
HL Paper 1
Prove by mathematical induction that for .
Hence or otherwise, determine the Maclaurin series of in ascending powers of , up to and including the term in .
Hence or otherwise, determine the value of .
Consider the function .
Determine whether is an odd or even function, justifying your answer.
By using mathematical induction, prove that
where .
Hence or otherwise, find an expression for the derivative of with respect to .
Show that, for , the equation of the tangent to the curve at is .
The function is defined by , where 0 ≤ ≤ 5. The curve is shown on the following graph which has local maximum points at A and C and touches the -axis at B and D.
Use integration by parts to show that , .
Hence, show that , .
Find the -coordinates of A and of C , giving your answers in the form , where , .
Find the area enclosed by the curve and the -axis between B and D, as shaded on the diagram.
Show that .
Show that .
Hence or otherwise find in the form where , .
Consider the function defined by where is a positive constant.
The function is defined by for .
Showing any and intercepts, any maximum or minimum points and any asymptotes, sketch the following curves on separate axes.
;
Showing any and intercepts, any maximum or minimum points and any asymptotes, sketch the following curves on separate axes.
;
Showing any and intercepts, any maximum or minimum points and any asymptotes, sketch the following curves on separate axes.
.
Find .
By finding explain why is an increasing function.
Consider the functions and defined on the domain by and .
The following diagram shows the graphs of and
Find the -coordinates of the points of intersection of the two graphs.
Find the exact area of the shaded region, giving your answer in the form , where , .
At the points A and B on the diagram, the gradients of the two graphs are equal.
Determine the -coordinate of A on the graph of .
A continuous random variable has the probability density function
.
The following diagram shows the graph of for .
Given that , find an expression for the median of in terms of and .
Consider the function defined by .
The curvature at any point on a graph is defined as .
Show that the function has a local maximum value when .
Find the -coordinate of the point of inflexion of the graph of .
Sketch the graph of , clearly indicating the position of the local maximum point, the point of inflexion and the axes intercepts.
Find the area of the region enclosed by the graph of and the -axis.
The curvature at any point on a graph is defined as .
Find the value of the curvature of the graph of at the local maximum point.
Find the value for and comment on its meaning with respect to the shape of the graph.
Let .
The graph of has a local maximum at A. Find the coordinates of A.
Show that there is exactly one point of inflexion, B, on the graph of .
The coordinates of B can be expressed in the form B where a, b. Find the value of a and the value of b.
Sketch the graph of showing clearly the position of the points A and B.
By using the substitution or otherwise, find an expression for in terms of , where is a non-zero real number.
The continuous random variable has probability density function
Find the value of .
Find .
A function is defined by where .
The graph of is shown below.
Show that is an odd function.
The range of is , where .
Find the value of and the value of .
Consider the function defined by , where and .
Consider the case where .
State the equation of the vertical asymptote on the graph of .
State the equation of the horizontal asymptote on the graph of .
Use an algebraic method to determine whether is a self-inverse function.
Sketch the graph of , stating clearly the equations of any asymptotes and the coordinates of any points of intersections with the coordinate axes.
The region bounded by the -axis, the curve , and the lines and is rotated through about the -axis. Find the volume of the solid generated, giving your answer in the form , where .
The curve is given by the equation .
At the point (1, 1) , show that .
Hence find the equation of the normal to at the point (1, 1).
Consider the function .
Express in the form .
Factorize .
Sketch the graph of , indicating on it the equations of the asymptotes, the coordinates of the -intercept and the local maximum.
Hence find the value of if .
Sketch the graph of .
Determine the area of the region enclosed between the graph of , the -axis and the lines with equations and .
Let
Find .
Find .
Let for .
Show that .
Use mathematical induction to prove that for .
Let .
Consider the function defined by for .
It is given that the term in the Maclaurin series for has a coefficient of .
Find the possible values of .
Consider .
For the graph of ,
Find .
Show that, if , then .
find the coordinates of the -intercept.
show that there are no -intercepts.
sketch the graph, showing clearly any asymptotic behaviour.
Show that .
The area enclosed by the graph of and the line can be expressed as . Find the value of .
Given that and , find
.
.
Using the substitution , find .
The function is defined by , where .
The function is defined by , where .
Find the Maclaurin series for up to and including the term.
Hence, find an approximate value for .
Show that satisfies the equation .
Hence, deduce that .
Using the result from part (c), find the Maclaurin series for up to and including the term.
Hence, or otherwise, determine the value of .
The graph of , 0 ≤ ≤ 5 is shown in the following diagram. The curve intercepts the -axis at (1, 0) and (4, 0) and has a local minimum at (3, −1).
The shaded area enclosed by the curve , the -axis and the -axis is 0.5. Given that ,
The area enclosed by the curve and the -axis between and is 2.5 .
Write down the -coordinate of the point of inflexion on the graph of .
find the value of .
find the value of .
Sketch the curve , 0 ≤ ≤ 5 indicating clearly the coordinates of the maximum and minimum points and any intercepts with the coordinate axes.
A function is defined by .
The region is bounded by the curve , the -axis and the lines and . Let be the area of .
The line divides into two regions of equal area.
Let be the gradient of a tangent to the curve .
Sketch the curve , clearly indicating any asymptotes with their equations and stating the coordinates of any points of intersection with the axes.
Show that .
Find the value of .
Show that .
Show that the maximum value of is .
Show that where .
The folium of Descartes is a curve defined by the equation , shown in the following diagram.
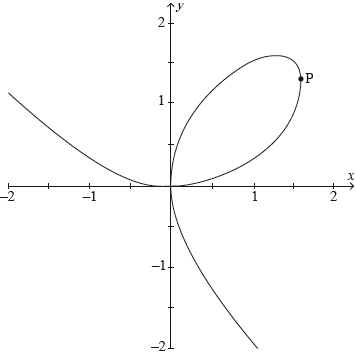
Determine the exact coordinates of the point P on the curve where the tangent line is parallel to the -axis.
A particle moves along a straight line. Its displacement, metres, at time seconds is given by . The first two times when the particle is at rest are denoted by and , where .
Find and .
Find the displacement of the particle when
Use l’Hôpital’s rule to determine the value of
.
Write in the form , where .
Hence, find the value of .
Consider the expression where .
The binomial expansion of this expression, in ascending powers of , as far as the term in is , where .
Find the value of and the value of .
State the restriction which must be placed on for this expansion to be valid.
Using the substitution show that .
Hence find the value of .
A curve has equation .
Find an expression for in terms of and .
Find the equations of the tangents to this curve at the points where the curve intersects the line .
Find the value of .
A function is defined by , where .
A function is defined by , where .
The inverse of is .
A function is defined by , where .
Sketch the curve , clearly indicating any asymptotes with their equations. State the coordinates of any local maximum or minimum points and any points of intersection with the coordinate axes.
Show that .
State the domain of .
Given that , find the value of .
Give your answer in the form , where .
Use the substitution to find .
Hence find the value of , expressing your answer in the form arctan , where .
A camera at point C is 3 m from the edge of a straight section of road as shown in the following diagram. The camera detects a car travelling along the road at = 0. It then rotates, always pointing at the car, until the car passes O, the point on the edge of the road closest to the camera.
A car travels along the road at a speed of 24 ms−1. Let the position of the car be X and let OĈX = θ.
Find , the rate of rotation of the camera, in radians per second, at the instant the car passes the point O .
Use l’Hôpital’s rule to determine the value of .
The acceleration, , of a particle moving in a horizontal line at time seconds, , is given by where is the particle’s velocity and .
At , the particle is at a fixed origin and has initial velocity .
Initially at , the particle moves in the positive direction until it reaches its maximum displacement from . The particle then returns to .
Let metres represent the particle’s displacement from and its maximum displacement from .
Let represent the particle’s velocity seconds before it reaches , where
.
Similarly, let represent the particle’s velocity seconds after it reaches .
By solving an appropriate differential equation, show that the particle’s velocity at time is given by .
Show that the time taken for the particle to reach satisfies the equation .
By solving an appropriate differential equation and using the result from part (b) (i), find an expression for in terms of .
By using the result to part (b) (i), show that .
Deduce a similar expression for in terms of .
Hence, show that .
Use l’Hôpital’s rule to find .
Consider the curves and defined as follows
,
,
Using implicit differentiation, or otherwise, find for each curve in terms of and .
Let P(, ) be the unique point where the curves and intersect.
Show that the tangent to at P is perpendicular to the tangent to at P.
Solve the differential equation , given that at .
Give your answer in the form .
A particle moves in a straight line such that at time seconds , its velocity , in , is given by . Find the exact distance travelled by the particle in the first half-second.
Consider the function .
Show that the graph of is concave up for .
Sketch the graph of showing clearly any intercepts with the axes.
Consider the curve defined by .
Show that .
Prove that, when .
Hence find the coordinates of all points on , for , where .
Find the coordinates of the points on the curve at which .
Find
The function is defined by .
Find the first two derivatives of and hence find the Maclaurin series for up to and including the term.
Show that the coefficient of in the Maclaurin series for is zero.
Using the Maclaurin series for and , find the Maclaurin series for up to and including the term.
Hence, or otherwise, find .
Find the equation of the tangent to the curve at the point where .
Given that , find the value of .
The lines and have the following vector equations where .
By using the substitution , find .
A right circular cone of radius is inscribed in a sphere with centre O and radius as shown in the following diagram. The perpendicular height of the cone is , X denotes the centre of its base and B a point where the cone touches the sphere.
Show that the volume of the cone may be expressed by .
Given that there is one inscribed cone having a maximum volume, show that the volume of this cone is .
Consider the functions defined for , given by and .
Hence, or otherwise, find .