
HL Paper 1
A cyclist accelerates in a straight line. At one instant, when the cyclist is exerting a forward force of 40 N, the air resistance acting on the cyclist is 10 N.
What is the rate of change of momentum of the cyclist at this instant?
A. 10 kg m s–2
B. 30 kg m s–2
C. 40 kg m s–2
D. 50 kg m s–2
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A mass is suspended from the ceiling of a train carriage by a string. The string makes an angle θ with the vertical when the train is accelerating along a straight horizontal track.
What is the acceleration of the train?
A. g sin θ
B. g cos θ
C. g tan θ
D.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A sunbather is supported in water by a floating sun bed. Which diagram represents the magnitudes of the forces acting on the sun bed?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A force acts on an object of mass 40 kg. The graph shows how the acceleration a of the object varies with its displacement d.
What is the work done by the force on the object?
A. 50 J
B. 2000 J
C. 2400 J
D. 3200 J
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A parachutist of total mass 70 kg is falling vertically through the air at a constant speed of 8 m s–1.
What is the total upward force acting on the parachutist?
A. 0 N
B. 70 N
C. 560 N
D. 700 N
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Three forces act at a point. In which diagram is the point in equilibrium?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A stationary nucleus of polonium-210 undergoes alpha decay to form lead-206. The initial speed of the alpha particle is v. What is the speed of the lead-206 nucleus?
A. v
B. v
C. v
D. v
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Two bodies each of equal mass travelling in opposite directions collide head-on.
What is a possible outcome of the collision?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
This question was well answered by HL candidates. Some students may have answered incorrectly due to consideration of speed rather than velocity.
A block of mass 1.0 kg rests on a trolley of mass 4.0 kg. The coefficient of dynamic friction between the block and the trolley is 0.30.
A horizontal force F = 5.0 N acts on the block. The block slides over the trolley. What is the acceleration of the trolley?
A. 5.0 m s–2
B. 1.0 m s–2
C. 0.75 m s–2
D. 0.60 m s–2
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A ball starts from rest and moves horizontally. Six positions of the ball are shown at time intervals of 1.0 ms. The horizontal distance between X, the initial position, and Y, the final position, is 0.050 m.
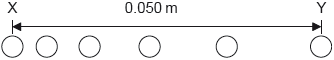
What is the average acceleration of the ball between X and Y?
A. 2000 m s–2
B. 4000 m s–2
C. 5000 m s–2
D. 8000 m s–2
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A student draws a graph to show the variation with time t of the acceleration a of an object.
What can the student deduce from this graph only, and what quantity from the graph is used to make this deduction?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A projectile is fired at an angle to the horizontal. The path of the projectile is shown.
Which gives the magnitude of the horizontal component and the magnitude of the vertical component of the velocity of the projectile between O and P?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t.
What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph?
A. 0.5 m s–1
B. 2.0 m s–1
C. 36 m s–1
D. 72 m s–1
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A stopper of mass 8 g leaves the opening of a container that contains pressurized gas.The stopper accelerates from rest for a time of 16 ms and leaves the container at a speed of 20 m s–1.
What is the order of magnitude of the force acting on the stopper?
A. 10–3 N
B. 100 N
C. 101 N
D. 103 N
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A block rests on a rough horizontal plane. A force P is applied to the block and the block moves to the right.
There is a coefficient of friction giving rise to a frictional force F between the block and the plane. The force P is doubled. Will and F be unchanged or greater?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
An astronaut is orbiting Earth in a spaceship. Why does the astronaut experience weightlessness?
A. The astronaut is outside the gravitational field of Earth.
B. The acceleration of the astronaut is the same as the acceleration of the spaceship.
C. The spaceship is travelling at a high speed tangentially to the orbit.
D. The gravitational field is zero at that point.
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
An object is thrown from a cliff at an angle to the horizontal. The ground below the cliff is horizontal.
Three quantities are known about this motion.
I. The horizontal component of the initial velocity of the object
II. The initial angle between the velocity of the object and the horizontal
III. The height of the cliff
What are the quantities that must be known in order to determine the horizontal distance from the point of projection to the point at which the object hits the ground?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A body is held in translational equilibrium by three coplanar forces of magnitude , and . Three statements about these forces are
I. all forces are perpendicular to each other
II. the forces cannot act in the same direction
III. the vector sum of the forces is equal to zero.
Which statements are true?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A ball is thrown upwards at time t = 0. The graph shows the variation with time of the height of the ball. The ball returns to the initial height at time T.
What is the height h at time t ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
This question proved challenging, many more candidates chose answer A instead of correct D. Candidates need to be aware that there are useful strategies for answering questions, especially ones they may find difficult. Eliminate choices that are clearly wrong - here A (and therefore B as well) are incorrect as they reflect an equation producing a height that always increases. It is also sometimes helpful to invent numbers to test the equations, e.g. assuming that the height is a known value, testing the possible answers given. Five metres would work here, as the height covered in free-fall from rest during one second. Thrown upwards at 5 m/s, it would take 1 second to go up and another to come back, therefore T = 2s. Only D would give the correct answer of 0 m after 1 s. The question also produced many comments on the G2 due to its difficulty. It must be remembered that questions appear in guide topic order so it is unlikely that harder questions will only appear towards the middle of the paper.
A ball falls from rest in the absence of air resistance. The position of the centre of the ball is determined at one-second intervals from the instant at which it is released. What are the distances, in metres, travelled by the centre of the ball during each second for the first 4.0 s of the motion?
A. 5, 10, 15, 20
B. 5, 15, 25, 35
C. 5, 20, 45, 80
D. 5, 25, 70, 150
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A block of weight W is suspended by two strings of equal length. The strings are almost horizontal.
What is correct about the tension T in one string?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A mass m attached to a string of length R moves in a vertical circle with a constant speed. The tension in the string at the top of the circle is T. What is the kinetic energy of the mass at the top of the circle?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A boy throws a ball horizontally at a speed of 15 m s-1 from the top of a cliff that is 80 m above the surface of the sea. Air resistance is negligible.
What is the distance from the bottom of the cliff to the point where the ball lands in the sea?
A. 45 m
B. 60 m
C. 80 m
D. 240 m
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A book of mass m lies on top of a table of mass M that rolls freely along the ground. The coefficient of friction between the book and the table is . A person is pushing the rolling table.
What is the maximum acceleration of the table so that the book does not slide backwards relative to the table?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Over half the candidates incorrectly chose option D. The book is only able to accelerate because of the friction force between the table and the book which depends on μ and the normal reaction force (mg) so independent of M, immediately eliminating options C and D.
A girl throws an object horizontally at time t = 0. Air resistance can be ignored. At t = 0.50 s the object travels horizontally a distance in metres while it falls vertically through a distance in metres.
What is the initial velocity of the object and the vertical distance fallen at t = 1.0 s?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
The correct response (D) was the most common selection by a minority of candidates, with incorrect responses being roughly equally distributed among the remaining options. This question has one of the highest discrimination indexes.
A block rests on a frictionless horizontal surface. An air rifle pellet is fired horizontally into the block and remains embedded in the block.
What happens to the total kinetic energy and to the total momentum of the block and pellet system as a result of the collision?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
An object of mass 2kg is thrown vertically downwards with an initial kinetic energy of 100J. What is the distance fallen by the object at the instant when its kinetic energy has doubled?
A. 2.5m
B. 5.0m
C. 10m
D. 14m
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A book is at rest on a table. What is a pair of action–reaction forces for this situation according to Newton’s third law of motion?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A nuclear particle has an energy of 108 eV. A grain of sand has a mass of 32 mg. What speed must the grain of sand have for its kinetic energy to equal the energy of the nuclear particle?
A. 1 mm s–1
B. 3 mm s–1
C. 10 mm s–1
D. 16 mm s–1
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A sports car is accelerated from 0 to 100 km per hour in 3 s. What is the acceleration of the car?
A. 0.1 g
B. 0.3 g
C. 0.9 g
D. 3 g
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Response D was the most common (but incorrect) response, with candidates neglecting to convert km/h to m/s.
A solid metal ball is dropped from a tower. The variation with time of the velocity of the ball is plotted.
A hollow metal ball with the same size and shape is dropped from the same tower. What graph will represent the variation with time of the velocity for the hollow metal ball?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A mass is released from the top of a smooth ramp of height . After leaving the ramp, the mass slides on a rough horizontal surface.
The mass comes to rest in a distance d. What is the coefficient of dynamic friction between the mass and the horizontal surface?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A horizontal spring of spring constant k and negligible mass is compressed through a distance y from its equilibrium length. An object of mass m that moves on a frictionless surface is placed at the end of the spring. The spring is released and returns to its equilibrium length.
What is the speed of the object just after it leaves the spring?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
The graph shows the variation of momentum with time for an object.
What net force acts on the object for the first 2.0 s and for the second 2.0 s of the motion?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A book is at rest on a table. One of the forces acting on the book is its weight.
What is the other force that completes the force pair according to Newton’s third law of motion?
A. The pull of the book on Earth
B. The pull of Earth on the book
C. The push of the table on the book
D. The push of the book on the table
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
The majority of candidates incorrectly selected option C for this question, resulting in a low difficulty index overall. This question highlights a typical misconception relating to Newton's 3rd law, and emphasises the importance of conceptual physics teaching.
A ball of mass m collides with a vertical wall with an initial horizontal speed u and rebounds with a horizontal speed v. The graph shows the variation of the speed of the ball with time.
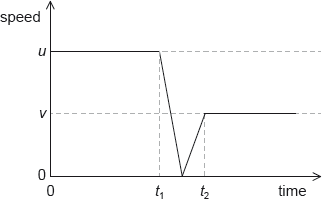
What is the magnitude of the mean net force on the ball during the collision?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A waiter carrying a tray is accelerating to the right as shown in the image.
What is the free-body diagram of the forces acting on the tray?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Response D was the most common response, with the free-body diagram in response A providing a significant distractor for roughly a third of candidates. Most candidates recognized that the only upward vector would be one perpendicular to the tray.
A toy car of mass 0.15 kg accelerates from a speed of 10 cm s–1 to a speed of 15 cm s–1. What is the impulse acting on the car?
A. 7.5 mN s
B. 37.5 mN s
C. 0.75 N s
D. 3.75 N s
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Masses X and Y rest on a smooth horizontal surface and are connected by a massless spring. The mass of X is 3.0 kg and the mass of Y is 6.0 kg. The masses are pushed toward each other until the elastic potential energy stored in the spring is 1.0 J.
The masses are released. What is the maximum speed reached by mass Y?
A. 0.11 m s−1
B. 0.33 m s−1
C. 0.45 m s−1
D. 0.66 m s−1
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A projectile is launched at an angle above the horizontal with a horizontal component of velocity and a vertical component of velocity . Air resistance is negligible. Which graphs show the variation with time of and of ?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A car is driven from rest along a straight horizontal road. The car engine exerts a constant driving force. Friction and air resistance are negligible. How does the power developed by the engine change with the distance travelled?
A. Power does not change.
B. Power decreases linearly.
C. Power increases linearly.
D. Power increases non-linearly.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Lowish discrimination with C the most popular choice. It was felt that candidates normally analyse in terms of the time taken whereas this question refers to the distance travelled so with a constant driving force the velocity increases linearly with time but non linearly with distance.
A cyclist rides up a hill of vertical height 100 m in 500 s at a constant speed. The combined mass of the cyclist and the bicycle is 80 kg. The power developed by the cyclist is 200 W. What is the efficiency of the energy transfer in this system?
A. 8 %
B. 20 %
C. 60 %
D. 80 %
Markscheme
D