
SL Paper 3
A uniform ladder of weight 50.0 N and length 4.00 m is placed against a frictionless wall making an angle of 60.0° with the ground.
Outline why the normal force acting on the ladder at the point of contact with the wall is equal to the frictional force F between the ladder and the ground.
Calculate F.
The coefficient of friction between the ladder and the ground is 0.400. Determine whether the ladder will slip.
A wheel of mass 0.25 kg consists of a cylinder mounted on a central shaft. The shaft has a radius of 1.2 cm and the cylinder has a radius of 4.0 cm. The shaft rests on two rails with the cylinder able to spin freely between the rails.
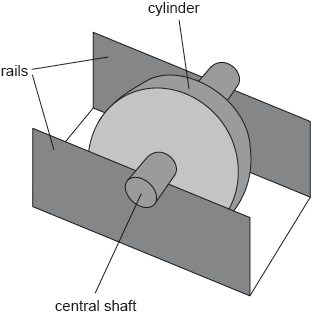
The stationary wheel is released from rest and rolls down a slope with the shaft rolling on the rails without slipping from point A to point B.
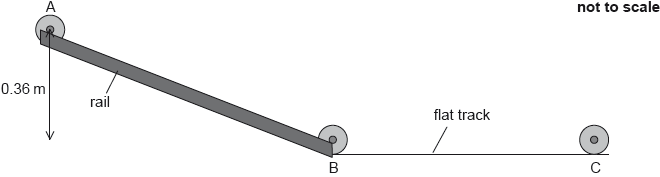
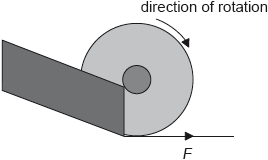
The wheel leaves the rails at point B and travels along the flat track to point C. For a short time the wheel slips and a frictional force F exists on the edge of the wheel as shown.
The moment of inertia of the wheel is 1.3 × 10–4 kg m2. Outline what is meant by the moment of inertia.
In moving from point A to point B, the centre of mass of the wheel falls through a vertical distance of 0.36 m. Show that the translational speed of the wheel is about 1 m s–1 after its displacement.
Determine the angular velocity of the wheel at B.
Describe the effect of F on the linear speed of the wheel.
Describe the effect of F on the angular speed of the wheel.