
SL Paper 2
Eddie decides to construct a path across his rectangular grass lawn using pairs of tiles.
Each tile is wide and long. The following diagrams show the path after Eddie has laid one pair and three pairs of tiles. This pattern continues until Eddie reaches the other side of his lawn. When pairs of tiles are laid, the path has a width of centimetres and a length centimetres.
The following diagrams show this pattern for one pair of tiles and for three pairs of tiles, where the white space around each diagram represents Eddie’s lawn.
The following table shows the values of and for the first three values of .
Find the value of
Write down an expression in terms of for
Eddie’s lawn has a length .
The tiles cost per square metre and are sold in packs of five tiles.
To allow for breakages Eddie wants to have at least more tiles than he needs.
There is a fixed delivery cost of .
.
.
.
.
Show that Eddie needs tiles.
Find the value of for this path.
Find the total area of the tiles in Eddie’s path. Give your answer in the form where and is an integer.
Find the cost of a single pack of five tiles.
Find the minimum number of packs of tiles Eddie will need to order.
Find the total cost for Eddie’s order.
The marks obtained by nine Mathematical Studies SL students in their projects (x) and their final IB examination scores (y) were recorded. These data were used to determine whether the project mark is a good predictor of the examination score. The results are shown in the table.
The equation of the regression line y on x is y = mx + c.
A tenth student, Jerome, obtained a project mark of 17.
Use your graphic display calculator to write down , the mean examination score.
Use your graphic display calculator to write down r , Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient.
Find the exact value of m and of c for these data.
Use the regression line y on x to estimate Jerome’s examination score.
Justify whether it is valid to use the regression line y on x to estimate Jerome’s examination score.
Scott purchases food for his dog in large bags and feeds the dog the same amount of dog food each day. The amount of dog food left in the bag at the end of each day can be modelled by an arithmetic sequence.
On a particular day, Scott opened a new bag of dog food and fed his dog. By the end of the third day there were cups of dog food remaining in the bag and at the end of the eighth day there were cups of dog food remaining in the bag.
Find the number of cups of dog food
In , Scott spent on dog food. Scott expects that the amount he spends on dog food will increase at an annual rate of .
fed to the dog per day.
remaining in the bag at the end of the first day.
Calculate the number of days that Scott can feed his dog with one bag of food.
Determine the amount that Scott expects to spend on dog food in . Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
Calculate the value of .
Describe what the value in part (d)(i) represents in this context.
Comment on the appropriateness of modelling this scenario with a geometric sequence.
Sophie is planning to buy a house. She needs to take out a mortgage for $120000. She is considering two possible options.
Option 1: Repay the mortgage over 20 years, at an annual interest rate of 5%, compounded annually.
Option 2: Pay $1000 every month, at an annual interest rate of 6%, compounded annually, until the loan is fully repaid.
Give a reason why Sophie might choose
Sophie decides to choose option 1. At the end of 10 years, the interest rate is changed to 7%, compounded annually.
Calculate the monthly repayment using option 1.
Calculate the total amount Sophie would pay, using option 1.
Calculate the number of months it will take to repay the mortgage using option 2.
Calculate the total amount Sophie would pay, using option 2.
option 1.
option 2.
Use your answer to part (a)(i) to calculate the amount remaining on her mortgage after the first 10 years.
Hence calculate her monthly repayment for the final 10 years.
Consider the function .
Sketch the graph of y = f (x), for −4 ≤ x ≤ 3 and −50 ≤ y ≤ 100.
Use your graphic display calculator to find the zero of f (x).
Use your graphic display calculator to find the coordinates of the local minimum point.
Use your graphic display calculator to find the equation of the tangent to the graph of y = f (x) at the point (–2, 38.75).
Give your answer in the form y = mx + c.
In this question, give all answers to two decimal places.
Bryan decides to purchase a new car with a price of €14 000, but cannot afford the full amount. The car dealership offers two options to finance a loan.
Finance option A:
A 6 year loan at a nominal annual interest rate of 14 % compounded quarterly. No deposit required and repayments are made each quarter.
Finance option B:
A 6 year loan at a nominal annual interest rate of % compounded monthly. Terms of the loan require a 10 % deposit and monthly repayments of €250.
Find the repayment made each quarter.
Find the total amount paid for the car.
Find the interest paid on the loan.
Find the amount to be borrowed for this option.
Find the annual interest rate, .
State which option Bryan should choose. Justify your answer.
Bryan’s car depreciates at an annual rate of 25 % per year.
Find the value of Bryan’s car six years after it is purchased.
Paul wants to buy a car. He needs to take out a loan for $7000. The car salesman offers him a loan with an interest rate of 8%, compounded annually. Paul considers two options to repay the loan.
Option 1: Pay $200 each month, until the loan is fully repaid
Option 2: Make 24 equal monthly payments.
Use option 1 to calculate
Use option 2 to calculate
Give a reason why Paul might choose
the number of months it will take for Paul to repay the loan.
the total amount that Paul has to pay.
the amount Paul pays each month.
the total amount that Paul has to pay.
option 1.
option 2.
A new café opened and during the first week their profit was $60.
The café’s profit increases by $10 every week.
A new tea-shop opened at the same time as the café. During the first week their profit was also $60.
The tea-shop’s profit increases by 10 % every week.
Find the café’s profit during the 11th week.
Calculate the café’s total profit for the first 12 weeks.
Find the tea-shop’s profit during the 11th week.
Calculate the tea-shop’s total profit for the first 12 weeks.
In the mth week the tea-shop’s total profit exceeds the café’s total profit, for the first time since they both opened.
Find the value of m.
The admissions team at a new university are trying to predict the number of student applications they will receive each year.
Let be the number of years that the university has been open. The admissions team collect the following data for the first two years.
It is assumed that the number of students that apply to the university each year will follow a geometric sequence, .
In the first year there were places at the university available for applicants. The admissions team announce that the number of places available will increase by every year.
Let represent the number of places available at the university in year .
For the first years that the university is open, all places are filled. Students who receive a place each pay an acceptance fee.
When , the number of places available will, for the first time, exceed the number of students applying.
Calculate the percentage increase in applications from the first year to the second year.
Write down the common ratio of the sequence.
Find an expression for .
Find the number of student applications the university expects to receive when . Express your answer to the nearest integer.
Write down an expression for .
Calculate the total amount of acceptance fees paid to the university in the first years.
Find .
State whether, for all , the university will have places available for all applicants. Justify your answer.
Boris recorded the number of daylight hours on the first day of each month in a northern hemisphere town.
This data was plotted onto a scatter diagram. The points were then joined by a smooth curve, with minimum point and maximum point as shown in the following diagram.
Let the curve in the diagram be , where is the time, measured in months, since Boris first recorded these values.
Boris thinks that might be modelled by a quadratic function.
Paula thinks that a better model is , , for specific values of and .
For Paula’s model, use the diagram to write down
The true maximum number of daylight hours was hours and minutes.
Write down one reason why a quadratic function would not be a good model for the number of hours of daylight per day, across a number of years.
the amplitude.
the period.
the equation of the principal axis.
Hence or otherwise find the equation of this model in the form:
For the first year of the model, find the length of time when there are more than hours and minutes of daylight per day.
Calculate the percentage error in the maximum number of daylight hours Boris recorded in the diagram.
The following table shows values of ln x and ln y.
The relationship between ln x and ln y can be modelled by the regression equation ln y = a ln x + b.
Find the value of a and of b.
Use the regression equation to estimate the value of y when x = 3.57.
The relationship between x and y can be modelled using the formula y = kxn, where k ≠ 0 , n ≠ 0 , n ≠ 1.
By expressing ln y in terms of ln x, find the value of n and of k.
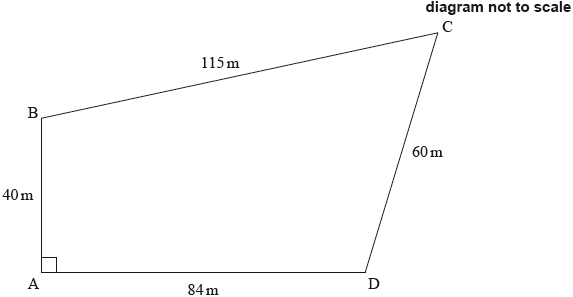
Abdallah owns a plot of land, near the river Nile, in the form of a quadrilateral ABCD.
The lengths of the sides are and angle .
This information is shown on the diagram.
The formula that the ancient Egyptians used to estimate the area of a quadrilateral ABCD is
.
Abdallah uses this formula to estimate the area of his plot of land.
Show that correct to the nearest metre.
Calculate angle .
Find the area of ABCD.
Calculate Abdallah’s estimate for the area.
Find the percentage error in Abdallah’s estimate.
On her first day in a hospital, Kiri receives milligrams (mg) of a therapeutic drug. The amount of the drug Kiri receives increases by the same amount, , each day. On the seventh day, she receives 21 mg of the drug, and on the eleventh day she receives 29 mg.
Kiri receives the drug for 30 days.
Ted is also in a hospital and on his first day he receives a 20 mg antibiotic injection. The amount of the antibiotic Ted receives decreases by 50 % each day. On the second day, Ted receives a 10 mg antibiotic injection, on the third day he receives 5 mg, and so on.
Write down an equation, in terms of and , for the amount of the drug that she receives on the seventh day.
Write down an equation, in terms of and , for the amount of the drug that she receives on the eleventh day.
Write down the value of and the value of .
Calculate the total amount of the drug, in mg, that she receives.
Find the amount of antibiotic, in mg, that Ted receives on the fifth day.
The daily amount of antibiotic Ted receives will first be less than 0.06 mg on the th day. Find the value of .
Hence find the total amount of antibiotic, in mg, that Ted receives during the first days.
A water container is made in the shape of a cylinder with internal height cm and internal base radius cm.
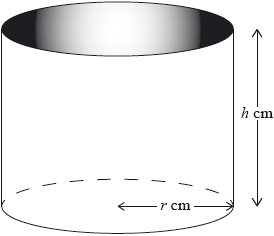
The water container has no top. The inner surfaces of the container are to be coated with a water-resistant material.
The volume of the water container is .
The water container is designed so that the area to be coated is minimized.
One can of water-resistant material coats a surface area of .
Write down a formula for , the surface area to be coated.
Express this volume in .
Write down, in terms of and , an equation for the volume of this water container.
Show that .
Find .
Using your answer to part (e), find the value of which minimizes .
Find the value of this minimum area.
Find the least number of cans of water-resistant material that will coat the area in part (g).
The Tower of Pisa is well known worldwide for how it leans.
Giovanni visits the Tower and wants to investigate how much it is leaning. He draws a diagram showing a non-right triangle, ABC.
On Giovanni’s diagram the length of AB is 56 m, the length of BC is 37 m, and angle ACB is 60°. AX is the perpendicular height from A to BC.
Giovanni’s tourist guidebook says that the actual horizontal displacement of the Tower, BX, is 3.9 metres.
Use Giovanni’s diagram to show that angle ABC, the angle at which the Tower is leaning relative to the
horizontal, is 85° to the nearest degree.
Use Giovanni's diagram to calculate the length of AX.
Use Giovanni's diagram to find the length of BX, the horizontal displacement of the Tower.
Find the percentage error on Giovanni’s diagram.
Giovanni adds a point D to his diagram, such that BD = 45 m, and another triangle is formed.
Find the angle of elevation of A from D.
The following table shows the average body weight, , and the average weight of the brain, , of seven species of mammal. Both measured in kilograms (kg).
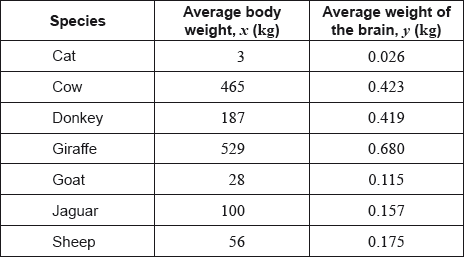
The average body weight of grey wolves is 36 kg.
In fact, the average weight of the brain of grey wolves is 0.120 kg.
Find the range of the average body weights for these seven species of mammal.
For the data from these seven species calculate , the Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient;
For the data from these seven species describe the correlation between the average body weight and the average weight of the brain.
Write down the equation of the regression line on , in the form .
Use your regression line to estimate the average weight of the brain of grey wolves.
Find the percentage error in your estimate in part (d).
Let , for x > 0.
The k th maximum point on the graph of f has x-coordinate xk where .
Given that xk + 1 = xk + a, find a.
Hence find the value of n such that .
Give your answers to parts (b), (c) and (d) to the nearest whole number.
Harinder has 14 000 US Dollars (USD) to invest for a period of five years. He has two options of how to invest the money.
Option A: Invest the full amount, in USD, in a fixed deposit account in an American bank.
The account pays a nominal annual interest rate of r % , compounded yearly, for the five years. The bank manager says that this will give Harinder a return of 17 500 USD.
Option B: Invest the full amount, in Indian Rupees (INR), in a fixed deposit account in an Indian bank. The money must be converted from USD to INR before it is invested.
The exchange rate is 1 USD = 66.91 INR.
The account in the Indian bank pays a nominal annual interest rate of 5.2 % compounded monthly.
Calculate the value of r.
Calculate 14 000 USD in INR.
Calculate the amount of this investment, in INR, in this account after five years.
Harinder chose option B. At the end of five years, Harinder converted this investment back to USD. The exchange rate, at that time, was 1 USD = 67.16 INR.
Calculate how much more money, in USD, Harinder earned by choosing option B instead of option A.
Give your answers in parts (a), (d)(i), (e) and (f) to the nearest dollar.
Daisy invested Australian dollars () in a fixed deposit account with an annual interest rate of compounded quarterly.
After months, the amount of money in the fixed deposit account has appreciated to more than .
Daisy is saving to purchase a new apartment. The price of the apartment is .
Daisy makes an initial payment of and takes out a loan to pay the rest.
The loan is for years, compounded monthly, with equal monthly payments of made by Daisy at the end of each month.
For this loan, find
After years of paying off this loan, Daisy decides to pay the remainder in one final payment.
Calculate the value of Daisy’s investment after years.
Find the minimum value of , where .
Write down the amount of the loan.
the amount of interest paid by Daisy.
the annual interest rate of the loan.
Find the amount of Daisy’s final payment.
Find how much money Daisy saved by making one final payment after years.
The first term of an infinite geometric sequence is 4. The sum of the infinite sequence is 200.
Find the common ratio.
Find the sum of the first 8 terms.
Find the least value of n for which Sn > 163.
Rosa joins a club to prepare to run a marathon. During the first training session Rosa runs a distance of 3000 metres. Each training session she increases the distance she runs by 400 metres.
A marathon is 42.195 kilometres.
In the th training session Rosa will run further than a marathon for the first time.
Carlos joins the club to lose weight. He runs 7500 metres during the first month. The distance he runs increases by 20% each month.
Write down the distance Rosa runs in the third training session;
Write down the distance Rosa runs in the th training session.
Find the value of .
Calculate the total distance, in kilometres, Rosa runs in the first 50 training sessions.
Find the distance Carlos runs in the fifth month of training.
Calculate the total distance Carlos runs in the first year.
John purchases a new bicycle for 880 US dollars (USD) and pays for it with a Canadian credit card. There is a transaction fee of 4.2 % charged to John by the credit card company to convert this purchase into Canadian dollars (CAD).
The exchange rate is 1 USD = 1.25 CAD.
John insures his bicycle with a US company. The insurance company produces the following table for the bicycle’s value during each year.
The values of the bicycle form a geometric sequence.
During the 1st year John pays 120 USD to insure his bicycle. Each year the amount he pays to insure his bicycle is reduced by 3.50 USD.
Calculate, in CAD, the total amount John pays for the bicycle.
Find the value of the bicycle during the 5th year. Give your answer to two decimal places.
Calculate, in years, when the bicycle value will be less than 50 USD.
Find the total amount John has paid to insure his bicycle for the first 5 years.
A large underground tank is constructed at Mills Airport to store fuel. The tank is in the shape of an isosceles trapezoidal prism, .
, , , and . Angle and angle . The tank is illustrated below.
Once construction was complete, a fuel pump was used to pump fuel into the empty tank. The amount of fuel pumped into the tank by this pump each hour decreases as an arithmetic sequence with terms .
Part of this sequence is shown in the table.
At the end of the hour, the total volume of fuel in the tank was .
Find , the height of the tank.
Show that the volume of the tank is , correct to three significant figures.
Write down the common difference, .
Find the amount of fuel pumped into the tank in the hour.
Find the value of such that .
Write down the number of hours that the pump was pumping fuel into the tank.
Find the total amount of fuel pumped into the tank in the first hours.
Show that the tank will never be completely filled using this pump.
The sum of an infinite geometric sequence is 33.25. The second term of the sequence is 7.98. Find the possible values of .
Maegan designs a decorative glass face for a new Fine Arts Centre. The glass face is made up of small triangular panes. The first three levels of the glass face are illustrated in the following diagram.
The level, at the bottom of the glass face, has triangular panes. The level has triangular panes, and the level has triangular panes. Each additional level has more triangular panes than the level below it.
Maegan has triangular panes to build the decorative glass face and does not want it to have any incomplete levels.
Find the number of triangular panes in the level.
Show that the total number of triangular panes, , in the first levels is given by:
.
Hence, find the total number of panes in a glass face with levels.
Find the maximum number of complete levels that Maegan can build.
Each triangular pane has an area of .
Find the total area of the decorative glass face, if the maximum number of complete levels were built. Express your area to the nearest .
An infinite geometric series has first term and second term , where .
Find the common ratio in terms of .
Find the values of for which the sum to infinity of the series exists.
Find the value of when .
In an arithmetic sequence, , and .
Consider the terms, , of this sequence such that ≤ .
Let be the sum of the terms for which is not a multiple of 3.
Find the value of .
Find the exact value of .
Show that .
An infinite geometric series is given as , .
Find the largest value of such that .
A new concert hall was built with seats in the first row. Each subsequent row of the hall has two more seats than the previous row. The hall has a total of rows.
Find:
The concert hall opened in . The average number of visitors per concert during that year was . In , the average number of visitors per concert increased by .
The concert organizers use this data to model future numbers of visitors. It is assumed that the average number of visitors per concert will continue to increase each year by .
the number of seats in the last row.
the total number of seats in the concert hall.
Find the average number of visitors per concert in .
Determine the first year in which this model predicts the average number of visitors per concert will exceed the total seating capacity of the concert hall.
It is assumed that the concert hall will host concerts each year.
Use the average number of visitors per concert per year to predict the total number of people expected to attend the concert hall from when it opens until the end of .
The first terms of an infinite geometric sequence, , are 2, 6, 18, 54, …
The first terms of a second infinite geometric sequence, , are 2, −6, 18, −54, …
The terms of a third sequence, , are defined as .
The finite series, , can also be written in the form .
Write down the first three non-zero terms of .
Find the value of .
Find the value of .
Consider a geometric sequence where the first term is 768 and the second term is 576.
Find the least value of such that the th term of the sequence is less than 7.