
HL Paper 1
An electric field acts in the space between two charged parallel plates. One plate is at zero potential and the other is at potential +V.
The distance x is measured from point P in the direction perpendicular to the plate.
What is the dependence of the electric field strength E on x and what is the dependence of the electric potential V on x?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Two point charges are at rest as shown.
At which position is the electric field strength greatest?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A charged sphere in a gravitational field is initially stationary between two parallel metal plates. There is a potential difference V between the plates.
Three changes can be made:
I. Increase the separation of the metal plates
II. Increase V
III. Apply a magnetic field into the plane of the paper
What changes made separately will cause the charged sphere to accelerate?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Option C was a very successful distractor, selected by the majority of candidates. Most candidates missed that change III ("Apply a magnetic field into the plane of the paper") can never be correct if the charge is stationary.
Which is a correct unit for gravitational potential?
A. m2 s−2
B. J kg
C. m s−2
D. N m−1 kg−1
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Two point charges Q1 and Q2 are one metre apart. The graph shows the variation of electric potential V with distance from Q1.
What is ?
A.
B.
C. 4
D. 16
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A moon of mass M orbits a planet of mass 100M. The radius of the planet is R and the distance between the centres of the planet and moon is 22R.
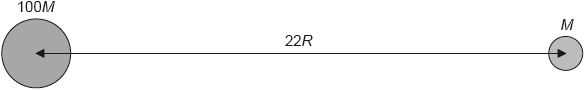
What is the distance from the centre of the planet at which the total gravitational potential has a maximum value?
A. 2R
B. 11R
C. 20R
D. 2R and 20R
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
An electron is fixed in position in a uniform electric field. What is the position for which the electrical potential energy of the electron is greatest?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
The force acting between two point charges is when the separation of the charges is . What is the force between the charges when the separation is increased to ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A negative charge Q is to be moved within an electric field E, to equidistant points from its position, as shown.
Which path requires the most work done?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
The most common answer was A, suggesting that students missed the prompt that Q is a negative charge.
What is the unit of Gε0, where G is the gravitational constant and ε0 is the permittivity of free space?
A. C kg–1
B. C2 kg–2
C. C kg
D. C2 kg2
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A satellite of mass 1500 kg is in the Earth’s gravitational field. It moves from a point where the gravitational potential is –30 MJ kg–1 to a point where the gravitational potential is –20 MJ kg–1. What is the direction of movement of the satellite and the change in its gravitational potential energy?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
The graph shows the variation of the gravitational potential V with distance r from the centre of a uniform spherical planet. The radius of the planet is R. The shaded area is S.
What is the work done by the gravitational force as a point mass m is moved from the surface of the planet to a distance 6R from the centre?
A. m (V2 – V1 )
B. m (V1 – V2 )
C. mS
D. S
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Two parallel metal plates are connected to a dc power supply. An electric field forms in the space between the plates as shown.
What is the shape of the equipotentials surfaces that result from this arrangement?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A positive charge Q is deposited on the surface of a small sphere. The dotted lines represent equipotentials.
A small positive point charge is moved from point P closer to the sphere along three different paths X, Y and Z. The work done along each path is WX, WY and WZ. What is a correct comparison of WX, WY and WZ?
A. WZ > WY > WX
B. WX > WY = WZ
C. WX = WY = WZ
D. WZ = WY > WX
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
P and S are two points on a gravitational equipotential surface around a planet. Q and R are two points on a different gravitational equipotential surface at a greater distance from the planet.
The greatest work done by the gravitational force is when moving a mass from
A. P to S.
B. Q to R.
C. R to P.
D. S to R.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Four uniform planets have masses and radii as shown. Which planet has the smallest escape speed?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
The diagram shows 5 gravitational equipotential lines. The gravitational potential on each line is indicated. A point mass m is placed on the middle line and is then released. Values given in MJ kg–1.
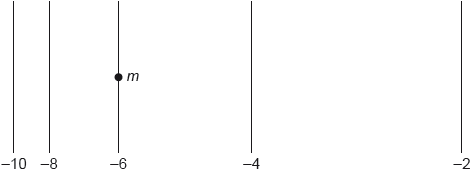
Which is correct about the direction of motion and the acceleration of the point mass?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A charge of −3 C is moved from A to B and then back to A. The electric potential at A is +10 V and the electric potential at B is −20 V. What is the work done in moving the charge from A to B and the total work done?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A satellite orbiting a planet moves from orbit X to orbit Y.
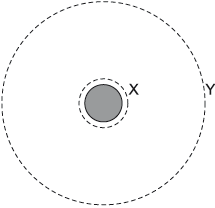
What is the change in the kinetic energy and the change in the gravitational potential energy as a result?
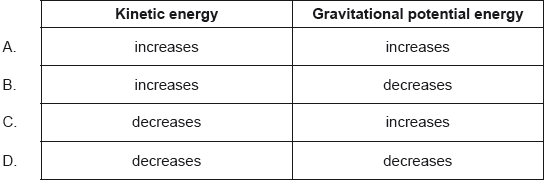
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
An electron of mass me orbits an alpha particle of mass mα in a circular orbit of radius r. Which expression gives the speed of the electron?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
The diagram shows the electric field and the electric equipotential surfaces between two charged parallel plates. The potential difference between the plates is 200 V.
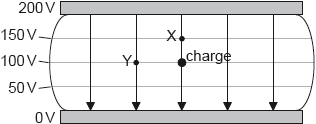
What is the work done, in nJ, by the electric field in moving a negative charge of magnitude 1 nC from the position shown to X and to Y?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
An object of mass is launched from the surface of the Earth. The Earth has a mass and radius . The acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the Earth is . What is the escape speed of the object from the surface of the Earth?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Options B and C were selected by a roughly equal number of candidates. Again, this is a situation where unit analysis is beneficial; options C and D would not produce units associated with speed (mass is already incorporated in the constant 'g').
The escape speed for the Earth is esc. Planet X has half the density of the Earth and twice the radius. What is the escape speed for planet X?
A.
B.
C. esc
D. esc
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
The gravitational potential at point P due to Earth is V.
What is the definition of the gravitational potential at P?
A. Work done per unit mass to move a point mass from infinity to P
B. Work done per unit mass to move a point mass from P to infinity
C. Work done to move a point mass from infinity to P
D. Work done to move a point mass from P to infinity
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A satellite in a circular orbit around the Earth needs to reduce its orbital radius.
What is the work done by the satellite rocket engine and the change in kinetic energy resulting from this shift in orbital height?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
This question was generally well answered, however a significant number of students (incorrectly) selected response A suggesting a lack of clarity around the work done as a result of changes in orbital height.
An electron enters a uniform electric field of strength E with a velocity v. The direction of v is not parallel to E. What is the path of the electron after entering the field?
A. Circular
B. Parabolic
C. Parallel to E
D. Parallel to v
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
The gravitational potential is at a distance above the surface of a spherical planet of radius and uniform density. What is the gravitational potential a distance above the surface of the planet?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
The escape speed from a planet of radius R is vesc. A satellite orbits the planet at a distance R from the surface of the planet. What is the orbital speed of the satellite?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
This had a very low discrimination index with the majority of candidates choosing B, followed by C. Response A, the correct answer, was third in popularity. The candidates missed that the satellite orbits at a distance of R from the surface of a planet of radius R so the total distance to be considered was 2R.
A spacecraft moves towards the Earth under the influence of the gravitational field of the Earth.
The three quantities that depend on the distance r of the spacecraft from the centre of the Earth are the
I. gravitational potential energy of the spacecraft
II gravitational field strength acting on the spacecraft
III. gravitational force acting on the spacecraft.
Which of the quantities are proportional to ?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A particle with charge −2.5 × 10−6 C moves from point X to point Y due to a uniform electrostatic field. The diagram shows some equipotential lines of the field.
What is correct about the motion of the particle from X to Y and the magnitude of the work done by the field on the particle?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Four identical, positive, point charges of magnitude Q are placed at the vertices of a square of side 2d. What is the electric potential produced at the centre of the square by the four charges?
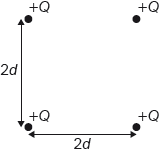
A. 0
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A satellite orbits planet with a speed at a distance from the centre of planet . Another satellite orbits planet at a speed of at a distance from the centre of planet . The mass of planet is and the mass of planet is . What is the ratio of ?
A. 0.25
B. 0.5
C. 2.0
D. 4.0
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
An object of mass released from rest near the surface of a planet has an initial acceleration . What is the gravitational field strength near the surface of the planet?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
The mass of the Earth is ME and the mass of the Moon is MM. Their respective radii are RE and RM.
Which is the ratio ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A satellite at the surface of the Earth has a weight W and gravitational potential energy Ep. The satellite is then placed in a circular orbit with a radius twice that of the Earth.
What is the weight of the satellite and the gravitational potential energy of the satellite when placed in orbit?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Two charged parallel plates have electric potentials of 10 V and 20 V.
A particle with charge +2.0 μC is moved from the 10 V plate to the 20 V plate. What is the change in the electric potential energy of the particle?
A. −20 μJ
B. −10 μJ
C. 10 μJ
D. 20 μJ
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A positive point charge is placed above a metal plate at zero electric potential. Which diagram shows the pattern of electric field lines between the charge and the plate?
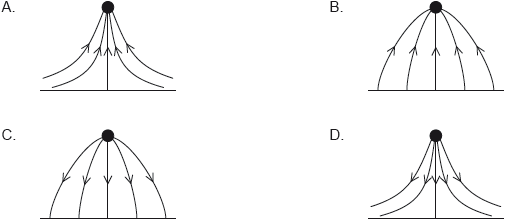
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Satellite X is in orbit around the Earth. An identical satellite Y is in a higher orbit. What is correct for the total energy and the kinetic energy of the satellite Y compared with satellite X?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
We accept the comment from G2 forms that the wording of this question could be improved. The correct answer (B) considers the total and kinetic energies of satellite X the most popular answer.
The points X and Y are in a uniform electric field of strength . The distance OX is and the distance OY is .
What is the magnitude of the change in electric potential between X and Y?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A satellite of mass orbits a planet of mass in a circular orbit of radius . What is the work that must be done on the satellite to increase its orbital radius to ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
The diagram shows equipotential lines for an electric field. Which arrow represents the acceleration of an electron at point P?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Two positive and two negative charges are located at the corners of a square as shown. Point X is the centre of the square. What is the value of the electric field E and the electric potential V at X due to the four charges?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Candidates were unsure about this question with almost equal numbers choosing A and C. Electric potential is a scalar quantity so unaffected by the sign of the charge and can only be 0 in this arrangement removing the choice of C.
An isolated hollow metal sphere of radius R carries a positive charge. Which graph shows the variation of potential V with distance x from the centre of the sphere?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
The escape velocity for an object at the surface of the Earth is vesc. The diameter of the Moon is 4 times smaller than that of the Earth and the mass of the Moon is 81 times smaller than that of the Earth. What is the escape velocity of the object on the Moon?
A. vesc
B. vesc
C. vesc
D. vesc
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
This question was well answered by candidates.
A planet has radius R. The escape speed from the surface of the planet is v. At what distance from the surface of the planet is the orbital speed 0.5v?
A. 0.5R
B. R
C. 2R
D. 4R
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
The graph shows the variation of electric field strength with distance from a point charge.
The shaded area X is the area under the graph between two separations and from the charge.
What is X?
A. The electric field average between and
B. The electric potential difference between and
C. The work done in moving a charge from to
D. The work done in moving a charge from to
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
The graph shows the variation with distance r of the electric potential V from a charge Q.
What is the electric field strength at distance s?
A. The area under the graph between s and infinity
B. The area under the graph between 0 and s
C. The gradient of the tangent at s
D. The negative of the gradient of the tangent at s
Markscheme
D