
SL Paper 3
A student wished to determine the concentration of a solution of sodium hydroxide by titrating it against a 0.100moldm−3 aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid.
4.00g of sodium hydroxide pellets were used to make 1.00dm3 aqueous solution.
20.0cm3 samples of the sodium hydroxide solution were titrated using bromothymol blue as the indicator.
Outline, giving your reasons, how you would carefully prepare the 1.00dm3 aqueous solution from the 4.00g sodium hydroxide pellets.
(i) State the colour change of the indicator that the student would see during his titration using section 22 of the data booklet.
(ii) The student added the acid too quickly. Outline, giving your reason, how this could have affected the calculated concentration.
Suggest why, despite preparing the solution and performing the titrations very carefully, widely different results were obtained.
Nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide are two air pollutants.
Nitrogen dioxide is formed in a two-stage process. Describe one anthropogenic (man-made) source of nitrogen dioxide and state the two chemical equations for its formation.
Both of these air pollutants also contribute to acid deposition. State one chemical equation for each gas to describe how each forms an acidic solution.
Acid deposition is a major environmental concern. Although it is usually associated with human activities, natural sources can also contribute to this phenomenon.
State one natural origin of acid deposition.
State equations which represent chemical transformations of elemental sulfur into sulfurous acid, H2SO3.
Discuss the possible ways of decreasing acid deposition and its adverse effects on the environment.
One major environmental problem that affects many countries is acid rain.
Nitrogen monoxide pollution is a major contributor of acid rain.
Explain, writing an appropriate equation, why, even in an unpolluted environment, rainwater is still slightly acidic.
(i) Outline the major source of this gas, including an equation.
(ii) Describe, including an equation, a chemical method used to control the emission of this pollutant.
(iii) Identify a compound, to which nitrogen monoxide is eventually converted, that is responsible for acidity in lakes and rivers.
Acid deposition is a consequence of industrial processes.
State what is meant by the term acid deposition.
Industrial processes, such as the burning of coal, generate non-metallic oxides of carbon and nitrogen into the atmosphere. State balanced equations for the reactions by which these oxides are produced and then removed from the atmosphere.
Oxide of carbon:
Produced:
Removed:
Oxide of nitrogen:
Produced:
Removed:
All shellfish have a calcium carbonate shell. Discuss, including a balanced equation, the long-term effect of acid deposition on these organisms.
Balanced equation:
The two major acids that cause acid rain originate from different sources.
State an equation that shows why rain water is naturally acidic.
Outline the process responsible for the production of each acid and state an equation to show its formation.
Acid rain has caused damage to limestone buildings and marble statues. State an equation to represent the reaction of acid rain with limestone or marble.
Acid deposition can have a significant impact on aquatic environments such as lakes or wetlands.
State what is meant by the term acid deposition.
Identify one oxide which causes acid deposit
One effect of acid deposition is to decrease the pH of lake water. Suggest how this effect could be reversed.
The exhaust gases of automobiles contribute significantly to air pollution in cities.
Outline how the pollutant gases nitrogen(II) oxide, NO, nitrogen(IV) oxide, \({\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}\) and carbon monoxide, CO, are formed as a result of the action of the internal combustion engine.
NO:
\({\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_2}\):
CO:
The normal pH of rainwater is 5.6, but in some parts of the world rainwater has been recorded with a pH of several units lower than this. This is associated with harmful effects on living and non-living things.
The decrease in the pH of rainwater is mainly caused by oxides of non-metals, principally nitrogen and sulfur. State chemical equations that show how the primary pollutant nitrogen(II) oxide can produce two different acids containing nitrogen.
Explain, including an equation, the effect of the acid rain produced in (a) on certain stone buildings.
The cumene process is used for the production of both propanone and phenol. The overall reaction is shown in the equation below.
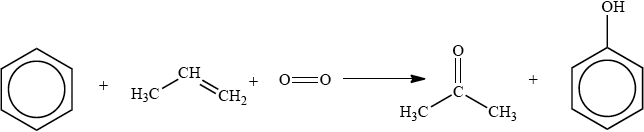
This process is important in the polymer industry. Propanone can be converted into methyl methacrylate, the monomer used to make Perspex®, and phenol is used in phenol-methanal resins, which are important thermosetting plastics.
State and explain how the presence of a halogen substituent might affect the acidity of carboxylic acids.
Propanone could also be formed from propene by reaction with steam over an acidic catalyst, followed by oxidation of the product.
The reaction of propene with water can yield two possible products. Explain, in terms of the stability of the intermediate carbocations, why one is formed in much greater quantities than the other.
Nitrogen monoxide gas, NO, is emitted by cars and leads to acid deposition.
Discuss the damage to the environment caused by acid deposition.
A class was determining the concentration of aqueous sodium hydroxide by titrating it with hydrochloric acid, whilst monitoring the pH of the solution. The sodium hydroxide solution was added into a glass beaker from a measuring cylinder and the hydrochloric acid added using a burette. One group of students accidentally used a temperature probe rather than a pH probe. Their results are given below.
Volume of aqueous NaOH = 25.0 ± 0.5 cm3
Concentration of HCl = 1.00 ± 0.01 mol dm−3
Deduce why more heat was produced in mixture B than in mixture A.
Deduce why the temperature is higher in mixture C than in mixture D.
Antacids react with hydrochloric acid in the stomach to relieve indigestion. A student investigated different brands of antacid to see which caused the largest increase in pH in a given time. She added the antacids to hydrochloric acid, and recorded the change in pH over five minutes.
State an equation for the reaction of magnesium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid.
Suggest two variables, besides the time of reaction, which the student should have controlled in the experiment to ensure a fair comparison of the antacids.
Calculate the uncertainty in the change in pH.
The student concluded that antacid B was the most effective, followed by A then C and finally D. Discuss two arguments that reduce the validity of the conclusion.
The combustion of fossil fuels produces large amounts of CO2, a greenhouse gas.
The diagram below illustrates a range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Synthesis gas, or syngas, mainly composed of CO(g) and H2(g), is an alternative form of fuel. It can be produced by coal or biomass gasification, passing steam over the source material in a low oxygen environment.
Identify which region, A or B, corresponds to each type of radiation by completing the table.
Oceans can act as a carbon sink, removing some CO2(g) from the atmosphere.
CO2(g) \( \rightleftharpoons \) CO2(aq)
Aqueous carbon dioxide, CO2(aq), quickly reacts with ocean water in a new equilibrium reaction. Construct the equilibrium equation for this reaction including state symbols.
Describe how large amounts of CO2 could reduce the pH of the ocean using an equation to support your answer.
Suggest an equation for the production of syngas from coal.
The Fischer-Tropsch process, an indirect coal liquefaction method, converts CO(g) and H2(g) to larger molecular weight hydrocarbons and steam.
Deduce the equation for the production of octane by this process.
Suggest a reason why syngas may be considered a viable alternative to crude oil.