prevent discrimination against race, gender, marital status, age, religion and sexual orientation? Why/not?
- Is it ethical for senior executives to receive end-of-year bonuses that are more than double their employee’s annual salary?
- Is it morally acceptable for firms to hire more part-time and flexitime workers in order to lower their production costs?
Unethical business behaviour can have major consequences for a business, such as poorer staff morale, lower productivity, an undesirable corporate image, and possible lawsuits against the organization. For example, Walmart has been accused of mistreating its workers, especially the exploitation of female workers on part time contracts.
Case Study 2 - Accusations of employee exploitation at iPhone factory

One of the key issues of using an offshoring strategy is the potential for suppliers to exploit workers, especially in parts of the world where labour laws are not so stringent.
In December 2020, it was reported that workers at an iPhone factory in India were being exploited by the Taiwanese-run Wistron Infocomm Manufacturing company, based near Bangalore - India’s IT hub. Workers were said to have smashed glass panels with rods and flipped cars on their side in protest. Local media sources reported that the factory workers claimed to not have been paid for up to four months yet were being forced to do additional shift work. A trade union representative claimed that there was “brutal exploitation” of factory workers in sweatshop conditions at the iPhone factory. Labour activists say the government legislation makes it difficult for workers to strike.
Labour disputes and industrial unrest are not uncommon in India, where many workers are still paid poorly and are provided with few if any social security benefits. Wistron Infocomm Manufacturing said in the statement that it “pledged to follow local labour [laws] and other related regulations”. The factory in India employs around 15,000 workers.
Source: adapted from the South China Morning Post, 13th December 2020
Human resource managers are increasingly relying on innovative technologies as part of their work. For example, developments in online and mobile banking have cut the need for banking staff. The huge popularity of social media networks (such as LinkedIn, Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter) has created opportunities for organizations to attract workers. LinkedIn, for example, is being increasingly used by businesses to headhunt employees.
Watch this Wall Street Journal video clip about the innovative culture at Google. The company prides itself on being innovative, so hiring employees who are free to be highly creative individuals is vital.
Key concept - Creativity
In business management, a creative workforce and culture of creativity can give a business competitive edges. Consider some of the examples below:
Airbnb has become the world’s largest property rentals company, but it does not own any properties.
Alibaba.com is the world’s largest B2B (business to business) online platform, but does not have any inventories.
Amazon.com transformed the (online) retail industry, putting lots of traditional retailers out of business in the process.
Cloud computing, such as Google Drive and Dropbox, has reduced the demand for computers and laptops with large physical storage devices.
Google Maps and mobile technologies have wiped out the demand for satellite navigation devices.
iTunes and Spotify have revolutionised the music industry.
Netflix is the world's largest provider of movies but doesn't own any cinemas of its own.
Skype, Teams, and Zoom have changed the way in which many multinational companies conduct their meetings and interviews (via video conferencing technologies), yet these companies do not own any telecommunications infrastructure.
Tesla’s creative and innovatively designed products have sparked huge interest in all-electric vehicles.
Uber, the world’s largest taxi operator, does not own any taxis.
How do the above cases impact on the role of human resource management?
Business Management Toolkit - Descriptive statistics
In order to support the HR department, organizations use a range of supporting quantitative information and statistical data, including:
Annual labour turnover figures
Absenteeism records
Business objectives
Demographic trends from government sources
Labour productivity data
Labour turnover rates
Management knowledge and experience
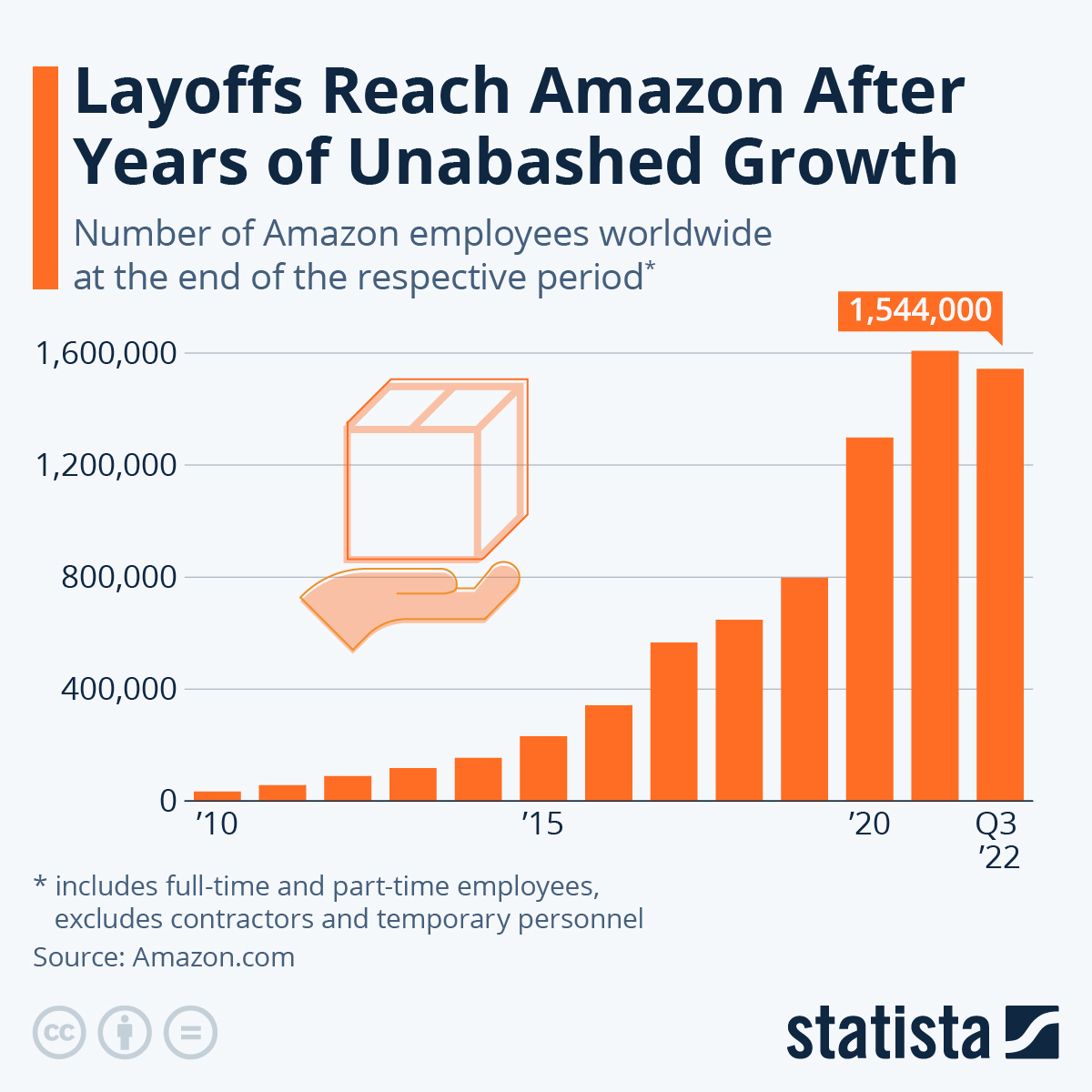
Growth rates of the organization (see chart below for Amazon from Statista)
Sales forecasts
The state of the economy, such as GDP, unemployment and inflation figures
Discuss the use of descriptive statistics in supporting the role of human resource management.
Business Management Toolkit - Hofstede's cultural dimensions

Culture is often described as "the way things are done here". Corporate culture refers to a set of beliefs and work attitude that is accepted in an organization. It can refer to the norms within an organization (such as the dress code within a business) and national or regional cultures (and how these impact on the organizational culture).
In terms of business management, culture refers to the norms, attitudes, values, goals, and practices that characterises an organization. It can apply to an organization, a country or a region of the world. Organizations will want to develop a strong and cohesive culture, where labour turnover is low and productivity is high, due to effective human resource management.
Attitudes and approaches to:
Appraisals
Dismissals and redundancies
Hiring migrant workers
Outsourcing, offshoring and re-shoring
Training and professional development
Individuals can shape organizational culture, just as organizations can shape individuals. Procedures and processes for managing human resources are explicitly shaped by traditions and cultures. National and regional cultural differences still exist within any organization, despite the forces of globalization bringing the world closer together. Hence, to manage human resources successfully, businesses have to adapt to cultural diversity within their organizations.
ATL Activity 2 - Looking after your parents

Read this interesting article from The Economist, titled ‘Which countries are most generous to new parents?’ Click the link here.
Contrast how these practices differ from a country that you are familiar with.
Theory of Knowledge (TOK)
Should a business deliberately/intentionally hire a culturally diverse workforce? Why or why not?
ATL Activity 3 - Video documentary review
Watch this 43-minutes Undercover Boss video documentary about Buffalo Wings & Rings in the USA. The video follows the CEO, Nader Masadeh, as he goes undercover to find out about the staff behind the Buffalo Wings & Rings franchise, with hopes of further expansion. Along the way, Nader Masadeh finds good employees but also a bully who needs to be dealt with.
Use this video as a real-world example of human resource management in action. The video covers many aspects of the Unit 2 syllabus, including human resource planning, organizational structure, leadership and management, motivation, and organizational culture.
Questions
Q1 - Where is Buffalo Wings & Rings headquartered and how many employees does the company have?
Q2 - Who is the President of Buffalo Wings & Rings, and how much does he earn a year?
Q3 - Where was the CEO of Buffalo Wings & Rings born?
Q4 - When did the first Buffalo Wings & Rings restaurant open?
Q5 - When did Masadeh buy the Buffalo Wings & Rings franchise, and how many stores did they have then?
Q6 - How many pounds (lbs) of chicken does Buffalo Wings & Rings use each year?
Q7 - What did Nader Masadeh purchase to celebrate the birth of the business in 1984?
Q8 - What is the reason behind Nader Masadeh going undercover?
Q9 - What was Nadeer Masadeh’s undercover name?
Q10 - Where is the first restaurant that Masadeh visited while going undercover?
Q11 - One of the employees is called Dave. What is his job at Buffalo Wings & Rings?
Q12 - Where is the location of the second restaurant that Masadeh visited?
Q13 - What was the second store’s staff turnover rate according to Amber?
Q14 - Where is the location of the 3rd restaurant that Masadeh visited while undercover?
Q15 - What is the name of the kitchen manager in the 3rd store that Masadeh visited?
Q16 - Who is the general manager in the third restaurant that Masadeh visited?
Q17 - What was the problem employees and “Pete” had with Wes?
Q18 - What was one of the company values that Nader Masadeh told Wes about?
Q19 - How much did Nader Masadeh award Dave for his retirement?
Q20 - What did Masadeh praise Amber for while undercover?
Answers
Video timings have been included here for your reference.
Q1 - Where is Buffalo Wings & Rings headquartered and how many employees does the company have? 1:35
Cincinnati, Ohio, 5,000 employees
Q2 - Who is the President of Buffalo Wings & Rings, and how much does he earn a year? 1:46
Nader Masadeh, US$1 million
Q3 - Where was the CEO of Buffalo Wings & Rings born? 2:40
Nader Masadeh was born in Jordan
Q4 - When did the first Buffalo Wings & Rings restaurant open? 4:28
1984
Q5 - When did Masadeh buy the Buffalo Wings & Rings franchise, and how many stores did they have then? 4:56
In 2005, with 4 restaurants
Q6 - How many pounds (lbs) of chicken does Buffalo Wings & Rings use each year? 5:14
5.5 million lbs (or approx. 2.5 million kilograms) - which includes 50 million chicken wings a year
Q7 - What did Nader Masadeh purchase to celebrate the birth of the business in 1984? 5:28
A new Ferrari, built in 1984
Q8 - What is the reason behind Nader Masadeh going undercover? 6:30
To investigate opportunities to expand the business, with the aim of having over 100 stores in the next several years
Q9 - What was Nadeer Masadeh’s undercover name? 7:08
Pete
Q10 - Where is the first restaurant that Masadeh visited while going undercover? 7:39
Cincinnati, Ohio
Q11 - One of the employees is called Dave. What is his job at Buffalo Wings & Rings? 8:19
A dishwasher
Q12 - Where is the location of the second restaurant that Nader Masadeh visited? 13:24
Chicago, Illinois
Q13 - What was the second store’s staff turnover rate according to Amber? 19:33
Around 80% - 90% staff turnover (due to the management staff not being caring)
Q14 - Where is the location of the 3rd restaurant that Masadeh visited while undercover? 23:34
Bardstown, Kentucky
Q15 - What is the name of the kitchen manager in the 3rd store that Masadeh visited? 23:55
Wes
Q16 - Who is the general manager in the third restaurant that Masadeh visited? 28:00
Red
Q17 - What was the problem employees and “Pete” had with Wes? 29:58
Bad behaviour / attitude and a total lack of respect for other employees
Q18 - What was one of the company values that Nader Masadeh told Wes about? 36:33
A safe working environment
Q19 - How much did Nader Masadeh award Dave for his retirement? 39:31
US$20,000
Q20 - What did Masadeh praise Amber following his undercover investigations? 40:22
Being honest about poor restaurant management
Download a PDF copy of the worksheet to use with your students by clicking the link here.
Return to the Unit 2.1 - Introduction to Human Resource Management homepage
Return to the Unit 2 - Human resource management homepage
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team