
HL Paper 1
Which is correct for a redox reaction where the standard electrode potential is negative?
ΔGΘ = −nFEΘ and ΔGΘ = −RT ln K
A. ΔGΘ is negative and K is less than 1.
B. ΔGΘ is negative and K is greater than 1.
C. ΔGΘ is positive and K is less than 1.
D. ΔGΘ is positive and K is greater than 1.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Which signs for both Eθcell and ΔGθ result in a spontaneous redox reaction occurring under standard conditions?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
An iron rod is electroplated with silver. Which is a correct condition for this process?
A. The silver electrode is the positive electrode.
B. The iron rod is the positive electrode.
C. The electrolyte is iron(II) sulfate.
D. Oxidation occurs at the negative electrode.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Which statement is correct for the overall reaction in a voltaic cell?
2AgNO3(aq) + Ni(s) → 2Ag(s) + Ni(NO3)2(aq) E θ= +1.06 V
A. Electrons flow from Ag electrode to Ni electrode.
B. Ni is oxidized to Ni2+ at the cathode (negative electrode).
C. Ag+ is reduced to Ag at the anode (positive electrode).
D. Ag has a more positive standard electrode potential value than Ni.
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Which statement is correct when a zinc spoon is electroplated with silver?
A. The cathode (negative electrode) is made of silver.
B. The anode (positive electrode) is the zinc spoon.
C. The anode (positive electrode) is made of silver.
D. The electrolyte is zinc sulfate solution.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Very pleasing to see that nearly 80% could identify the material best suited as anode in an electrolytic cell. Many candidates, however, thought that the material being electroplated should be the anode.
What are the products when concentrated aqueous copper (II) chloride is electrolysed using platinum electrodes?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
What would be the electrode potential, E⦵, of the Mn2+ (aq)|Mn (s) half-cell if Fe3+ (aq)|Fe2+ (aq) is used as the reference standard?
Mn2+ (aq) + 2e− Mn (s) E⦵ = −1.18 V
Fe3+ (aq) + e− Fe2+ (aq) E⦵ = +0.77 V
A. −1.95 V
B. −0.41 V
C. +0.41 V
D. +1.95 V
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Which gives the equation and cell potential of the spontaneous reaction?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
What are the major products of electrolysing concentrated aqueous potassium iodide, KI(aq)?
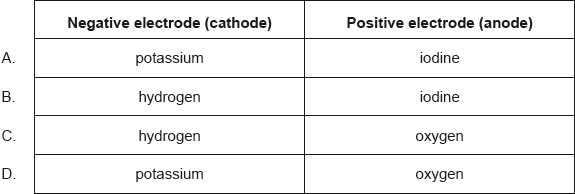
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
What does not affect the mass of products formed in electrolysis of an aqueous solution?
A. Current
B. Duration of electrolysis
C. Initial mass of cathode
D. Charge on the ions
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Consider the following standard electrode potentials:
Which species will react with each other spontaneously under standard conditions?
A. Zn2+ (aq) + Pb (s)
B. Pb2+ (aq) + Br2 (l)
C. Zn (s) + Br− (aq)
D. Pb (s) + Br2 (l)
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
What are the products when dilute aqueous copper (II) nitrate is electrolysed using platinum electrodes?
E⦵ (Cu | Cu2+) = –0.34 V.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Average performance with a lower discrimination index and no clear misconception based on the incorrect choices.
Consider the following table of standard electrode potentials.
Which is the strongest oxidizing agent?
A. Pb2+
B. Pb
C. Al3+
D. Al
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
This was a challenging question with a high discrimination index. 57 % of the candidates identified the strongest oxidizing agent given the standard electrode potentials. The most commonly chosen distractor was Al3+ (C).
Which factors affect the amount of product formed at the cathode during electrolysis of molten salts?
I. current
II. time
III. charge on the cation
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Majority of candidates answered this correctly with the most common mistake being omission of time as a factor affecting electrolysis quantities.
Three cells with platinum electrodes are connected in series to a DC power supply.
What is the ratio of moles formed at each cathode (negative electrode)?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Which conditions deposit the greatest mass of copper when solutions containing copper ions are electrolysed for 10 minutes?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Nearly all candidates understood that larger current would produce more mass in electrolysis, however quite a few also thought that more copper would be deposited if the ion had a +2 rather than +1 charge.
Which combination would electroplate an object with copper?
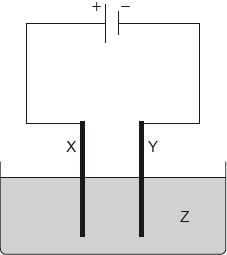
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
What are the products when an aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate is electrolysed using inert graphite electrodes?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Consider the standard electrode potentials:
Cr3+ (aq) + 3e− Cr (s) EΘ = −0.74 V
Hg2+ (aq) + 2e− Hg (l) EΘ = +0.85 V
What is the cell potential, in V, for the voltaic cell?
2Cr (s) + 3Hg2+ (aq) → 3Hg (l) + 2Cr3+ (aq)
A. −1.59
B. +0.11
C. +1.07
D. +1.59
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
What are the products of electrolysis when concentrated calcium bromide solution is electrolysed using graphite electrodes?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Which E⦵ value, in V, for the reaction Mn (s) + Zn2+ (aq) → Mn2+ (aq) + Zn (s) can be deduced from the following equations?
Mn (s) + 2Ag+ (aq) → Mn2+ (aq) + 2Ag (s) E⦵ = 1.98 V
Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu (s) E⦵ = 1.10 V
Cu (s) + 2Ag+ (aq) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2Ag (s) E⦵ = 0.46 V
A. 0.42
B. 1.34
C. 2.62
D. 3.54
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
56% of candidates were able to deduce the EƟ of the reaction.
What is the order of increasing mass deposited by this electrolytic cell?
Ar Ag = 108, Cu = 64, Sb = 122
A. Ag < Cu < Sb
B. Sb < Ag < Cu
C. Cu < Ag < Sb
D. Cu < Sb < Ag
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A rather challenging question. Only 30% of the candidates were able to deduce the relative masses of metals deposited in three electrolytic cells in series. Candidates had to take into account the charge of the metal ions and the molar masses of the metals therefore it was a time-consuming question. The most commonly chosen distractor, C, only took the molar masses into account.
What are the products when concentrated KBr (aq) is electrolyzed?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Another challenging question with a high discrimination index. 57 % of the candidates were able to identify the electrode products during the electrolysis of concentration KBr (aq). The most commonly chosen distractor was C where K was the product at the cathode (instead of H2). Some teachers commented that the data booklet was needed to solve this question and others said “concentrated” was vague. But the effect of concentration is clearly stated in the syllabus and does not need the data booklet to be determined. As for the cation, potassium is known as a reactive metal according to the periodic trends and should have been easy to recognize as more reactive than hydrogen. Similar questions have appeared in past papers.
In the electrolysis of aqueous potassium nitrate, KNO3(aq), using inert electrodes, 0.1 mol of a gas was formed at the cathode (negative electrode).
Which is correct?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
What are the relative volumes of gas given off at E and F during electrolysis of the two cells in series? Assume all electrodes are inert.
A. 1:1
B. 1:2
C. 2:1
D. 5:2
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Which is not a requirement of the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)?
A. V = 1 dm3
B. p(H2) = 100 kPa
C. use of platinum as the electrode material
D. [H3O+] = 1 mol dm−3
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
This was a poorly answered question on the standard hydrogen electrode. Many candidates believed what was not required was a Pt electrode material
What is the standard half-cell potential of copper if the “zero potential reference electrode” is changed from the standard hydrogen electrode to a standard zinc electrode?
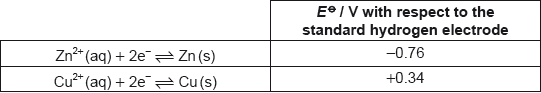
A. –1.1
B. –0.34
C. +0.34
D. +1.1
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
In the electrolysis apparatus shown, 0.59 g of Ni is deposited on the cathode of the first cell.
What is the mass of Ag deposited on the cathode of the second cell?
A. 0.54 g
B. 0.59 g
C. 1.08 g
D. 2.16 g
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
A poorly answered question with low discrimination factor. Several teachers asked whether this question of "cells in series" was in the Chemistry Guide (see Topic 19.1, Electrochemical cells, on page 96) and it is likely that this topic may not have been covered in class by some teachers.
Two cells undergoing electrolysis are connected in series.
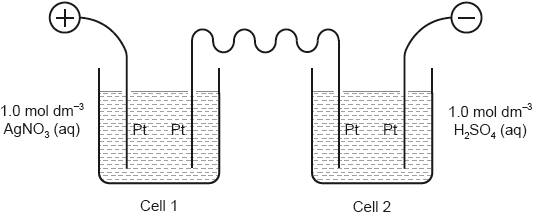
If g of silver are deposited in cell 1, what volume of oxygen, in dm3 at STP, is given off in cell 2?
Ar(Ag) = 108; Molar volume of an ideal gas at STP = 22.7 dm3 mol−1
A.
B.
C.
D.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Which aqueous solutions produce oxygen gas during electrolysis?
I. Dilute CuCl2 (aq) with inert electrodes
II. Dilute FeSO4 (aq) with inert electrodes
III. Dilute CuCl2 (aq) with copper electrodes
The standard electrode potentials are provided in the table:
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
What happens to the mass of each copper electrode when aqueous copper(II) sulfate solution is electrolysed?
Markscheme
C