
HL Paper 1
The Sankey diagram shows the energy input from fuel that is eventually converted to useful domestic energy in the form of light in a filament lamp.
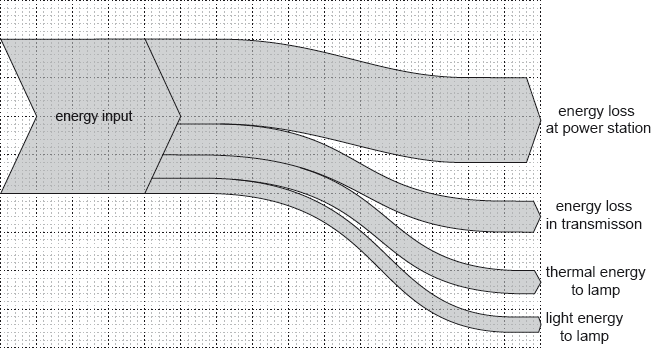
What is true for this Sankey diagram?
A. The overall efficiency of the process is 10%.
B. Generation and transmission losses account for 55% of the energy input.
C. Useful energy accounts for half of the transmission losses.
D. The energy loss in the power station equals the energy that leaves it.
X and Y are two spherical black-body radiators that emit the same total power. The absolute temperature of X is half that of Y.
What is ?
A. 4
B. 8
C. 16
D. 32
The solar constant is the intensity of the Sun’s radiation at
A. the surface of the Earth.
B. the mean distance from the Sun of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
C. the surface of the Sun.
D. 10km above the surface of the Earth.
An object can lose energy through
I. conduction
II. convection
III. radiation
What are the principal means for losing energy for a hot rock resting on the surface of the Moon?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
A nuclear particle has an energy of 108 eV. A grain of sand has a mass of 32 mg. What speed must the grain of sand have for its kinetic energy to equal the energy of the nuclear particle?
A. 1 mm s–1
B. 3 mm s–1
C. 10 mm s–1
D. 16 mm s–1
The average albedo of glacier ice is 0.25.
What is ?
A. 0.25
B. 0.33
C. 2.5
D. 3.0
Burning one litre of gasoline produces more energy than burning one kilogram of coal, and the density of gasoline is smaller than 1 g cm−3. What can be deduced from this information?
A. Energy density is greater for gasoline.
B. Specific energy is greater for gasoline.
C. Energy density is greater for coal.
D. Specific energy is greater for coal.
A model of an ideal wind turbine with blade length is designed to produce a power when the average wind speed is . A second ideal wind turbine is designed to produce a power when the average wind speed is . What is the blade length for the second wind turbine?
A.
B.
C.
D.
The dashed line on the graph shows the variation with wavelength of the intensity of solar radiation before passing through the Earth’s atmosphere.
The solid line on the graph shows the variation with wavelength of the intensity of solar radiation after it has passed through the Earth’s atmosphere.
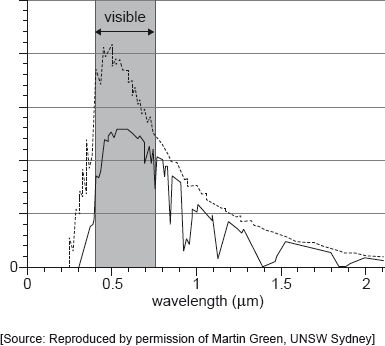
Which feature of the graph helps explain the greenhouse effect?
A. Infrared radiation is absorbed at specific wavelengths.
B. There is little absorption at infrared wavelengths.
C. There is substantial absorption at visible wavelengths.
D. There is little absorption at UV wavelengths.
Three statements about fossil fuels are:
I. There is a finite amount of fossil fuels on Earth.
II. The transfer of energy from fossil fuels increases the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere.
III. The geographic distribution of fossil fuels is uneven and has led to economic inequalities.
Which statements justify the development of alternative energy sources?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
A nuclear reactor contains atoms that are used for moderation and atoms that are used for control.
What are the ideal properties of the moderator atoms and the control atoms in terms of neutron absorption?
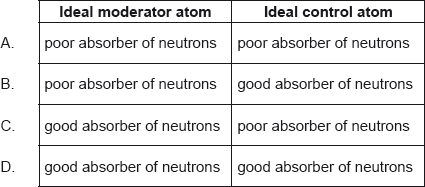
What part of a nuclear power station is principally responsible for increasing the chance that a neutron will cause fission?
A. Moderator
B. Control rod
C. Pressure vessel
D. Heat exchanger
The diagram shows a simple model of the energy balance in the Earth surface-atmosphere system. The intensities of the radiations are given.
What is the average intensity radiated by the atmosphere towards the surface?
A. 100 W m−2
B. 150 W m−2
C. 240 W m−2
D. 390 W m−2